Concept Map (Page 2 of packet)
advertisement
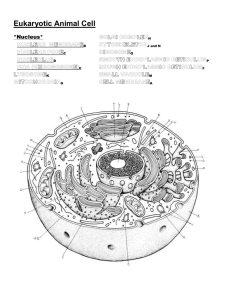
Topics 6 & 7 The Cell Theory & Cell Structure & Function Learning Targets I will be able to: Describe the Cell Theory Differentiate the function of various types of microscopes Explain how continuous investigations and new scientific information has influenced the cell theory over time Differentiate the general structures and their function found within a Prokaryotic cell and a Eukaryotic cell Differentiate the general structures of a plant cell and an animal cell. Explain how the structure of an organelle is directly related to its function in the cell, i.e. surface area Textbook Chapter 3, Cell Structure & Function Biology New Smyrna Beach High School Key Terms Theory Law Cell Theory Compound Light Microscope SEM TEM Prokaryote vs Eukaryote Organelle Cell wall Chloroplast Vacuole Cell membrane Nucleus Nuclear envelope/membrane Ribosome Mitochondria Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Apparatus Cytoplasm Microtubules Microfilaments Flagella 2014-15 The Cell Theory …has three major principles: Part 1 Part 2 Part 3 The Cell Theory was based on the early work of several men including… Robert Hooke Zacharias Janssen Who in the 1500’s, got credit for inventing a very important tool used in biology… the …who looked at slices of… He saw what he called “a lot of little rooms” that reminded him of the room that monks lived in, so be called them by the same name… Anton von Leeuwenhoek …who developed an even better microscope & ‘went to town’ looking at living things. He discovered… … and called them… As people continued to improve the microscope, others started examining even more organisms; Three men stand out as early contributors of what is now called THE CELL THEORY Matthias Schleiden He proposed that cells make up all… Theodor Schwann He concluded that cells make up all… 2 Rudolph Virchow He reported that cells come from… Comparing Microscopes 1. Compound Light Microscope: contains 2 or more lenses; Reference page R8 5.__________________ 2.________________ 6.__________________ 3.________________ 7. _____________________ 4.________________ 8._____________________ 9.__________________ 10. Dissecting (Stereo) Microscope: ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ 11. TEM __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ 12. SEM __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ 3 The TWOTWO TYPES MAJOR OF EUKARYOTIC TYPES OF CELLS: CELLS: Prokaryotic Cells vs Eukaryotic Animal Cells vs Plant Cells Cells 1._____________ _ 2.______________ CELL A CELL B 1.____________ (dots) 3.______________ 2.______________ (jelly-like fluid) 3._____________ 5._______________ Capsule (outside protective cover) (just inside cell wall) 4.______________ 4.______________ (just inside capsule) Bacteria Cell Plant Cell Animal Cell Questions to consider: 1. Which cell (A or B) is a Prokaryotic cell?_____________________________________________________ Questions to Consider: 2. What is the ONLY of this type of cell in the “whole wide world”?______________________ 1.What makes theseexample cells Eukaryotic?___________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Is there a nucleus in Cell A?_______________ What is the Nucleoid region?______________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What do you notice about the vacuoles in the animal cell as compared to the one in cell?_______________________________________________________________________ 4. the Theplant flagellum is a long hair-like structure used for locomotion. What might you infer about the _____________________________________________________________________________________ absence of this structure in other types of bacteria cells?_____________________________________ How are Cell A and Cell the B similar?___________________________________________________________ 3.5. What is different about outermost boundary in a plant cell as compared to an ___________________________________________________________________________________________ animal cell?_________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ How are types Cell A of and Cellhave B different?_________________________________________________________ 4.6. Do both cells mitochondria? ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Do both types of cells have chloroplasts? _____________________________________________ 6. Compare the shape of the two cells: ________________________________________________ 4 Cell Organelles 1. What are organelles?_____________________________________________________________ 2. Once you read about the following organelles, place them in their proper category of basic function: Cell Wall – Plasma (Cell) Membrane – Nucleus – Chloroplast – Endoplasmic Reticulum – Vacuole – Golgi Apparatus (Body) – Ribosomes – Mitochondria CELL BOUNDARIES DIRECTION & ASSEMBLY ENERGY CONVERTERS PACKAGING & TRANSPORT 5