Chapter 2 Vocabulary
advertisement

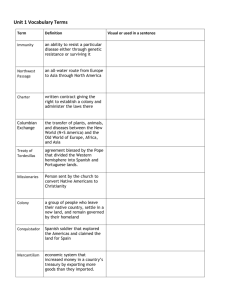
Chapter 2 Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. missionaries – people who work to convert others to their religion presidio – Spanish fort located near Spanish mission viceroy – ruler of a section of the Spanish empire in the Americas, appointed by the Spanish king mestizo – child of mixed Spanish and Indian ancestry mission – a location for missionary work Northwest Passage – a supposed water route to Asia through the cold waters of presentday Canada Quebec – first permanent European settlement in Canada Samuel de Champlain – Quebec’s founder coureurs de bois – French fur traders who married Indian women metis – children of French and Indian marriages charter – a certificate of permission from the king to colonize an area in the Americas joint-stock company – a group of investors in the colonizing effort who shared in profits and losses of a colony Powhatan – powerful chief of 30 Indian tribes in area of Jamestown colony John Smith – leader in Jamestown colony House of Burgesses – first representative body in colonial America proprietary colonies – English colonies in America that belonged to powerful individuals or companies Bacon’s Rebellion – a revolt in September 1676, where Nathaniel Bacon marched his armed followers to Jamestown, drove out the governor, and burned the town Lord Baltimore – owner and governor of the colony of Maryland James Oglethorpe – leader of the colony of Georgia Puritan – people who wanted to purify the Anglican church, the official and legal church of England Separatist – people who started their own church separate from the Anglican church Pilgrims – the first Puritan emigrants to New England in 1620 Mayflower Compact – agreement in which pilgrims agreed to form a government and obey its laws John Winthrop − leader who, in 1630, led a large group of Puritans to America, settling first in present-day Boston Roger Williams − religious dissenter who criticized Puritans’ Indian policy and was banned from Massachusetts Bay Colony Anne Hutchinson − religious dissenter who was banned from Massachusetts Bay Colony Pequot War − begun in 1636, battle between Indians and Puritans over Puritan expansions of land and control of trade 28. King Philip’s War − 1675 Indian uprising that included many Indian villages in Massachusetts Bay Colony 29. Metacom − Indian leader also called King Philip by colonists 30. push factor – events and circumstances that motivate people to leave their homes 31. pull factor − events and circumstances that attract people to a new location 32. William Penn − wealthy Quaker Englishman who founded Pennsylvania 33. Quaker − unlike Puritans, sought inner understanding of Bible, considered women equal, and were pacifists