Tissues
advertisement
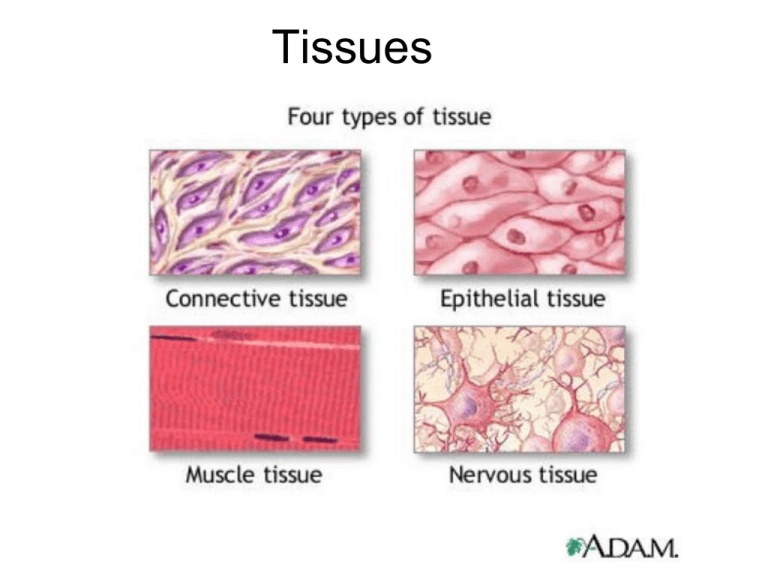
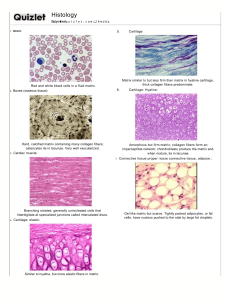
Tissues And this type..... Epithelial Tissue - Covers all body surfaces both inside and out. - Main glandular (glands) tissue. - Usually has no vascular tissue - blood supply but does have nerves - Cells reproduce rapidly (rapid healing). - Cells tightly packed together If a girl weighs 100 pounds. How much of her weight is skin? It takes about 27 days for the outer layer of skin to shed and be replaced; that works out to 1.5 pounds of skin cells per year. Where does all the dead skin you shed go? Epithelial tissue Naming is based on description simple = single layer stratified = multiple layers squamous = flat cuboidal = square columnar = column (rectangle) One type of tissue can be arranged in different forms, each form has a different function. Simple Squamous Simple Squamous Tissue Form: Flat and thin Function: diffusion and filtration. Air sacs in lungs, walls of capillaries Simple Cuboidal Function: Secretion and Absorption Found in kidneys tubules, ducts and covering the ovaries Simple Columnar Function: Secretion and Absorption Found in Digestive tract and uterus *Contains goblet cells to secrete mucus *Can have microvilli Stratified Squamous Multi layer squamous, functions in protection Found in skin and mouth The ink of tattoos must be injected below the basement membrane. Tissues often come in layers on the body superficial cuts on the skin may need to be stitched if they also go through the underlying tissue. This will definitely need stitches! Pseudostratified Columnar Single layer, nuclei are uneven which gives it a layered appearance Can have goblet cells and cilia Location: lining air passages and tubes of the reproductive system Transitional Epithelium Stretchable Blocks diffusion (no leaking) Found in the urinary bladder Glandular Epithelium Cells are specialized to produce and secrete substances They make up the GLANDS exocrine glands salivary, sweat | endocrine glands hormones Identify the tissues Connective Tissue -Most abundant tissue in your body, found throughoutBinds structures together -Provides support, protection, framework, fills space, stores fat, produces blood cells, fights infection -Composed of more scattered cells within matrix -Made up of a ground substance (fluid, semi-solid) and fibers -Most has a good blood supply -Cells can reproduce Types of Cells in Connective Tissue ●Mast cells (prevents clots) ●Macrophages (consumers) ●Fibroblasts (produce fibers) Collagenous (bones, ligaments, tendons) Elastic (respiratory) Mast Cell Main types of Fibers Collagenous fibers strong and flexible bones tendons ligaments Elastic fibers - very flexible, ears and vocal cords Basement Membrane Ground substance Categories of Connective Tissue Loose Connective Tissue or Areolar Tissue Binds underlying organs to skin and to each other Forms delicate thin membranes throughout the body Adipose Tissue (fat) Fibrous Connective Tissue Tendons = muscles to bones Ligaments = bones to bones DENSE CONNECTIVE TISSUE CARTILAGE Cartilage cells are called chondrocytes Provides support and attachments, also cushions bones Hyaline Cartilage Covers ends of joints, nose and respiratory passages Elastic cartilage External Ear and Larynx Hyaline cartilage Hyaline cartilage Fibrocartilage Tough, shock absorbing Bone Tissue (Osseus) Blood Tissue Muscle Tissue Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle Smooth muscle Nerve Tissue Neuroglia (nerve glue): 1. To surround neurons and hold them in place 2. To supply nutrients and oxygen to neurons 3. To insulate one neuron from another 4. To destroy pathogens and remove dead neurons. Nervous tissue (spinal cord)