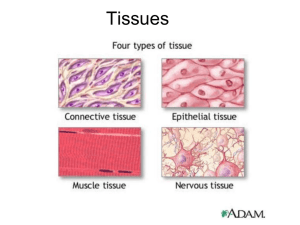
HISTOLOGY Four Basic Types of Tissue
advertisement

HISTOLOGY Four Basic Types of Tissue 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nerve EPITHELIAL TISSUE Cells are bound tightly together Little extracellular material Arranged in sheets Cover internal and external surfaces Often control passage of material Classified by shape of cells and number of layers EPITHELIAL TISSUE CELL SHAPE Squamous shape Thin, flat cells Look like fried eggs Cubodial shape square shape- cross section 6sided polygon- surface Columnar Rectangular- cross section Polygonal- surface view CELL NUMBER Simple Single layer Stratified 2+ layers Pseudostratified Appear stratified- but not Transitional Change shape EPITHELIAL TISSUE SIMPLE SQUAMOUS Single layer Squamous shape Lining of body cavity, lungs, blood vessels EPITHELIAL TISSUE SIMPLE CUBOIDAL Single layer Cuboidal shaped Kidney tubules, glands EPITHELIAL TISSUE SIMPLE COLUMNAR Single layer Columnar shape Lining of digestive tract Modified by presence of cilia EPITHELIAL TISSUE STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS Multi layer Outer most layer- squamous cells Inner- cuboidal or columnar Lining of mouth, esophagus, skin EPITHELIAL TISSUE PSEUDOSTRATIFIED COLUMNAR One layer Appears stratified Respiratory tract Types CONNECTIVE TISSUE Fibrous Loose – Areolar, Adipose, Reticular Dense – Regular, Irregular Cartilage – Hyaline, Elastic, Fibrocartilage Bone Blood Abundant extracellular material Matix (dominant part) Fiber, cells in liquid, gel, or solid matrix Function Bind and/or support other tissue Fibrous - CONNECTIVE TISSUE LOOSE Connective Areolar Few fibers Delicate arrangement Reticular Loose network of reticular fibers and cells Forms supportive stroma (framework) for lymphatic organs Found in lymph nodes, spleen, thymus and bone CONNECTIVE TISSUE LOOSE Connective Adipose Tissue Store large droplets of fat Connective Tissue • Dense Connective – Regular – Densely, packed, parallel collagen fibers • Ex: Tendons and ligaments Connective Tissue • Dense Connective – Irregular • Densely packed, randomly arranged, collagen fibers and few visible cells • Ex: Deep layer of skin & capsules around organs ConnectiveTissue • Cartilage – Supportive connective tissue with rubbery matrix – Chondroblasts produce matrix – No blood vessels • heals slowly • Types of cartilage vary with fiber types – hyaline, fibrocartilage and elastic cartilage Hyaline Cartilage • Rubbery matrix; dispersed collagen fibers; clustered chondrocytes in lacunae • Ends of bones at movable joints; sternal ends of ribs; and fetal skeleton Elastic Cartilage • Hyaline cartilage with elastic fibers • Provides flexible, elastic support – external ear and epiglottis Fibrocartilage • Hyaline cartilage with extensive collagen fibers (never has perichondrium) • Resists compression and absorbs shock – pubic symphysis, meniscus and intervertebral discs Connective Tissue • BLOOD – Lymph – Liquid matrix – RBC- Red Blood Cells – WBC- White Blood Cells CONNECTIVE TISSUE BONE Osteocytes Small cavities- lacunae Hardest CT Impregnated w/ calcium salts Spongy Loose rods of bones Ends of arms and legs Compact Shafts of long bones Tightly organized MUSCLE TISSUE Cells have ability to contract Function Locomotion Other body movement SKELETAL MUSCLE TISSUE Voluntary movement Long and cylindrical Transverse striation Each fiber is multi-nuclear MUSCLE TISSUE SMOOTH Involuntary movement Predominant Long, spindle shape Single nucleus Internal organs MUSCLE TISSUE CARDIAC Striations Involuntary One nucleus Deep center Heart muscle NERVE TISSUE Cells very high ability to Respond to stimuli Transmit impulses NERVE TISSUE NEURON Cell Body(3) Dendrites (5) Axon(1)