Test 1 Review Chapter 1 Needs vital to homeostasis/survival

Test 1 Review
Chapter 1
Needs vital to homeostasis/survival
Negative and positive feedback
Cavities and organs within
Directional terms
Organization of organisms
Quadrants and organs within
Homeostatic imbalance, what it is
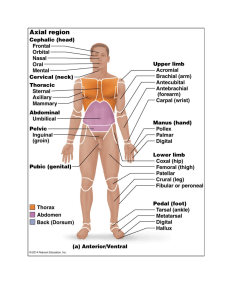
Anatomical terms
Anatomical position
Membranes, where they are found, function of each
Chapter 2
Most abundant protein in the body
Storage of carbohydrates
Coenzymes, what are they, an example
Chemical reactions, speed/rate influencer, types pH
Organic molecules, what are they, example of
Plasma proteins and their function
Redox reactions, what are they, what happens during
ATP, how made, where and when used
Chapter 3
Membrane potential, generation of, types of
Calcium ions, purpose, where stored
Plasma membrane, function of, what it’s made of
Organelles and specific structures that might be on or in a cell, functions of each
Cell junctions, types, functions of
Hypertonic/Hypotonic solutions, affect on cells
RNA, types, function of
Mitosis, function, steps
Hyperplasia
Translation of DNA to RNA using base sequences
Phospholipids
Transport within and into a cell
DNA replication
Cell theory
Molecules that make up a cell
Fluid mosaic model of a cell
Second messengers, what are they, what do they do
Chapter 4
Types of tissue, function of, classification of each, characteristics of each
Fibers, function of
Steps in tissue repair
Glands, types, structures
Germ layers
Chapter 5
Skin layers, function of each, specific characteristics of each
Specialized structures found within the skin, function of each
Cutaneous receptors, function of each
Cell types within the epidermis/dermis, function of each
Function of skin
Fetal characteristics of skin
Glands and secretion of each
Movement of nutrients/wastes through skin
Hair growth
Burns