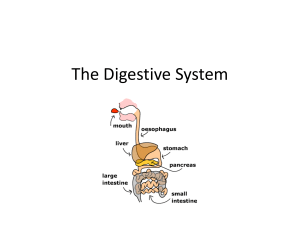
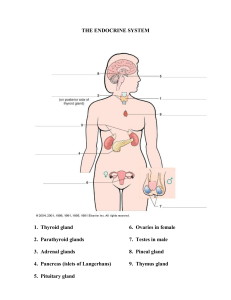
Chapter 1 - anatomy: science of body structures and the relationships between - physiology: body functions - structure often relates function levels of structural organization: chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, system and organism (1) Chemical level: smallest unit; join to form molecules (2+ atoms) and combine to form... (2) Cellular: cells; basic structural/functional units of organism; groups of cells form... (3) Tissue: epithelial (covers body surfaces, line hollow organs and cavities, forms gland), connective (connects, support, protects body organs while distributing blood v. to other tissues), muscular (generate movement, heat), nervous (carries information via nerve impulses) (4) Organ level: structures that are composed of 2+ types of tissues - ex. stomach; ET covering and CT tissue to reduce friction, provide cushioning w/ underlying smooth m. tissue which contracts to churn/mix food + push towards digestive tract (5) System level: consists of related organs - ex. digestive system including mouth, salivary glands, small intestines, large intestines, liver, etc. (6) Organismal level: an organism, consisting of all parts of the human body functioning together 11 systems of the body (identify, repre. organs, functions) (1) Integumentary system --- skin and associated structures (hair, fingernails, toenails, sweat glands, oil glands); function: protection, body temp. regulation, eliminate waste, produce vitamin D; detect sensations (touch, pain, warmth, cold), stores fats/insulates (2) Skeletal System --- bones, joints, cartilage; provide support and protection, surface for m. attachment, aid movement, storage for blood cell production, stores minerals/lipids (3) Muscular System --- skeletal muscle tissue; functions: movement, maintain posture, produce heat (4) Nervous System --- brain, spinal cord, nerves, special sense organs (eyes, ears); gen. AP to regulate action, detect + interpret changes both int/ext, respond w/ muscular contraction or glandular secretion (hormones) (5) Endocrine System --- hormone-producing glands (pineal gland, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thymus, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, testes - function: regulation of activity via hormone release (chem. messengers transported through blood from endocrine/ tissue gland to target organ) (6) Cardiovascular system --- blood, heart, blood v.; pump out blood via blood v., carry oxy/nutrients to/ CO2 away from cell, reg. acid-base balance, temp, water content of body fluid, defence against disease, blood v. repair (7) Lymphatatic system and immunity --- lymphatic fluid and vessels; spleen, thymus, lymph nodes, tonsils: cells involved in immune response (B cells, T cells, etc.) - funct: return protein + fluid to blood, carry lipids from gastrointestinal tract to blood, contains site of maturation/proliferation of B/T cells that protect against disease-causing microbes (8) Respiratory System --- lungs, air passageways (pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tubes); transfer oxygen (air to blood) + CO2 (b. to air), reg. acid-base balance, outward flow of air through vocal cords produces sound (9) Digestive System --- organs of gastrointestinal tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small/large intestines, anus). accessory organs (salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas) - function: physical and chemical breakdown of food, absorbs nutrients, eliminate waste (10) Urinary System --- kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra; funct: produce, store, elim. urine/waste; regulates volume/ chem. composition of blood: maintain acid-base balance; reg. production of red blood cells (11) Reproductive systems --- gonads (testes or ovaries) and asso. organs (uterine tubes, uterus, vagina, mammary glands; epididymis, ductus, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate, penis) - function: gonads produce gametes, reproduction; associated organs transport and store gametes, mammary glands produce milk