Let There Be Light! • Electromagnetic spectrum song Bozeman light
advertisement

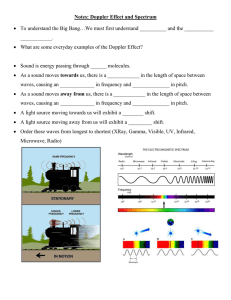
Let There Be Light! • Electromagnetic spectrum song • Electromagnetic spectrum song • Bozeman light Project Benchmark #2 Build Your Instrument To get full credit on this benchmark, your group must do the following: • A different type of instrument for each group member • Hand made • Can make 5 or more notes • Built and checked in ON TIME! Extra Credit Opportunities: • Able to match up your notes to the actual notes that professional instruments make (for example: C, D, F#, B♭, etc.) • Design your instruments in an artistic way or create a theme for your instruments. p118 LIGHT Light is the fist of painters. There is no object so foul that intense light will not make it beautiful. Ralph Waldo Emerson, Nature (ch. III) NATURE OF WAVES • Waves (Def.) – A wave is a disturbance that transfers energy. Light travels in waves. • Medium – Substance through which a wave is transmitted (ex. - air, glass, water, etc.) • Speed of Waves – Depends on the properties of the medium. Speed slows down through thicker mediums. Waves red violet wavelength Of the colors we see, red has the longest wavelength (lowest frequency) Violet has the shortest wavelength (highest frequency) Electromagnetic Spectrum p123 The light waves that humans SEE are only a tiny part of the EM spectrum. EM Spectrum: Solar Radiation • The sun produces EM radiation of all frequencies, Radio waves and visible light can easily reach us. • X-rays from outerspace are fortunately stopped by our atmosphere. • Some UV rays DO ENTER our atmosphere and DAMAGE our bodies. •Radio Waves –Longest wavelength & lowest frequency. –Used for Radio & TV transmission. Short Wavelength Microwave • Infrared Rays • Light rays with a longer wavelength than the red light humans can see. • Uses: Cooking, Medicine, T.V. remote controls Electromagnetic Spectrum Visible Spectrum – Light humans can see Roy G. Biv – Acronym for Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, & Violet. Largest to Smallest Wavelength. Electromagnetic Spectrum Ultraviolet rays. • Electromagnetic waves with frequencies (shorter wavelength) a bit higher than visible light • Uses: food processing & other places to kill germ cells. (It’s how we clean safety glasses) • Helps your body use vitamin D, but causes skin cancer! Electromagnetic Spectrum X-Rays X-ray waves are shorter than UV rays. Uses: Medicine – Bones absorb xrays; soft tissue does not. Lead absorbs X-rays. You put a lead apron over vital organs when you receive an X-ray to protect your cells from damage. Electromagnetic Spectrum Gamma rays • Highest frequency EM waves; Shortest wavelength. They naturally come from outer space. • Uses: Doctors use strong doses of gamma rays (cancer treatment) to kill tumor cells. Light model p116 DQ: How is light different from sound waves 1. The EM spectrum consists of radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, UV, x-rays, and gamma rays 2. Radio waves have long wavelengths and relatively low frequencies (making them low energy); gamma rays have short wavelengths and high frequencies (making them high energy) 3. The speed of light in a vacuum is 3.0 x 108 m/s. Nothing can travel faster! Portfolio entry #1- Pitch p109 Write what you KNOW about pitch Read about pitch Add to your written response…In YOUR OWN WORDS! Did you use many physics words (frequency, transverse wave, wave length)? Use your RUBRIC. Do you have • Definition • Relationship (what happens to the pitch when frequency changes?) • Musical instrument example • Great detail • Picture or diagram (label pictures of high and low pitch) Share out with a partner…partner, what score would you give this response? How can it be made better? Edit your response until it becomes a perfect 4! Portfolio entry #2- Wavelength p113 Write what you KNOW about wavelength Read about wavelength (Active physics p498-501) Add to your written response…In YOUR OWN WORDS! Did you use many physics words (base line, crest, trough, transverse wave, longitudinal wave, rarefaction, compression)? Use your RUBRIC. Do you have • Definition • Relationship (what happens to the wavelength when frequency changes…the wave equation!) • Musical instrument example • Great detail • Picture or diagram (show how to measure a wavelength on both kinds of waves) Share out with a partner…partner, what score would you give this response? How can it be made better? Edit your response until it becomes a perfect 4! Investigation #5 (p530-533) P114Shadows 115 • What do you see in the picture? Why does this make a funny image? • What do you think…Explain why the length of your shadow changes during the day. When is it longest? • You may use a cell phone instead of the lamp provided • Do steps 1-9 and record in your notebook. Get a stamp when finished p115 Shadows • The penumbra only gets half as much light as the umbra resulting in the shadow edge being “fuzzy” or lighter in color Light model Shadow: What Is It? 4. Shadows are formed by an absence of light 5. Light waves travel in straight lines from a light source 6. A shadow will look larger if the object is close to the light source or smaller if it moves away from the light source 7. A shadow may appear fuzzy if the light source is large compared to the object p116 creating an umbra and penumbra Portfolio entry #3- Amplitude p117 Write what you KNOW about Amplitude Read about Amplitude (Active Physics p499) Add to your written response…In YOUR OWN WORDS! Did you use many physics words (base line, crest, trough, transverse wave, longitudinal wave)? Use your RUBRIC. Do you have • Definition • Relationship (what happens to the volume when the amplitude changes?) • Musical instrument example • Great detail • Picture or diagram (that shows how to measure amplitude) Share out with a partner…partner, what score would you give this response? How can it be made better? Edit your response until it becomes a perfect 4! Finish CU (p534) 1-3 PtoGo (p537) 1-6 CDP 27-1 Get a stamp when you are finished p115 Special effect: Strobe lights p119 • A strobe light produces regular flashes of light • How could you use a strobe light in your project? (the strobe light is available for practice during lunch, and available for your project presentation IF you come in and practice during lunch) • How could you use shadows in your presentation? Investigation #6 (p538-541) Reflected Light • What do you see in the cartoon window compared to the cartoon mirror? • What do you think? • Do steps 1-13. Record in your notebook • CU (p543) 1-3 • PtoGo (p546-547) 1-7 Get a stamp when you are finished P114115 Sniper Reflection Lab • What do you know about the word “reflection”? Answer all 4 questions Before You Start • Follow all directions and answer all the questions on the handout p119 Get a stamp when you are finished Light Model: Reflection 8. A reflection happens when light rays bounce off a shiny surface. 9. The light path can be determined by drawing an imaginary line (the normal) to the mirrored surface. 10. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. 11. The (virtual) image formed by the mirror appears behind the surface 12. The image in a mirror is backwards. p116 Bill Nye What’s wrong with this picture? • How can you use this idea in your presentation? p121 Reflection: Flat Mirror • When light reflects from a flat mirror, the incoming incident angle and outgoing reflection angle are equal. Note: Angles are always measured with respect to the perpendicular (or normal) to the mirror plane. p121 Reflection: Construct a Periscope • The periscope uses two mirrors so that you can observe an object above your line of sight. • Click here for directions to make one! LIGHT & ITS USES - Reflection Reflection – Bouncing back of light waves Regular reflection – A mirror’s smooth surface scatters light very little. Images are clear & exact. Diffuse reflection – Reflected light is scattered due to an irregular surface (think of crumpled foil). Finish Sniper Lab CU (p543) 1-3 PtoGo (p546-547) 1-7 Get a stamp when you finish p122 Portfolio entry #4- Interference p124 Write what you KNOW about (sound wave) Interference Read about (sound wave) Interference (Active Physics p847) Add to your written response…In YOUR OWN WORDS! Did you use many physics words (constructive and destructive) Use your RUBRIC. Do you have • Definition • Relationship (what happens to the amplitude when two waves meet?) • Musical instrument example • Great detail • Picture or diagram (demonstrate how two waves combine) Share out with a partner…partner, what score would you give this response? How can it be made better? Edit your response until it becomes a perfect 4! Project Benchmark #3 Wave Property Pitch *also known as? How the instrument demonstrates the property Wind Instruments Pan flute frequency Percussion Instruments String Instruments Brass Instruments p125 How to change the property on the instrument Investigation #7 (p548) p125 • What do you see in the cartoon? • How do you think these images are made? • How could you use a curved mirror in your sound and light show? Reflection: Convex Mirror • A convex mirror is bent outwards and “distorts” the image. • The reflection always appears upright (virtual image) and is smaller. p125 Reflection: Convex Mirror Application • Because images always appear smaller in a convex mirror, a larger “field of view” is possible. • Such mirrors are used for car side-view mirrors and surveillance mirrors in stores. • Do you understand why car mirrors have the warning given in the cartoon? Reflection: Concave Mirror • A concave mirror is bent inwards and also “distorts” the image. • When an object is outside the focus of a concave mirror, the reflection appears upside-down (real image). p125 Reflection: Concave Mirror (Inside Focus) • When an object is inside the focus of a concave mirror, the reflection appears upright (virtual image). • Try this with a spoon! p125 Lenses: Convex and Concave Convex Lens Concave Lens Focal Point OBJECT Your EYE IMAGE A convex glass lens uses refraction to bend light inwards (converging), whereas a concave lens bends light outwards (diverging). In a convex lens, parallel light rays can be bent to a focal point. Convex Lens Convex Lens A convex lens curves outward; “is rounded”. Light passing through a convex lens is bent inward, or made to converge. Concave Lens A concave lens is curved inward (caves in). Light passing through a concave lens bends outward, or diverges. Concave lenses are generally prescribed for myopic, or near-sighted, people. Benchmark #3 Wave Property Pitch *also known as? How the instrument demonstrates the property How to change the property on the instrument Wind Instruments the length of each pipe is different. The length of the pipe determines the frequency, or pitch. A short pipe is a high pitch, a long pipe is a low pitch. Pan flute frequency Percussion Instruments String Instruments Brass Instruments Benchmark #3 Wave Property Pitch *also known as? How the instrument demonstrates the property How to change the property on the instrument Wind Instruments when your fingers plug the hole(s) on a flute, you change the length of the pipe. The length of the pipe determines the frequency, or pitch. A short pipe is a high pitch, a long pipe is a low pitch. each drum plays a different note (pitch) because the drums are different sizes. The distance (either height or diameter) determines the pitch. A large drum has a low pitch, a small drum has a high pitch. flute frequency Percussion Instruments drums String Instruments Brass Instruments Benchmark #3 Wave Property Pitch *also known as? How the instrument demonstrates the property How to change the property on the instrument Wind Instruments when your fingers plug the hole(s) on a flute, you change the length of the pipe. The length of the pipe determines the frequency, or pitch. A short pipe is a high pitch, a long pipe is a low pitch. each drum plays a different note (pitch) because the drums are different sizes. The distance (either height or diameter) determines the pitch. A large drum has a low pitch, a small drum has a high pitch. A guitar changes pitch by changing the length of the strings (when you press the string against the fret) A long string produces a low pitch, a short string produces a high pitch. flute frequency Percussion Instruments drums String Instruments Guitar Brass Instruments Benchmark #3 Wave Property Pitch *also known as? p125 How the instrument demonstrates the property How to change the property on the instrument Wind Instruments the length of each pipe is different. The length of the pipe determines the frequency, or pitch. A short pipe is a high pitch, a long pipe is a low pitch. Pan flute frequency Percussion Instruments drums String Instruments Guitar Brass Instruments Horn/trombone each drum plays a different note (pitch) because the drums are different sizes. The distance (either height or diameter) determines the pitch. A large drum has a low pitch, a small drum has a high pitch. A guitar changes pitch by changing the length of the strings (when you press the string against the fret) A long string produces a low pitch, a short string produces a high pitch. A horn changes pitch when you change the length of the tube. A longer pipe produces a low pitch, a shorter pipe produces a high pitch. Portfolio entry #5Resonance or Doppler Effect p126 Write what you KNOW about ____________ Read about _____________( Resonance CP p521-522)(Doppler AP p44-45) Add to your written response…In YOUR OWN WORDS! Did you use many physics words ? Use your RUBRIC. Do you have • Definition • Relationship (what happens to the ______ when ________?) • Musical instrument example • Great detail • Picture or diagram (label to demonstrate the connection to your word) Share out with a partner…partner, what score would you give this response? How can it be made better? Edit your response until it becomes a perfect 4! Get a stamp Another Sound Quiz Tomorrow! Sound Quiz #3 no electronics during the quiz! Turn in quiz when finished Finish notebook pages 124-127 Work on project (Benchmarks 2,3,4) Portfolio entry #6- Shadow Write what you KNOW about Shadows p129 Read about Shadows (AP p533-534) Add to your written response.. In YOUR OWN WORDS! Did you use many physics words (light source, object, light rays, umbra, penumbra)? Use your RUBRIC. Do you have • Definition • Relationship (position of the object to the light source and the type of shadow produced) • Presentation example (how could you demonstrate shadows?) • Great detail • Picture or diagram (show how shadows are formed) Share out with a partner…partner, what score would you give this response? How can it be made better? Edit your response until it becomes a perfect 4! Project Benchmark #4 p128 To get full credit for this benchmark, you must do the following: • Have a set pattern of music for your group. • Have at least 6 notes played in the composition. • Plan out an entertaining presentation for this song/melody • Write out your plans here ON TIME! Extra Credit Opportunities: • Impressive and original (made by your group) musical score. • Use the music ideas of playing loudly (forte) and softly (piano) to make a message. • Learn and play a traditional song from another culture. Portfolio Entry # 7 - Reflection p130 Write what you KNOW about Reflection Read about Reflection (AP page 541-543) Add to your written response…In YOUR OWN WORDS! Did you use many physics words (plane/flat mirror, convex mirror, concave mirror)? Use your RUBRIC. Do you have • Definition • Relationship (angle of incidence, normal, angle of reflection) • Presentation example (how could you demonstrate reflection?) • Great detail • Picture or diagram Share out with a partner…partner, what score would you give this response? How can it be made better? Edit your response until it becomes a perfect 4! How will we use these effects in our presentation? Spring - Summer- Winter - Fall - Optical Tools • • • • • • Lenses Eyeglasses Microscope Camera Kaleidoscope Binoculars • • • • • • Flashlight Light boxes Telescope Prism Spectroscope Mirror p132 Checkpoint Due today! Benchmark #2 • Musical instrument – can you play at least 5 notes? Benchmark #3 • Chart completed (p125) • Questions answered Benchmark #4 • Music chosen • Image of notes played visible p133 Coin Under the Cup • Disappearing penny Refraction: “Tricks” on our Eyes Due to refraction of light from the water to the air, the fish appears closer to the surface than it actually is! Have you seen this phenomenon before? Where? p133 Figure from Niculescu Draw the light rays (include the normal and angles) P134 Investigation #8 Refraction • Active Physics Invest#8 (p558-560) • Steps 1-10 • Turn in laser Name pointer and get another stamp when finished • Finish CDP and get stamps Angle of incidence 30 45 60 ? You decide Angle of refraction P135136 Angle of reflection Investigation #8 • The angle of incidence is larger than the angle refraction when light travels from air (less dense) to plastic (more dense) p134 p134 Light is bent towards the normal when the speed of the new medium is lower. Light is bent away from the normal in the opposite case. Light model: Laws of Refraction p116 13. Light is bent when it travels from one medium to another of a different density. 14. The law of refraction- Snell’s Law(1621) – When the light passes through a denser medium, the light is bent toward the normal, because the light slows down (velocity decreases). – When light passes through a less dense medium the light is bent away from the normal because the light speeds up. P134 Draw the light rays (include the normal and angles) Reflection vs. Refraction Trapping the Light Fantastic. P138 • Steps 1-4 together • Finish all parts of the lab with your group • Do CU (p562) 1-3 • Get stamps when finished Refraction: Air/Glass Boundary Denser Material Light “bends” or refracts between different types of material (due to slower speed in denser materials). It is bent closer to the perpendicular (normal) in denser materials (water, glass). Can you draw the path of a light ray from air through a piece of glass? Through water? Critical angle When do light rays reflect, and when do they refract? The critical angle depends on the density of the medium Dispersion: “Spreading” of Visible Light When light is refracted, blue light bends more than red. Refraction therefore causes light to “spread” or disperse into its colors, just as you see when sunlight hits a prism. Remember: LIGHT RAYS DO NOT CURVE(They change direction) Figure from Cutnell & Johnson Figure from Halliday p139 p137 Refraction of Light • Refraction – Bending of light due to a change in speed from one medium to another. – Index of Refraction – Amount (measure of an angle) by which a material refracts light. – Prisms – Glass that bends light. Light is broken out into different colors because each frequency is bent at a different angle. – Bill Nye P134 Mirage Tank Demo p139 1.) Describe what happens to the beam before adding sugar. 2.) Describe what happens to the beam after the sugar dissolves. 3.) Why does this happen? 4.) Describe what happens to the beam after the sugar is mixed into the water. 5.) How is a mirage formed? 6.) Describe a mirage you have seen outside (or in the movies) Portfolio Entry # 8 - Refraction Write what you KNOW about Refraction Read about Refraction (Active Physics p561-562) Add to your written response…In YOUR OWN WORDS! Did you use many physics words (density, speed, medium)? p140 Use your RUBRIC. Do you have • Definition • Relationship (angle of incidence, angle of refraction, snell’s law) • Presentation example (how could you demonstrate refraction?) • Great detail • Picture or diagram Share out with a partner…partner, what score would you give this response? How can it be made better? Edit your response until it becomes a perfect 4! Reflection vs. Refraction P139 • PtoGo (p565) 1-4/CU (p562) 1-3 Stamp! • Benchmark #5 (front side only this week) P132 •Light Quiz Tuesday! Project Checkpoint • Poster • Musical instrument • 5 sound principles • Play a song • 5 light principles • 2 minute presentation • You may have back-up music • 2 light effects Benchmark #6 5 SOUND principles Describe and represent them here Title Team members names Evidence of student learning Pictures and diagrams of student project 5 LIGHT principles Describe and represent them here . SOUND principles Pitch: Our instruments each represent different levels of pitch. For example, the shoe-box the six marks have different pitch. Vibrations: are a rapid back-and-forth movement. All sounds make vibrations, so our instruments also make vibrations. Volume: The drum boxes make louder noise when got bigger. This way the volume of the sound changes. Wave Diffractions: when waves hit an obstacle they will spread out. That is show in this image >. LIGHT principles Best Song Ever Alex Vasilenko, Alex Shylo Evidence of student learning Pictures and diagrams of student project Shadow: An area that is not covered by light, mostly blocked by an object. Color: is the visual perceptual property corresponding in humans to the categories called red, green, blue and others Harmonics: When a object vibrates it propagates sound waves of a certain frequency. This frequency, in turn, sets in motion frequency waves called harmonics. Reflections: When light its something and bounces off. Not all objects reflect light, some do more then others. . Project Benchmark #5 Light Wave Property Chart Light Wave Effect How could it be used? What materials would you need to do this idea? Reflection Describe it using Physics p132 Light Quiz #1 • • • • Turn in quiz when finished Finish notebook pages Work on project Extra credit: Ch 29 focus notes due monday RAINBOWS - HOW DO THEY HAPPEN? p138 1.) What atmospheric events combine to make a rainbow? 2.) How is a rainbow made? 3.) What would a rainbow look like if you were in a helicopter (and there was no earth in the picture)? 4. How do you make a double rainbow? What happens to the colors? Dispersion: Rainbow White light is refracted inside raindrops and spreads to form the rainbow colors: roy g biv Then the light reflects forward and refracts more as it passes out of the raindrop p138 p138 Why is the sky blue? 1.) Explain why the sky is blue (what do the air molecules do to different wavelengths of light? 2.) Why are sunsets red (instead of blue)? 3.) How can astronomers use this information when they look at distant planets? Transmission of Light QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. • Transparent Objects: – All light gets transmitted through (no scattering). – Color transmitted is color you see. All other colors are absorbed. • Translucent Objects: – Some light is scattered and some is transmitted. • Opaque: – Light is either reflected or absorbed. (mirrors count as opaque) – Color of opaque objects is color it reflects. Click to test your knowledge Light model: Color of Light 15. White light is the presence of ALL the colors of the visible spectrum. Notice the center of the Venn diagram above. Black objects absorb ALL the colors and no light is reflected back. 16. Each color of light has a different frequency and wavelength (ROY G BIV) – Bill Nye p117 Mixing Colored Light When red, blue, and green light are projected onto a screen, the overlapping areas appear different colors. Where all the three overlap, white is produced. p RED + GREEN =YELLOW RED+ BLUE = MAGENTA GREEN + BLUE = CYAN Additive primary colors are red, blue, and green because these colors produce the highest number of different colors. Complementary Colors When two colors are added together to produce white, they are called complementary colors. YELLOW + BLUE = WHITE ( Yellow is a combination of Green + Red ) MAGENTA + GREEN = WHITE ( Magenta is a combination of Red + Blue) CYAN + RED = WHITE ( Cyan is a combination of Green+ Blue) p Color vision The eye has three types of light receiving units, red, green and blue cones Stimulation of Cones in Your Eyes • If you stimulate only red and green cones, not blue, you see YELLOW. Organization of the retina Science Continues to Succeed! • The genes controlling the three cone pigments have been located on specific chromosomes Images of two different living human retinas showing the diversity of numbers of cones sensitive to different colors. P138139 • Use colored pencils to complete the handout Phet:Color simulation P140 • Is Light More Like a Particle or a Wave? p140 Get a stamp when done Is light particles or waves? • Can you knock over a book from your seat? • List how… p140 Particle or wave? Particle or wave? Diffraction is *Diffraction animation Particle or wave? Interference is **Wave interference animation Annotation Guide Circle key scientists, and dates What ideas or words grab your attention? Where does it say light is a wave or particle? What puzzles you or makes you question what you thought you knew? or words that are unfamiliar to you (to look up) Place by things that connect to you, a text you’ve read, or something you knew already knew (video) Wave particle duality – day 2 P141142 Wave particle duality – day 3 Turn in your paper when finished Light Model: LIGHT & USES p117 17. Diffraction – Bending of waves around the edge of a barrier. New waves are formed from the original. breaks images into bands of light & dark and colors. 18. Interference from thin films creates iridescence (the color in bubbles) 19. Polarized lenses reduce glare by sifting light 20. LASERs = Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation = produces light waves that are all the same frequency, phase, and direction LIGHT & USES: Diffraction © 2000 Microsoft Encarta • A diffraction grating. Each space between the ruled grooves acts as a slit. The light bends around the edges and gets refracted. Polarized light Portfolio Entry # 9 - Color p142 Write what you KNOW about color Read about color Add to your written response…In YOUR OWN WORDS! Did you use many physics words (black, white, complimentary)? Use your RUBRIC. Do you have • Definition • Relationship (between wave length and color observed) • Presentation example ( how can you use color in your presentation?) • Great detail • Picture or diagram Share out with a partner…partner, what score would you give this response? How can it be made better? Edit your response until it becomes a perfect 4! Portfolio Entry # 10 – your choice (dispersion (rainbows), polarization (sunglasses), diffraction (ultrasound/microscopy), EM Spectrum, interference (bubbles), lasers) Write what you KNOW about _________ Read about __________ Add to your written response…In YOUR OWN WORDS! Did you use many physics words ? p144 Use your RUBRIC. Do you have • Definition • Relationship • Presentation example • Great detail • Picture or diagram Share out with a partner…partner, what score would you give this response? How can it be made better? Edit your response until it becomes a perfect 4! • Portfolio #9: Color…page 142 • Portfolio #10: your choice page 144 (dispersion, polarization, diffraction, EM Spectrum, interference, lasers) • project Benchmark 5 – finish the back side • Project Benchmark 6 - Bring materials to make posters tomorrow • Unit Test Monday! Study your quizzes and notes. Practice test and jeopardy on my website for review Waves Unit Test There are sample test problems for sound and light on my website! Sound Properties Longitudinal Amplitude/volume Wavelength/pitch Interference Musical instruments Wave equation Period/frequency Doppler effect Resonance Light Properties Transverse/EM spectrum Shadows Reflection Refraction Critical angle Color Diffraction Polarization