Followings are what you will find at the end of... For LEARNING OBJECTIVES: Highlight the main idea for EACH...
advertisement

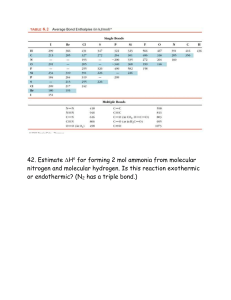
Pre CH10 HW for Silberberg Followings are what you will find at the end of the chapter in your textbook. For LEARNING OBJECTIVES: Highlight the main idea for EACH objective. Ready carefully so you don’t highlight everything. For MASTER THESE SKILLS: Highlight the main idea for each skill. Ready carefully so you don’t highlight everything. For KEY TERMS: Make sure you can define it and/or give an example of it. Pick TWO terms of your choice and actually write the definition or an example. For KEY EQUATIONS AND RELATIONSHIP: Next to EACH, define each term. Be very specific. CHAPTER REVIEW GUIDE Learning Objectives Relevant section (§) and/or sample problem (SP) numbers appear in parentheses. Understand These Concepts 1. How Lewis structures depict the atoms, bonding pairs, and lone electron pairs in a molecule or polyatomic ion (§10.1) 2. How resonance and electron delocalization explain bond properties in many compounds with double bonds adjacent to single bonds (§10.1) 3. The meaning of formal charge and how it is used to select the most important resonance structure; the difference between formal charge and oxidation number (§10.1) 4. The octet rule and its three major exceptions—molecules with a central atom that has an electron deficiency, an odd number of electrons, or an expanded valence shell (§10.1) 5. How electron-group repulsions lead to molecular shapes (§10.2) 6. The five electron-group arrangements and their associated molecular shapes (§10.2) 7. Why double bonds and lone pairs cause deviations from ideal bond angles (§10.2) 8. How bond polarities and molecular shape combine to give a molecule polarity (§10.3) Page 422 Master These Skills 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Using a stepwise method for writing a Lewis structure from a molecular formula (SPs 10.1–10.3, 10.5) Writing resonance structures for molecules and ions (SP 10.4) Calculating the formal charge of any atom in a molecule or ion (SP 10.5) Predicting molecular shapes from Lewis structures (SPs 10.6–10.8) Using molecular shape and electronegativity values to predict the polarity of a molecule (SP 10.9) Key Terms Page numbers appear in parentheses. Section 10.1 Lewis structure (Lewis formula) (395) resonance structure (resonance form) (399) resonance hybrid (399) electron-pair delocalization (400) formal charge (401) electron deficient (403) free radical (403) expanded valence shell (404) Section 10.2 valence-shell electron-pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory (406) molecular shape (406) bond angle (407) linear arrangement (407) linear shape (407) trigonal planar arrangement (408) bent shape (V shape) (408) tetrahedral arrangement (409) trigonal pyramidal shape (410) trigonal bipyramidal arrangement (410) equatorial group (410) axial group (410) seesaw shape (411) T shape (411) octahedral arrangement (411) square pyramidal shape (412) square planar shape (412) Section 10.3 molecular polarity (416) dipole moment (μ) (417) Key Equations and Relationships Page numbers appear in parentheses. 10.1 Calculating the formal charge on an atom (401): Formal charge of atom 10.2 Ranking the effect of electron-pair repulsions on bond angle (410): Answer the following questions. Show your work. • (a) Figure 10.1 on page 396 has the steps to convert a molecular formula into a Lewis structure. Re-write the steps. (b) Using the steps from (a), convert PCl3 to Lewis Dot structure. (c) Read about Resonance Structures. Explain in your own words. Give one example. (d) Compare "polar bond" with 'polar molecule'. (e) Study Figure 10.10 on Pg 413. Summarize the information given.