BIOLOGY Properties of Water
advertisement
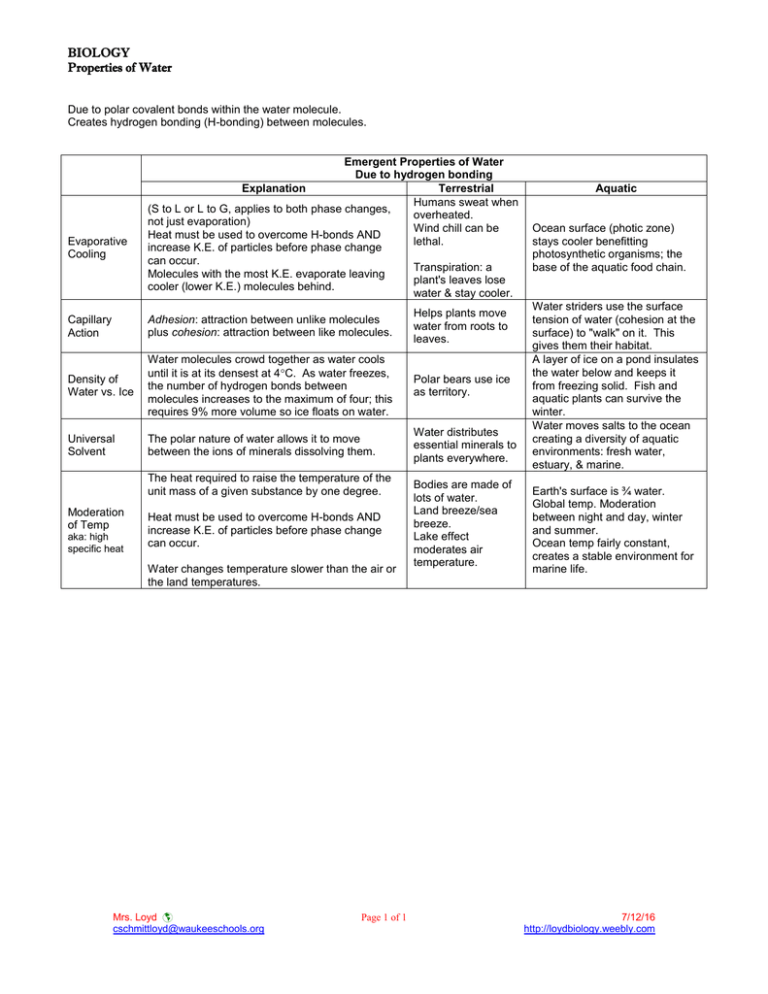
BIOLOGY Properties of Water Due to polar covalent bonds within the water molecule. Creates hydrogen bonding (H-bonding) between molecules. Evaporative Cooling Emergent Properties of Water Due to hydrogen bonding Explanation Terrestrial Humans sweat when (S to L or L to G, applies to both phase changes, overheated. not just evaporation) Wind chill can be Heat must be used to overcome H-bonds AND lethal. increase K.E. of particles before phase change can occur. Transpiration: a Molecules with the most K.E. evaporate leaving plant's leaves lose cooler (lower K.E.) molecules behind. water & stay cooler. Capillary Action Adhesion: attraction between unlike molecules plus cohesion: attraction between like molecules. Helps plants move water from roots to leaves. Density of Water vs. Ice Water molecules crowd together as water cools until it is at its densest at 4C. As water freezes, the number of hydrogen bonds between molecules increases to the maximum of four; this requires 9% more volume so ice floats on water. Polar bears use ice as territory. Universal Solvent The polar nature of water allows it to move between the ions of minerals dissolving them. Water distributes essential minerals to plants everywhere. The heat required to raise the temperature of the unit mass of a given substance by one degree. Moderation of Temp aka: high specific heat Heat must be used to overcome H-bonds AND increase K.E. of particles before phase change can occur. Water changes temperature slower than the air or the land temperatures. Mrs. Loyd cschmittloyd@waukeeschools.org Page 1 of 1 Bodies are made of lots of water. Land breeze/sea breeze. Lake effect moderates air temperature. Aquatic Ocean surface (photic zone) stays cooler benefitting photosynthetic organisms; the base of the aquatic food chain. Water striders use the surface tension of water (cohesion at the surface) to "walk" on it. This gives them their habitat. A layer of ice on a pond insulates the water below and keeps it from freezing solid. Fish and aquatic plants can survive the winter. Water moves salts to the ocean creating a diversity of aquatic environments: fresh water, estuary, & marine. Earth's surface is ¾ water. Global temp. Moderation between night and day, winter and summer. Ocean temp fairly constant, creates a stable environment for marine life. 7/12/16 http://loydbiology.weebly.com








