Anatomy and Physiology II Exam II Instructor: Brian Cambron BIOL 122
advertisement

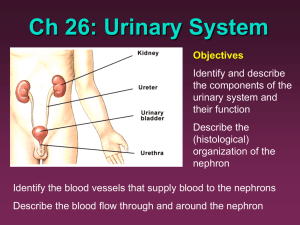
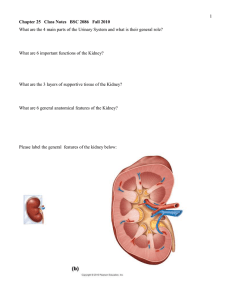
Anatomy and Physiology II Exam II Instructor: Brian Cambron BIOL 122 Where are the kidneys located? What does the term retroperitoneal mean? The kidney has two main regions to its structure. What do we call the inner portion? The outer portion? What are the main blood vessels called for the kidney? Each nephron can be broken down initially into two parts. What do we call the swollen beginning piece? What do we call the long tubular second part? The Glomerular Capsule is also called what? What is another name for the Nephron Loop? What does PCT stand for? What does DCT stand for? What does NFP stand for? What does GFR stand for? The renal pelvis, a part of the ureter, is divided into two to three main branches, what do we call them? Each of those will divide further into 8 to 14 smaller branches, what do we call those? What substance is the main waste product of amino acid metabolism and is secreted in urine? What other waste product is the result of purine metabolism and also secreted in the urine? What is the technical word for the process of voiding urine from the body, the urination reflex? In which organs is urine produced? What is the functional unit of the kidney? The tuft of capillaries where renal filtration begins is called? Which of the pressures promotes glomerular filtration? What are the functions of the kidneys? The majority of tubular reabsorption occurs in what part of the kidney? Approximately how many nephrons are in each kidney? Nephrons whose corpuscles are located close to the renal medulla are called? What do we call those whose corpuscles are located well within the cortex? In response to low blood pressure or low ion levels in blood, the kidney will secrete what substance? What is the equation that describes how urine volume is determined? What are the proteins called that ADH stimulates the tubule cells to insert in their plasma membranes? What are the structures that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder called? Under normal conditions, how much glucose should urine contain? Which of the following best describes the function of aldosterone on kidney function? Between which two structures is the space, the renal capsule, where the filtrate is collected in the kidney? By what process does water move from the tubules and collecting ducts back into the blood plasma? Which part of the nephron is the specific target of ADH? The juxtaglomerular apparatus consists of the juxtaglomerular cells and the cells of the? The juxtaglomerular apparatus, as part of the kidneys autoregulation, is responsible for the secretion of? A renal corpuscle includes what two structures? The renal medulla is composed of triangular sections of tissue made up of collecting ducts and nephron loops called? The opening in the side of the kidney which allows the passage of blood and lymphatic vessels, nerves and the ureter is called the? The renal cortex is covered by a tough, fibrous outer layer called the? The visceral layer of the glomerular capsule is composed of highly modified epithelial cells called? Collecting ducts of the kidney merge and empty into a renal calyce through openings located in what? What do we call the network of fine blood vessels that surround the nephron and is involved in reabsorbing material? What will Glomerular filtrate not contain? The capillary wall of glomerular capillaries is more permeable than ordinary capillaries because of small holes or openings in them called? What hormone is secreted in response to high blood pressure to increase sodium excretion? The point where more solute is entering the glomerular filtrate than the kidneys can physically reabsorb is called the? The rate at which any one particular chemical is filtered by the kidney is called the? The counter current mechanism functions primarily in which part of the nephron? The triangular area on the internal floor of the urinary bladder where the openings for the ureters and urethra are located is called the? A ureter or urethra may be obstructed by calcified bodies called what? The micturition reflex can only be voluntarily controlled by the? Will Antidiuretic hormone lead to increased or decreased urine volume? What is the urethra responsible for doing? How many layers of squamous epithelial cells is the wall of the Glomerular capsule composed of? What blood vessel (arteriole) supplies blood to the Glomerulus? Which one drains blood away from the Glomerulus? Is the urinary bladder above or below the parietal peritoneum? Which of the two arterioles has a wider diameter, the afferent or efferent? If the osmotic pressure of the blood is increased, will the glomerular filtration rate be increased or decreased? There is a matching part to the exam. It consists of a picture and labeling the parts of the urinary system in the body. A diagram of the body is included with the exam. Short Answer Describe, in detail, the sequence of events for the Angiotensin II System. Explain; using the formula to determine NFP: Decreased GFR due to hypovolemic shock and decreased GFR due to urinary tract obstruction.