Modules 1-3 Study Guide
advertisement

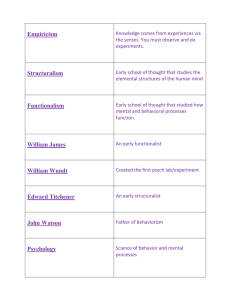
Modules 1-3 Study Guide Definition of psychology Know ideas of early philosophers Freud, Calkins, William James, Titchener, Wundt Empiricism Structuralism o Introspection Functionalism Nature-Nurture Debate Natural Selection Understand biopsychosocial approach Know all the perspectives Humanism Cognitive Neuroscience Know the different types of professionals in the psychology field (ex: psychiatrist) Hindsight bias Overconfidence Aspects of scientific attitude Theory Hypothesis Replication Operational Definition Using animals in studies—ethics and procedures Ethics and procedures for working with human participants Possible influences of researchers’ values and opinions Case study Naturalistic Observation Survey False Consensus Effect Population vs. Sample Importance of random sampling/random selection Experimentation o Cause and effect o o Placebo and Placebo Effect Independent variable vs. Dependent Variable o Double-blind procedure o Control group vs. Experimental Group o Random Assignment Correlation o Remember: CORRELATION DOES NOT PROVE CAUSATION o Positive vs. Negative o Correlation Coefficient o Scatterplot Illusory Correlation Mean, Median, and Mode Measures of Variation o Range o Variance o Standard Deviation Statistical Significance Normal and Skewed Distributions