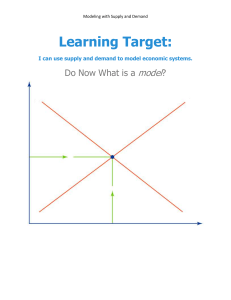
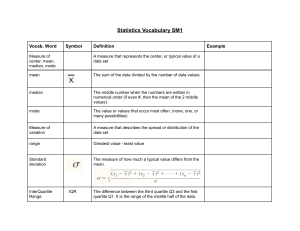
UNIT 1 REVIEW Science • 1880 • Wundt• Psycho physics • Structuralists• Mind = “machine” 1st “atoms” • Introspection• Study self • Functionalist• mind • “ghost” • James a “stream of consciousness” “Schools” of Psych • “approaches”- emphasis • “behaviorism” - actions Intro • Little bit, few questions… • Early appoaches, techniques • Wundt, James 3. “Psychology today” • Approaches– “style” (focus) Psychodynamic • “unconscious” Behaviorism • Watson • “observable” • Environment • learning • Skinner Evolutionary Psych • Natural • Selection- traits • Allow survival 6-8% •RESEARCH •METHODS “Research Methods” • “Success is peace of mind which is a direct result of self-satisfaction in knowing you made the effort to become the best of which you are capable.” • John Wooden Psychology • Science • Behavior • Mental Processes Scientists • “fair” • ”open to truth” • Curious • Skeptical •- Science “Research” • Hypothesis (?) • Research= test • Empirical • Data (#s) • Theory (explain it) Scientific attitude • Curious • Skeptical • “truth” • hindsight • Variables • Operational definitions • Replicate • generalize “Science” • Hypothesis (?). Kids sleep in class…. Up late with social media/video games? • Research= test? • Empirical = observe? • Data (#s)? • Operational definitions= ? • Theory (explain it) Kids are up late on social media METHOD 1 •DESCRIPTIVE •RESEARCH . • Natural Observation Observe learning? Evaluate Research methods: • Good for? Surveys– Prejudice? data “Sample” who Sample? (who asked) Evaluate Research methods: • Good for? Evaluate Surveys Case Study• 4. Correlational Research notes METHOD 2 •CORRELATIONAL •RESEARCH **Remember: all research techniques • Hypothesis • Empirical • Test • Data (#s/operational definitions • Theory • 2 variables (factors) • “relationship” Positive correlation (+) Rise and fall Negative correlation (-) • “INVERSE” • -.46 • (TV & Vocab) Causation? Causation? Never!! •CORRELATION •NEVER SHOW •CAUSATION!!!! • 3RD (unknown) Variable? Correlational coefficient # • -1.0 .9. .8. .7. .6. .5 .4. .3. .2. .1 • .20 very weak • .20-.40 weak • .40-.60 moderate • .60-.99 very strong • 1.0 “perfect” 0 +.1. .2. .3. .4. .5. .6. .7. .8. .9 1.0 Positive correlation (+) • go together • Ex. +.55 (SATs & college success) • Up—up • Down- down • Negative correlation (-) • opposite • -.46 (TV & Vocabulary) • Up---down • Down----up SCATTERPLOTS Graphing correlations • • • • • • • • • • • • Test 1 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 test 2 John: 80 on test 1, 80 on test Gloria: 90 on test 1, 90 on test Squibob: 20 on test 1, 20 on test 2 • • • • • • • • • • • • Psych Test 1 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 psych test 2 Scatterplots- graph # DRAWING CORRELATIONS Correlational research •Good: predictive •Bad: No causation • Electronic textbook • Modules 4-6 • Multiple choice questions • Vocab Correlations POSITIVE OR NEGATIVE? • AP Readiness & success in AP class • Smart phone use & teenager happiness • Social media use & teen anger happiness • GPA & hours studied • Hours of sleep and alertness Ice cream sales & violent crime • Rain and business at starbucks • Sunny weather and business at a beach restaurant • Distance Learning and learning • Happiness and worker productivity • Happiness and kindness •13. EXPERIMENTAL •RESEARCH 8. “LECTURE: Experimental research • Good: CAUSE AND EFFECT • Bad: “artificial” (difficult) • Control all variables IV vs DV • Cause • IV (independent variable) • Effect • DV (dependent variable) • Confounding variables IV? • Experimental group Control Group Population • • Experimental Group IV • • DV? *RANDOM ASSIGNMENT!! Sample Control Group placebo Population Sample Experimental Group IV DV? Statistical significance Control Group placebo replication • Repeat • Operational definitions #s PROBLEMS • “confirmation bias” • “overconfidence” Experimenter bias? • “unfair” Double blind • Experimenter & • subjects Ethics-- APA • H--- HARM (no) • D -- debrief (explain) • V – voluntary • I--- informed consent • P --- private (confidential • Harley Davidson was a Very Important person •H D V I P Measures of central tendency • normal curve– mean, median, mode in center • Mean average • Median- “middle”, equal 3 scores above and below • Mode- most frequent score • Mean- average • Median- “middle” • Mode– frequent • 1,1, 2,3,7 , 9, 10 • 1, 5, 1 • 2, 3, 1 • 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 • 1, 3, 5, 5, 7, 9 Variabliity • Range- low to high • Standard deviation- “spread-outedness” • Skewed curve= not “normal” • Median, mode in middle-----mean is “skewed” • Mean- average • Median- “middle” • Mode– most frequent % scores within 1 standard deviation? % within 2 standard deviations? Within 3? Standard deviation • “spreadoutedness” of scores • Range: low to high Population Sample Experimental Group IV DV? Statistical significance Control Group placebo