Empiricism
advertisement
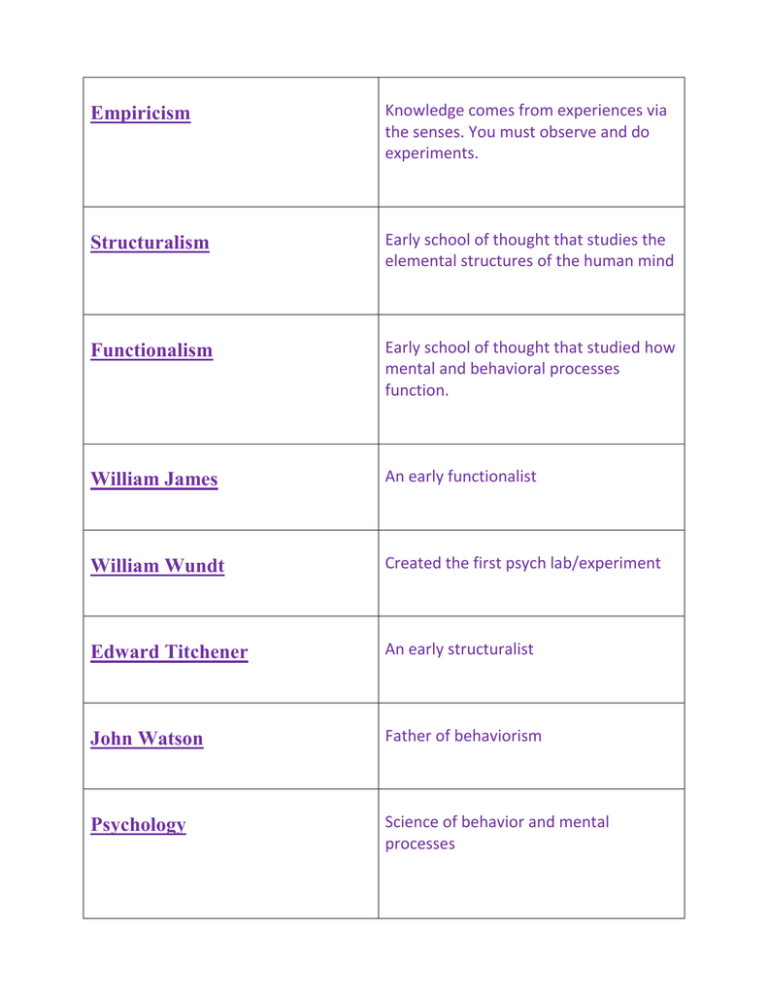
Empiricism Knowledge comes from experiences via the senses. You must observe and do experiments. Structuralism Early school of thought that studies the elemental structures of the human mind Functionalism Early school of thought that studied how mental and behavioral processes function. William James An early functionalist William Wundt Created the first psych lab/experiment Edward Titchener An early structuralist John Watson Father of behaviorism Psychology Science of behavior and mental processes Nature/Nurture Debate on whether we are more a product of our genes or our environment Natural Selection The stronger traits will survive and be passed down to future generations Basic Research Research that aims to increase scientific knowledge Applied Research Research that is used to study and solve practical problems. Clinical Psychology A branch of psychology that studies, assesses and treats people with psychological problems Psychiatry A branch of medicine that provides treatments (such as drugs). Hindsight Bias I –Knew –it –all –along phenomenon Theory An explanation that organizes and interprets observations Hypothesis A testable prediction Operational Definitions A statement of the procedures used to define research variables. Needed for replication. Replication Repeating the research study, with new participants in different situations, to see whether the basic findings extend to other participants and circumstances. Case study Studies one person in depth Survey A technique for ascertaining the self reported attitudes or behaviors of people, by questioning a representative, random sample of people False Consensus Effect The tendency to overestimate the extent to which others share our beliefs and behaviors Population All the cases in a group from which samples may be drawn for a study. Random Sample A sample that fairly represents a population because each member has an equal chance of inclusion. Naturalistic observation Observing and recording behaviors in a natural setting Correlation Coefficient A statistical measure of the extent to which 2 factors vary together, and thus how well they can predict each other Scatterplot A graphed cluster of dots, each of which represents the values of 2 variables. Little scatter indicates high correlation. Illusory Correlation The perception of a relationship where none exists. Experiment A research method that can establish a cause and effect relationship Double blind procedure An experimental procedure in which both the research participants and the research staff are ignorant about who was given the treatment or placebo. Commonly used in drug trials Placebo effect Experimental results caused by expectations alone; any effect on behavior caused by the administration of an inert substance or condition, which is assumed to be an active agent. Experimental Condition The group of people who receives the independent variable or placebo in an experiment Control Condition The group of people that contrasts with the experimental condition and serves as a comparison. Random Assignment Assigning participants to experimental and control conditions by chance, thus minimizing preexisting differences between those assigned to the different groups Independent Variable The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied Dependant Variable The experimental factor that is being studied or measured. In psych it is usually a mental process. Mode The most frequently occurring number in a distribution. Mean The average Median The middle score in a distribution. Range The difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution. Standard Deviation A computed measure of the how scores vary around the mean American Psychological Association (APA) is a scientific and professional organization that represents psychologists in the United States. Sets ethical standards for the field of psychology. Obtain consent of potential participants Ethical Guidelines set by the APA- (need to find all 4) Protect from harm Make sure info is kept confidential Fully explain research after the study has been completed. Biological Perspective How our brain and body chemistry enable emotions, memories, and sensory experiences. Evolutionary Perspective How the natural selection of traits promoted the survival of genes. Darwin Psychodynamic Perspective How behavior springs from unconscious drives and conflicts. Freud. Behavioral Perspective How we learn observable responses. Skinner Cognitive Perspective How we encode, process, store and retrieve information Humanistic Perspective How we meet our needs for love and acceptance and achieve self-fulfillment Social-Cultural Perspective How behavior and thinking vary across situations and cultures



