Exhibit ES-1. Synergistic Strategy: Potential Cumulative Savings –2023
advertisement

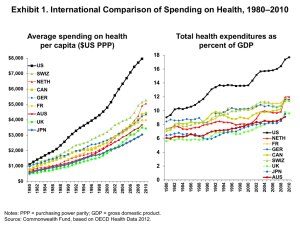
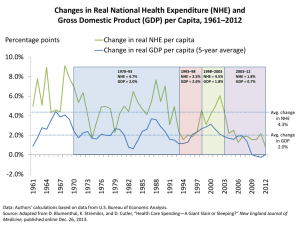
Exhibit ES-1. Synergistic Strategy: Potential Cumulative Savings Compared with Current Baseline Projection, 2013–2023 Net impact in $ billions* Total NHE State Federal and local government government Private employers Households 2013–2018 –$686 –$345 –$84 –$66 –$192 2013–2023 –$2,004 –$1,036 –$242 –$189 –$537 Note: NHE = national health expenditures. * Net effect does NOT include potential impact of spending target policy. Source: Estimates by Actuarial Research Corporation for The Commonwealth Fund. Current baseline projection assumes that the cuts to Medicare physician fees under the sustainable growth rate (SGR) formula are repealed and basic physician fees are instead increased by 1% in 2013 and held constant from 2014 through 2023. Exhibit ES-2. Projected National Health Expenditures (NHE), 2013–2023: Potential Impact of Synergistic Strategy NHE in $ trillions $6.0 Current baseline NHE projection $5.5 Projected NHE net of policy impacts $5.0 $5.1 $4.0 $2.9 $3.0 $2.0 $1.0 NHE as percentage of GDP— Current projection: 18% in 2013→21% in 2023 Under unified strategy: 18% in 2013→19% in 2023 Cumulative NHE savings under synergistic strategy: $2.0 trillion $0.0 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 Note: GDP = gross domestic product. Source: Estimates by Actuarial Research Corporation for The Commonwealth Fund. Current baseline projection assumes that the cuts to Medicare physician fees under the sustainable growth rate (SGR) formula are repealed and basic physician fees are instead increased by 1% in 2013 and held constant from 2014 through 2023. Exhibit ES-3. Cumulative Net Impacts of Payment, Engaging Consumers, and Systemwide Policies, 2013–2023 Net savings in $ billions 2013– 2018 2019– 2023 Total 2013–2023 Payment reforms to pay for value to accelerate delivery system innovation –$442 –$891 –$1,333 Policies to expand and encourage high-value choices by consumers –$41 –$148 –$189 Systemwide actions to improve how health care markets function* –$203 –$279 –$481 Cumulative NHE impact** –$686 –$1,318 –$2,004 Note: NHE = national health expenditures. Totals may not add because of rounding. * Net savings do NOT include the potential impact of the spending target policy. Malpractice savings included in impact of provider payment reforms. ** Cumulative NHE impact adjusted for potential overlap of component policy impacts. Source: Estimates by Actuarial Research Corporation for The Commonwealth Fund. Current baseline projection assumes that the cuts to Medicare physician fees under the sustainable growth rate (SGR) formula are repealed and basic physician fees are instead increased by 1% in 2013 and held constant from 2014 through 2023. 4 Exhibit 1. International Comparison of Spending on Health, 1980–2010 Average spending on health per capita ($US PPP) Total health expenditures as percent of GDP 18 $8,000 US $7,000 16 SWIZ NETH $6,000 14 CAN 12 GER FR 10 AUS UK 8 JPN US NETH FR GER CAN SWIZ UK JPN AUS Notes: PPP = purchasing power parity; GDP = gross domestic product. Source: Commonwealth Fund, based on OECD Health Data 2012. 2004 2002 2000 1998 1996 1994 1992 1990 1988 1986 1984 1982 2010 2008 2006 2004 2002 2000 1998 1996 1994 1992 1990 0 1988 $0 1986 2 1984 $1,000 1982 4 1980 $2,000 1980 6 2010 $3,000 2008 $4,000 2006 $5,000 Exhibit 2. Medicare Spending per Enrollee Projected to Increase More Slowly Than Private Insurance Spending per Enrollee and GDP per Capita Annual rate of growth (percent) 8.0 GDP per capita 7.0 6.0 Medicare spending per enrollee Employer-sponsored insurance spending per enrollee 5.0 3.7 4.0 3.0 4.6 4.5 3.8 2.9 2.7 2.0 1.0 0.0 2008–2011 2011–2021 (projected) Note: GDP = gross domestic product. Source: CMS Office of the Actuary, National Health Expenditure Projections, 2011–2021, updated June 2012. Exhibit 3. Premiums Rising Faster Than Inflation and Wages Cumulative changes in insurance premiums and workers’ earnings, 1999–2012 Projected average family premium as a percentage of median family income, 2013–2021 Percent Percent 200 Health insurance premiums 175 180% Workers' contribution to premiums 150 Workers' earnings 125 Overall inflation 35 30 172% 25 22 23 20 100 15 12 13 75 50 25 47% 10 38% 5 15 17 18 18 18 18 19 24 26 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 20 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2004 2003 2002 2001 2000 1999 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 0 0 Projected Sources: (left) Kaiser Family Foundation/Health Research and Educational Trust, Employer Health Benefits Annual Surveys, 1999– 2012; (right) authors’ estimates based on CPS ASEC 2001–12, Kaiser/HRET 2001–12, CMS OACT 2012–21. Exhibit 4. Projected U.S. National Health Expenditures (NHE) by Source, 2013–2023 NHE in $ billions 6000 $5.5 trillion Federal government 5000 $4.0 trillion 32% State and local government 4000 $2.9 trillion 31% 28% 18% 3000 2000 18% 24% 18% 25% 1000 26% 26% 28% 26% 2013 2018 2023 17.9% 18.7% 20.5% 0 % GDP: Note: GDP = gross domestic product. Source: Estimates by Actuarial Research Corporation for The Commonwealth Fund. Private employers (including "other private revenue") Households Exhibit 5. High Performance Health System Criteria for Developing Options to Stabilize Spending Growth • Set targets for total spending growth • Pay for value to accelerate delivery system reform for better outcomes, better care, at lower costs • Address the systemwide causes of health spending growth―not just federal health costs • Align incentives for providers and consumers across public and private payers • Protect access and enhance equity, but also engage and inform consumers • Invest in information systems to guide action Exhibit 6. Synergistic Strategy: Potential Cumulative Savings Compared with Current Baseline Projection, 2013–2023 Net impact in $ billions* Total NHE State Federal and local government government Private employers Households 2013–2018 –$686 –$345 –$84 –$66 –$192 2013–2023 –$2,004 –$1,036 –$242 –$189 –$537 Note: NHE = national health expenditures. * Net effect does NOT include potential impact of spending target policy. Source: Estimates by Actuarial Research Corporation for The Commonwealth Fund. Current baseline projection assumes that the cuts to Medicare physician fees under the sustainable growth rate (SGR) formula are repealed and basic physician fees are instead increased by 1% in 2013 and held constant from 2014 through 2023. Exhibit 7. Synergistic Strategy: Cumulative Savings, 2013–2023 Payment reforms to accelerate delivery system innovation ($1,333 billion) • Pay for value: replace the SGR with provider payment incentives to improve care • Strengthen patient-centered primary care and support care teams • Bundle hospital payments to focus on total cost and outcomes • Align payment incentives across public and private payers Policies to expand and encourage high-value choices ($189 billion) • Offer new Medicare Essential plan with integrated benefits through Medicare, offering positive incentives for use of high-value care and care systems • Provide positive incentives to seek care from patient-centered medical homes, care teams, and accountable care networks (Medicare, Medicaid, private plans) • Enhance clinical information to inform choice Systemwide actions to improve how health care markets function ($481 billion) • Simplify and unify administrative policies and procedures • Reform malpractice policy and link to payment* • Target total public and private payment (combined) to grow at rate no greater than GDP per capita** Notes: SGR = sustainable growth rate formula; GDP = gross domestic product. * Malpractice policy savings included with provider payment policies. ** Target policy was not scored. Exhibit 8. Projected National Health Expenditures (NHE), 2013–2023: Potential Impact of Synergistic Strategy NHE in $ trillions $6.0 Current baseline NHE projection $5.5 Projected NHE net of policy impacts $5.0 $5.1 $4.0 $2.9 $3.0 $2.0 $1.0 NHE as percentage of GDP— Current projection: 18% in 2013→21% in 2023 Under unified strategy: 18% in 2013→19% in 2023 Cumulative NHE savings under synergistic strategy: $2.0 trillion $0.0 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 Note: GDP = gross domestic product. Source: Estimates by Actuarial Research Corporation for The Commonwealth Fund. Current baseline projection assumes that the cuts to Medicare physician fees under the sustainable growth rate (SGR) formula are repealed and basic physician fees are instead increased by 1% in 2013 and held constant from 2014 through 2023. Exhibit 9. Impact of Synergistic Strategy on Projected Annual Hospital and Physician Spending, 2013–2023 Spending in $ billions $2,000 Hospital (baseline) Hospital (net of policy impacts) $1,750 $1,646 Physician (baseline) $1,500 Physician (net of policy impacts) $1,509 $1,250 $1,122 $1,000 $902 $750 $597 $1,055 Projected growth of hospital spending, 2013–2023: • Baseline projection: 82% (6.2% annual) • Net of policy impact: 67% (5.3% annual) Projected growth of physician spending, 2013–2023: • Baseline projection: 88% (6.5% annual) • Net of policy impact: 77% (5.9% annual) $500 $250 $0 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 Source: Estimates by Actuarial Research Corporation for The Commonwealth Fund. Current baseline projection assumes that the cuts to Medicare physician fees under the sustainable growth rate (SGR) formula are repealed and basic physician fees are instead increased by 1% in 2013 and held constant from 2014 through 2023.