War in the Pacific
advertisement

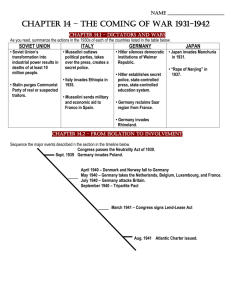
War in the Pacific Pearl Harbor • December 7, 1941 Japan attacks the US Pacific fleet at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. The US can no longer remain neutral and we enter the war. Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto Pearl Harbor from the Cockpit of a Japanese Pilot Pearl Harbor - Dec. 7, 1941 A date which will live in infamy! USS Arizona, Pearl Harbor President Roosevelt Signs the US Declaration of War Pacific Theater of Operations “Tokyo Rose” Singapore Surrenders [February, 1942] U.S. Surrenders at Corregidor, the Philippines [March, 1942] Bataan Death March: April, 1942 76,000 prisoners [12,000 Americans] Marched 60 miles in the blazing heat to POW camps in the Philippines. Bataan: British Soldiers A Liberated British POW The Burma Campaign General Stilwell Leaving Burma, 1942 The “Burma Road” Battle of the Coral Sea: May 7-8, 1942 • Coral Sea – This was the first victory for the Americans against the Japanese. Battle of Midway Island: • Battle of Midway – The turning point in the war in the Pacific. American aircraft carriers defeated Japanese aircraft carriers. 3 of their 4 carriers were sunk in this battle. Japan goes backward after this point. June 4-6, 1942 Battle of Midway Island: June 4-6, 1942 Turning point of the war in the Pacific Allied Counter-Offensive: “Island-Hopping” • Island hoping – The allies plan to take back one island at a time. Each time getting closer to Japan for the final invasion. “Island-Hopping”: US Troops on Kwajalien Island Farthest Extent of Japanese Conquests Japanese Kamikaze Planes: The Scourge of the South Pacific Kamikaze Pilots Suicide Bombers Gen. MacArthur “Returns” to the Philippines! [1944] • Navajo Code Talkers – Used in the Pacific. They spoke in Navajo and in code. Navajo is not a written language and it’s very complex. Battleship was a whale and Germany was the Iron Hat. The code was never broken. • Iwo Jima and Okinowa – These were the last two islands before Japan. The Japanese would not surrender. Death was the only thing to stop them. Iwo Jima was where the marines raised the flag on Mount Suribachi. US Marines on Mt. Surbachi, Iwo Jima [Feb. 19, 1945] Hiroshima and Nagasaki • Invasion of Japan? Z-Day – Allies believed invasion would lead to a huge loss of life – Truman hoped to shorten the war and save lives – US makes the decision to drop the atomic bomb on Japan – Hiroshima: 8/6/1945, Fatman (uranium) – Japan does not surrender – Nagasaki: second bomb dropped 8/9/1945, Little Boy (plutonium) – Japan Surrenders 9/2/1945 V-J Day (September 2, 1945) V-J Day in Times Square, NYC Effects of War 1. Death – 50 million died – More than half were civilians 2. Physical and Economic Destruction – Cities across Europe and Asia were demolished – Economies were devastated 3. Two Super Powers – US and USSR emerge as the two World Super Powers