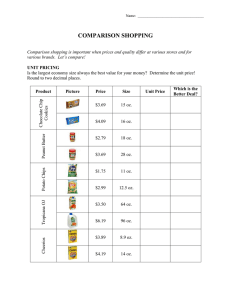
CHRM 2390 Research and Development of Food Products
advertisement

CHRM 2390 Research and Development of Food Products 1 Why go into new food product development? For profitable and to survive. 2 Forces Driving New Food Product Development Life cycles Long range goals Marketplace New technology and knowledge Changes in government legislation, policies, and programs 3 The Product Life Cycles 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Introduction period Growth period Decline in sales No-growth period Decline in volume 4 Corporate Reasons for New Product Development To achieve growth and be profitable Growth by Expansion to new markets or market segments-Expensive and hazardous Market penetration -selling more in existing market-Expensive New products for current marketcontinuous growth and profitability Diversification-new product for new markets 5 Marketplace Reasons for New Product Development New food purveying method Changing habits of consumer Competition 6 Technological Reasons for New Product Development Information technology-accessible Packaging technology Increased knowledge of: Food science preservative and processing new ingredients Health and nutrition 7 Governmental Influences on New Product Development Purpose: to ensure safe and contaminant-free food to develop standards for food composition and labeling to maintain fair-trade and competition to protect employees and the environment Affect: technical development of new food products marketing personnel 8 Governmental Influences on New Product Development... Other regulatory aspects: International Regulatory Agencies: Examples: WTO, EEC, ISO Quasi-governmental agencies: Marketing boards: supply, import, price Professional and trade associations Wages and rules of conduct 9 New Product Development Could be defined as: the development and introduction of a product not previously manufactured by a company into the marketplace, or the presentation of an old product into a new market not previously explored by a company 10 New Product Classifications Line Extension Established products in a new niche New form of existing products Reformulation of existing products New packaging on an old product Innovative or added-value products Never-before-seen products 11 Line Extensions A new variant of an established line of food products Examples: A new flavor A new varieties A new texture 12 Advantages of Line Extensions Little time or effort for development, manufacturing, production systems and storage Few change in marketing strategy No new purchasing skills (commodity trading) or raw material sources No new storage or handling techniques for either the raw ingredients or the final product. 13 Problems with Line Extensions developmental problems if extension requires processing changes manufacturing and other support systems change if extension is complex marketing techniques 14 Repositioning a Product Discovery of a new use for an existing product Baking soda, oatmeal Manufacturing unaffected Minimal development time New marketing strategy needed 15 New Forms of Existing Product Often the downfall of new product ventures New product must have a perceived advantage over old Extensive development time Major equipment purchases Different warehousing and distribution systems 16 Reformulation of existing product.. ”new, improved” High probability of technical success Relatively inexpensive and short development time The result of: Unavailable ingredients Lower costs Meet the challenge of competitors Consumer driven 17 New Packaging of Existing Products Packaging of bulk products into unit packages Utilize new technologies such as MAP, CAP Branding May require an overhaul of packaging operation 18 Innovative Products Making changes to an existing product Some paths may be easy but some are more risk and costly The more innovation in a product, the longer the development time and the higher the research and development costs 19 Creative Products Rare, never-before-seen product Difficult to define, e.g. surimi, reformed meat products Can be characterized by: Extensive development time High research and development time Expensive marketing strategies Expensive sapital costs for equipment Risky If successful, imitators will flood market 20 Conclusion Economics, consumer and competition necessitate new product development New products should be consistent with goals and strategies of a business Success of new products depend on the availability of inputs, and the management of cost and quality 21