Skin and Body Membranes Chapter Four
advertisement

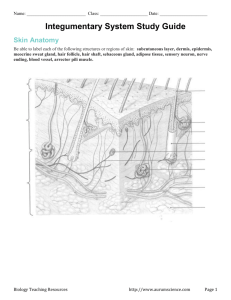
Chapter Four Skin and Body Membranes Classification of Membranes • Epithelial – Cutaneous • Skin • Stratified squamous – Mucous (mucosa) • Lines cavities • Simple columnar • Serous – One layer – Simple squamous – Serous fluid • Parietal & Visceral – – – – Lines body cavities Around organs Pleura & Pericardium Simple squamous Functions of the Skin • Protection – – – – Against disease Insulates & cushions UV protection Chemical protection • Defense – 1st line of defense • Prevention of Dehydration – Keratin – Keeps H2O in & out Functions of the Skin • Maintenance of Body Temp. – Heat loss – sweat – Heat retention – blood flow • Excretion of Wastes – Salts – Urea – H2O • Reception of Stimuli – Touch, pressure, pain, cold, heat • Vitamin D Synthesis – Cholesterol molecules Vitamin D (sunlight) Layers of the Skin integumentary • Epidermis – Strata • Stratum basale – Closest to dermis – Undergoes mitosis – Nutrients from diffusion • Stratum spinosum – Flattened cells w/ spines • Stratum granulosum – Granules w/ keratin • Stratum corneum – “horny” – 20-30 cell layers – Soles. Palms, fingertips-stratum lucidum Cell Types • Keratinocytes – Make keratin • Melanocytes – Make melanin – Secretes melanin – basale layer • Langerhans cell – Macrophages-eat foreign substances Skin Color – amount and kind • Pigments – Melanin • Reddish brown, or black – Carotenes • yellow – Hemoglobin • rosy • Emotional – Redness (sympathetic) • • • • Embarrassment Anger Fear Allergies Dermis – “hide” leather • Thick connective tissue layer beneath stratum basale. – Collagen – Elastin • Papillary layer – Upper, uneven – Receptors (pain, touch) – Dermal papillae • Fingers-fingerprints • Soles-footprints Dermis cont… • Reticular layer – Deepest – Blood vessels – Sweat and oil glands – Blood supply when restricted • Degeneration • Ulceration – bed sore Appendages of the Skin • Glands – Sebaceous glands • • • • Oil Sebum: lubricant, bacteria killing Whiteheads (blocked oil gland) blackhead acne Seborrhea – excess oil – Sweat glands – 500 ml a day (25 million) • Eccrine – – – – – Sweat Clear 99% water Salts, urea, lactic acid, pH 4-6 • Apocrine – Axillary & genital areas – Fatty acids, proteins, sweat (yellowish) – Empty into hair follicles Appendages of the Skin cont.. • Nails – Modified epidermal cells – Keratin • Hair – 100,000 hairs scalp – Follicle • Keratinized cells • Arrector Pili (goose bumps)– smooth muscles -Hairs erect-increase blood flow to skin – Cuticle • Keep hairs separate Infections and Allergies 1000 different conditions • Fungi – Athletes foot fungus – Ringworm • Bacterial – Boils and carbuncles • Staphylococcus into hair follicles • Oil glands – Impetigo • Viruses – Herpes “cold sores” – Warts • Allergies – Eczema – Contact dermatitis – “rash” • Unknown – Eczema – Psoriasis – Hives • Yeasts Skin in Stress • Wound Repair – Wound – Inflammatory reaction • Blood flow – Edema • swelling – Clots • Stop bleeding – WBC’s • Fight bacteria – Pus • Dead blood cells • Dead bacteria – Scabs • Burns Skin in Stress cont… – Thermal • Heat • Chemical – electrical - UV – First degree • Epidermis “red” • Heal 2-3 days – Second degree • Epidermis & dermis • Blisters – Third degree • Skin blackens • Skin grafts – Risk of death • Fluid loss , imbalance of electrolytes • Kidney failure • Replace proteins , infection Skin Cancer • Basal Cell Carcinoma – Most common – Alters stratum basale cells • Uncontrolled mitosis can’t form keratin • Squamous Cell Carcinoma – Stratum spinosum – Scaly reddish papulae – Spreads to lymph nodes • Malignant Melanoma – (5%) – – – – Brown black patches Lymph & blood vessels ABCD rule moles Asymmetrical, border, color, diameter 76mm Disease States • Erythema – Turns red • Pallor, blanching – Anemia – Low blood pressure • Jaundice – Yellowing – Liver disorder • Porphyria – purple • Bruises – Hematoma – Broken capillaries • Cyanosis – “bluish” – Low 02 in blood