BIOLOGY Class Notes 9-2
advertisement

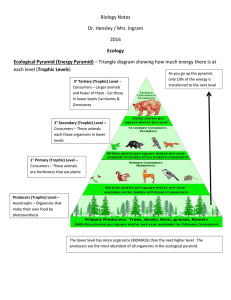
BIOLOGY Class Notes 9-2 Aim: Energy Transfer (A) Producers Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth Some types of organisms use energy that is stored inorganic compounds Autotrophs: organisms that take energy from the sun and convert it to food—producers Producers can either use energy from the sun or from chemicals o Photosynthesis: autotrophs use light energy to power chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and water to carbohydrates—gives off oxygen Land—plants Water—algae (B) Consumers Acquire energy from other organisms Heterotrophs o Herbivores—eat only plants o Carnivores—eat only animals o Omnivores—eat both o Decomposers—break down organic matter (C) Feeding Relationships Energy flows through an ecosystem in one direction from producers to consumers o Food chains: series of steps in which energy is transferred from one organism to another o Food webs: more complex—links all the food chains in an ecosystem together o Each step—trophic level o Food webs are more complex and more accurate than food chains (D) Ecological Pyramids Shows the relative amounts of energy or matter within each trophic level o Energy: only part of the energy that has been stored gets passed on to the next trophic level—most of the energy is used by the organisms for life processes—only 10% of the energy is passed on o Biomass: the total amount of living tissue in a given trophic level—represents the amount of potential food available for each trophic levels The further along the food chain you go, the less food (and hence energy) remains available. The above energy pyramid shows many trees & shrubs providing food and energy to giraffes. Note that as we go up, there are fewer giraffes than trees & shrubs and even fewer lions than giraffes. In other words, a large mass of living things at the base is required to support a few at the top.