File
advertisement

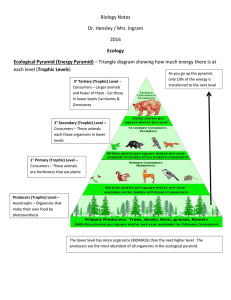
Energy Flow Study Guide 3.2 Producers and Consumers (pages 67 – 69) 1) ______________ is the ultimate source of energy in almost all organisms on the earth. 2) What are autotrophs? 3) What color is most often associated with autotrophs? 4) What is another name for an autotroph? 5) What do autotrophs do during photosynthesis? 6) What is a consumer? 7) What is another name for a consumer? 8) For each of the following, give examples of the main types of producers. a) on land b) in the upper layers of the ocean c) in ponds 9) Directions: match the terms on the right with their definitions on the left. _____ step in the transfer of energy and matter in a community a. autotroph _____ autotrophs that make food for the entire community b. carnivore _____ consumers that feed on the tissues of dead animals c. food chain _____ organisms that eat only plants d. producers _____ animals that eat only meat e. omnivores _____ animals that eat producers and other consumers f. consumers _____ model of energy flow from one organism to another through each trophic level g. decomposers _____ organisms that make their own food h. herbivores _____ organisms that feed directly on producers i. trophic level _____ organism that feeds on wastes and dead organic matter, forming soil _____ all consumers obtain their energy and nutrients by eating other organisms j. detritivores k. heterotrophs Feeding Relationships (pages 69-71) 10) Types of Heterotrophs Type herbivore Definition Examples cows, rabbits heterotrophs that eats other living animals omnivore humans, bears, crows detritivore decomposer 11) What does a food web link together? 12) What is a trophic level? 13) In a food web, what organisms make up the first trophic level? 14) Why do consumers in a food chain need the organisms below them? Ecological Pyramids ((pages 72-73) 15) Describe an ecological pyramid. 16) Why is it that only a portion of the energy stored in one trophic level is passed on to the next level? 17) Directions: Complete the fill-in-the-blanks portion of the pyramid below by writing the source of energy for the food web and how much energy is available to first-, second-, and third level consumers. 18) What is biomass? 19) What does a biomass pyramid represent? 20) Why can each trophic level support only about 1/10th the amount of living things of the level below it?