Ionic Solids Characteristics

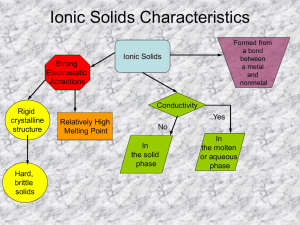
Ionic Solids Characteristics
Strong
Electrostatic
Attractions
Ionic Solids
Formed from a bond between a metal and nonmetal
Rigid crystalline structure
Relatively High
Melting Point
No
In the solid phase
Conductivity
Yes
In the molten or aqueous phase
Hard, brittle solids
The First Couple
• # 1) Energy is released when bonds are formed. Energy is absorbed when bonds are broken.
• #2) As a bond forms the PE decreases.
• #3) Energy is released -> stability increases
• #4) Two atoms combine to form a molecule, bond formed, energy is released
#5 Which electron-dot diagram represents H
2
?
Both hydrogen’s will equally share their valence electron
H H
H H
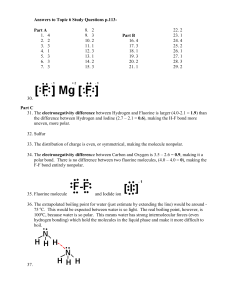
#9) In which compound do the atoms have the greatest difference in electronegativity?
(1) NaBr
|
0.9 – 3.0
|
= 2.1
(3) KF
|
0.8 – 4.0
|
= 3.2
(2) AlCl
3
|
1.6 – 3.2
|
= 1.6
(4) LiI
|
1.0 – 2.7
|
= 1.7
#13) Given the reaction:
M + 2H
2
O -> M (OH)
2
+ H
2
The metal represented by M is most likely a metal from Group
The subscript of 2 on the hydroxide came from the charge on the metal (M) .
M (OH)
2
M +2 (OH) -1
So the Metal (M) must be from Group 2 because of its +2 oxidation state!
#16) Element X has an electron configuration of
2-8-3. This element will combine with the phosphate ion to form a compound with the formula
3 Valence e’s means that is will have an oxidation state of +3
X
+3
(PO
4
Criss
Cross w/out charges
X
3
3
(PO
4
Reduce to
)
3
3
Lowest
Ratio
X (PO
4
)
)
-3 From Table
E: phosphate has a -3
#33 a.
H H b.
H H
H
2 is nonpolar and H
2
O is polar, like dissolves like, therefore H
2 will not dissolve in H
2
O.
c.
1 Mg + 1 H
2
SO
4
1 H
2
+ 1 MgSO
4
#34
H N H
H
H
H N H
H
+
#35
a.
H Cl b.
+ H Cl c. H-Cl is polar, water is polar; like dissolves like
#36
a.
N N
OR
N N b. N
2 is very stable, unreactive because of triple bond (a lot of energy was released when this bond was formed).