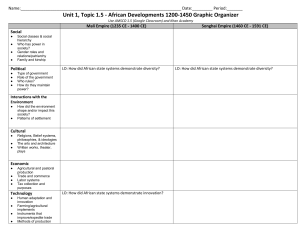
Rivers Deserts Mts. Savanna
advertisement

Rivers Nile, Chad,Congo,Niger Deserts Sahara, Kalahari Mts.Atlas- (NW), Drakensberg(SE) Rainforest –West Africa Savanna Remember!!! Sahel&Desertification •Largest Land Mass •3X the size of US •Petroleum,gold, copper, diamonds, cotton, coffee, peanuts, lumber •Kush, Axum, Ghana, Mali, Songhai •Ruled by Pharaohs & kings •Established trade routes ( Med. Sea, Red Sea, etc.) • Trade of Gold and Salt • 3100 B.C.-56 B.C. • Nile River Valley • Hieroglyphics, Mummification, Pyramids, Temples, Mathematics • First African Kush Civilization after Egypt • 1700-1500 B.C. • Major Trading center of Gold • Polytheistic, shared Egyptian Gods Ghana • Earliest West African Civilization • “Land of Gold” • Brought Necessary salt and gold between North and South Africa Songhai • Niger River Valley in W. Africa • Fishing and Trading Civilization • Accepted Islam from the North in Mali • Mansa Musa brought Islam to Mali • Timbuktu was a center of education, literature, arts • Pilgrimage to Mecca in 1324 •Matrilineal vs. Patrileneal •Ancestor worship/ lineage/ clans th 7 century Islam overcomes Christianity • Self-Sufficient Villages • Tribal Communities • No Central Government • Animism-All living and non-living things have a spirit • Monotheistic • Ancestor Worship •Slave Trade (Triangular Trade, Middle Passage) •Colombian exchange •Social upheaval,violence •Political realignments • 1700’s • An exchange of raw materials, finish products, medicine, slaves among 4 continents •After Belgium claimed the Congo sets off scramble for Africa •By 1914 only Liberia & Ethiopia remain independent • 1600-1700’s Dutch found trading posts • Scramble for Africa • 1884 Berlin Conference European Countries met to divide up the continent of Africa • European boundaries disregarding tribal borders Causes: • Industrialization-Need for raw materials and markets • Social Darwinism-Belief that the strongest race would survive • “White Man’s Burden”-It was the white man’s responsibility to civilize and enlighten the Africans • Missionaries-Covert people to Christianity •British defeat Boers (Dutch Farmers) •The Union of South Africa is formed as a British Commonwealth •Becomes independent in 1961 as Republic of South Africa •Government policy of total separation of races •Began under Boers & continued after British rule •1913 Native Land Act forbade blacks to own land outside reservations •1950 Groups Area Actdivided 13 % of land among blacks & the rest reserved for whites (17% of the population) • 1913 African National Congress formed & began fighting segregation •Leaders of anti-Apartheid movement •Served about 30 yrs in prison •Mandela became the countries first black president 1994 •Fought to end apartheid Peaceful resistance Noble Peace Prize Winner 1984 1. equal civil rights for all 2. the abolition of South Africa's passport laws 3. a common system of education 4. the cessation of forced deportation from South Africa to the so-called "homelands" •International economic pressure •1989 reform minded F.W. De Klerk frees Mandela and The ANC is legalized •In 1992 white voters abolished apartheid •1994-first black election •Nationalist movements were led by educated elite (anti imperialist) •Focused on human rights & self rule •Most nations achieved independence in 1950’s & 60’s •Conflicts among neighbors made Pan Africanism difficult Movement to celebrate African culture, heritage, and values •Led by Leopold Senghor- the First President of Senegal •Jomo Kenyatta-Kenyan Nationalist •Kwame Nkrumah-Independence leader •Severe Economic Problems •Government Corruption •Rely on Cash Crops and corporate investments •Non-aligned •Desertification and overuse of land Rwanda • 1994 Genocide of Tutsi population by the Hutus and supported by the government • More than 500,000 people died in a few months