1. Urinary System WEB
advertisement
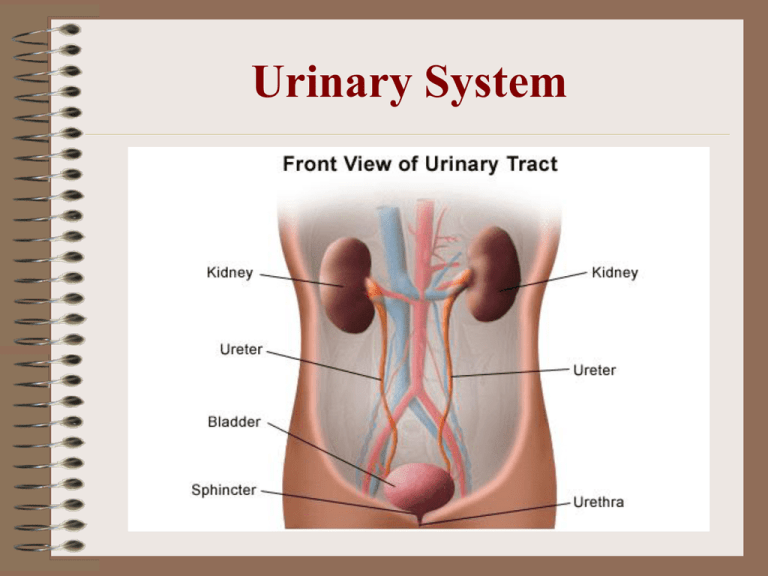
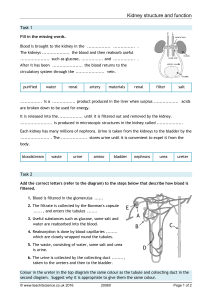
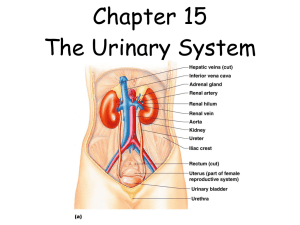
Urinary System MAIN FUNCTIONS • Ammonia (formed by the breakdown of old proteins) is converted to urea in kidneys • Cleans the blood by removing urea, excess salts, water and metabolic wastes and excreting them as urine • Keeps the volume of water in your body constant • Regulate blood pressure by renin (enzyme) • Stimulate production of RBCs by erythropoietin • Increase calcium absorption by calcitriol (vit. D) MAIN STRUCTURES Kidneys – filter blood and remove waste (maintain homeostasis) Nephron – filtering unit of the kidney (each kidney has a million nephrons) MAIN STRUCTURES CONT. Renal Capsule – connective tissue that surrounds each kidney Renal Cortex – outer part, lighter in color; contains parts of nephrons Renal Medulla – middle, darker part; contains parts of nephrons Renal Pelvis – inner part, http://www.biologymad.com/re collecting region of urine sources/kidney.swf MAIN STRUCTURES CONT. Ureter – tube that takes urine from kidneys to urinary bladder Urinary Bladder – stores urine Urethra – allows urine to pass from the urinary bladder out of the body Factors that affect kidney function • Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) – prevents excess water loss from kidneys • Alcohol – inhibits secretion of ADH = more urine volume • Aldosterone – prevents excess loss of sodium and water from kidneys • Caffeine – increases rate of salt and water loss from kidneys • Increased blood pressure – increase rate of water loss from kidneys.