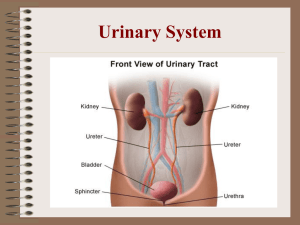
Task 1. Match the picture and complete the sentences: bladder, urine, urethra, kikney, filters, ureter, ammonia, liver, urea, nephron. a) b) The liver _____ a very toxic waste out of our blood called _____, and then it turns it into a waste called _____ that will be sent to the kidneys. Task 2. Match the functions listed in column A to the parts of the urinary system listed in column B B A 1 Takes urine from the kidney to the bladder A Sphincter 2 Prevents urine from leaking from the bladder B Renal artery 3 Removes urea from the blood C Renal vein 4 Carries urine out of the body D Nephron 5 Carries ‘dirty’ blood to the kidney E Kidney 6 Is the working unit of the kidney F Urethra 7 Carries blood away from the kidney G Ureter Task 3. Answer the questions: 1. Besides excretion, list two other functions of the kidneys in mammals. 2. What is ‘osmoregulation’? Why is it important in living organisms? 3. A student plays volleyball on the beach on a hot day. She sweats a lot and she swim to cool down, but she does not drink much. a. What will happen to this student’s blood? Why? b. How will her body react to this change? c. What role will her kidneys play in maintaining her water balance? Explain fully. 4. Why do you produce lots of light coloured urine if you drink a lot of water? Answers: Task 1: Liver, nephron, kidney, ureter, bladder, urethra, filtrates, ammonia, urea. Task 2: A 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Takes urine from the kidney to the bladder Prevents urine from leaking from the bladder Removes urea from the blood Carries urine out of the body Carries ‘dirty’ blood to the kidney Is the working unit of the kidney Carries blood away from the kidney B ureter sphincter kidney urethra Renal artery nephron Renal vein Task 3. 1. Besides excretion, list two other functions of the kidneys in mammals. Answers: (1) Regulation of water balance (osmoregulation), (2) Maintain osmotic pressure of body fluids by removing excess salts and retaining water as needed, (3) Regulation of pH. The kidneys prevent blood plasma from becoming too acidic or basic by regulating ions. 2. What is ‘osmoregulation’? Why is it important in living organisms? Answer: The process of maintaining a balance between water and salts in the body fluids. It is important since without this process the body would accumulate harmful toxic waste and water. It may also lead to unstable blood pressure with harmful effects on other organs and systems. 3. A student plays volleyball on the beach on a hot day. She sweats a lot and she swims to cool down, but she does not drink much. a. What will happen to this student’s blood? Why? Answer: Her blood would become more concentrated due to the loss of fluids from sweating. b. How will her body react to this change? Answer: The osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus region of the brain detect that the blood is more concentrated and causes the pituitary gland to produce an antidiuretic hormone (ADH) to try to restore fluid balance. c. What role will her kidneys play in maintaining her water balance? Explain fully. Answer: The ADH causes the walls of the collecting ducts in the kidneys to become permeable and reabsorb most of the water from the nephrons back into the blood. This results in less urine being produced but it is more concentrated. 4. Why do you produce lots of light coloured urine if you drink a lot of water? Answer: When you drink a lot of water the blood becomes dilute and the osmoreceptors in the brain stop the production of ADH, the walls of the collecting ducts in the kidneys remain impermeable and the kidneys do not reabsorb much water which makes the urine more dilute/ less concentrated and therefore has a lighter colour.