Chapter 15 The Urinary System
advertisement
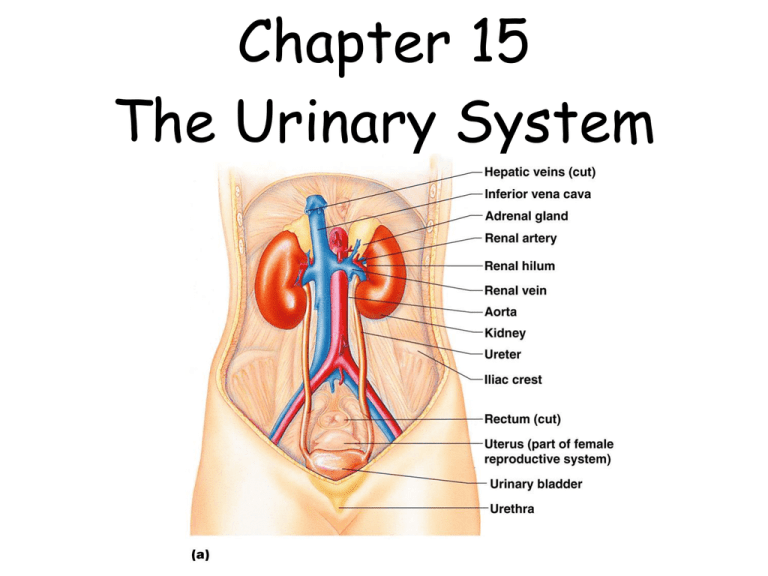
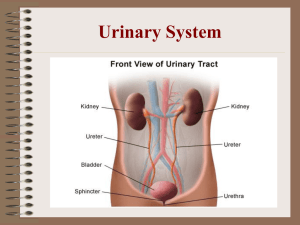
Chapter 15 The Urinary System Anatomy of the Kidney • General – filter all blood every 30 minutes • kidneys organs of excretion – eliminate nitrogenous wastes (urea) – eliminate toxins – eliminate drugs – excess ions – excess water – metabolic wastes • Regulate blood volume • make enzymes for blood pressure and red blood cell productions • composition of system – paired kidneys – urinary bladder – ureters – urethra • renal blood supply • renal artery --> kidney »kidney --> renal vein – Nephrons • functional unit of kidney – 1 million per kidney, clean blood form urine • glomerulus – ball of capillaries, forces material to be filtered into • bowman’s capsule – transports materials (filtrate) into tubule • renal tubule – 1.25 inches » proximal convoluted tubule - reabsorption of water and solutes » loop of henle - reabsorption of Na and Cl ions » distal convoluted tubule - reabsorption of water » Na, Cl • collecting tubule – contains urine - nitrogenous wastes, water and salts Label with functions 23-7 Urine Formation • Filtration • glomerulus • blood pressure • nonselective • Reabsorption • tubules --> capillaries • materials which need to be returned to blood • Secretion • capillaries --> tubules get rid of substances not contained in the filtrate Kidney Control of Blood Composition • Nitrogenous wastes • urea - break down of proteins • uric acid - breakdown of nucleic acids • creatinine - breakdown of creatine phosphate CP • Water and electrolyte balance • water – – – – ADH ~ water to be reabsorbed aldosterone ~ causes Na + to be going back to blood polyuria ~ lose water and salt, DEHYDRATED ANH ~ atrail natriueretic hormone lose Na+, lose water • electrolytes – Na +, K +, Cl -, Ca ++ • Blood acid - base balance • • • • blood pH 7.35 - 7.45 alkalosis acidosis buffers – pH goes up when kidneys excrete bicarbonate ions – pH goes down when kidneys reabsorb bicarbonate ions Urine Characteristics • Urinalysis • physical aspects – color, clarity, specific gravity, odor • chemical aspects - water, urea, salt, ions, pH • microscopic aspects – types of cells • Characteristics • • • • • color - clear to yellow clarity - transparent odor - odorless pH - 5.5 to 8 specific gravity - 1.001 - 1.035 • Urine output • 1-2 liters per day • 95 % water 5% organic and inorganic • volume • dilute urine or concentrated urine • Factors- heat, amount of sweat produced amount of liquids consumed, salt in diet • abnormal urine • • • • • • • glucose (glycosuria) , proteins – albumin & ketones, hemoglobin, bile pigments (brown) reddish - blood, liver problem red blood cells - bleeding, kidney stones leukocytes - pus , milky - pus green - bacterial infection • Structure Ureters • slender tubes, 10 -12 inches long • function • collect and transfer urine from all collecting tubules to bladder • Problems • kidney stones: • Uric Acid - forms crystals • Calcium (oxalate or phosphate) • Struvite (infection) Urinary Bladder • Functions • stores urine 500 ml can hold 1000 ml • expels urine 1-2 liters a day • Urethra • tube thru which urine is expelled • males - 8 inches , urine & sperm • females - 1.5 inches Urethritis inflammation of urethra • Sphincters • internal - smooth muscle relaxes 200 -300 ml • external – skeletal muscle • Micturition • voiding - empty bladder • bladder contracts internal sphincter relaxes and external • incontinence - can’t control external sphincter • urinary retention - surgery, diseases, use catheter • cystitis • bladder inflammation can lead to kidney inflammation- pyelitis Aging of the Urinary System • Renal Function decreases with age • incontinence increases, nocturia • urinary tract infections increase • dysuria • painful urination • polyuria • frequent urination • oliguria - low urinary output • increase in prostate cancer Disorders • Infections • E. Coli • streptococcus --> glomerulonephritis • sexually transmitted diseases • polycystic kidney disease