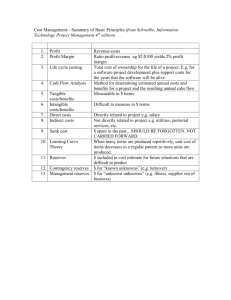
G3 - Another Actuary’s Work
advertisement

Case Study G4 – Reserve Ranges Guide – Mr. K.K. Dharni Date : 18 December 2014 Presenters – Vandana Baluni Irvinder Singh Kohli Abhijit Pal In this presentation Scope Introduction Professional Standards Considered Factors Influencing Reserves Regulations Governing Reserves Finance Director’s suggestion Options for Resolution of Issue Options Available to Appointed Actuary Conflict of Interest Conclusion 2 Scope Scope The case study should be approached principally how to maintain the professional standard when carrying out professional activities. It should also take into consideration how to strike balance with the consideration of internal relationship with professional matters. The practices, GNs & Regulations considered are in Indian market context. Other professional matters and technical considerations should be identified but dealt briefly. 4 Introduction to Case Study Introduction A new Company Actuary (AA) of a general insurance company has submitted reserving reports in accordance with GN12 to the Finance Director(FD). FD has commented that recommended reserve will reduce profit below market expectation hence affecting: o Downgrading of companies' rating by rating agencies. o Impact of future business of the company. o Previous AA had explained FD that actuarial reserving methods subjective. o The actuaries set the reserves slightly above the mid-point of an implicit range of values and it will be acceptable if the actual reserves are within this range. FD’s is suggesting AA to reconsider recommended reserves and if possible recommend lower reserves which is with in the implicit range of values. AA has to review the recommended reserve and suggest the possible solution. Additionally AA point of view is to be explained if AA’s bonus depends on “good” results of the company or AA owns company shares ( or options), which can be exercised by him/her. 6 Professional Standard Considered Professional Standards Considered Professional Standard - PCS section 2 “An Actuary has a duty to the profession must not act in a manner which denigrates its reputation & impugns its integrity” Breach of standards set by the regulator and the profession should not be recommended o Advice given should comply with Section 3.1 & 4.1 of PCS “An actuary is expected to use best judgment in formulating advice, while paying proper regard to any relevant professional guidance or other guidance. He must keep himself abreast with updated professional guidance and adhere to that.” Also, “Any material breach of PCS/GN is a ground for complaint under the disciplinary procedures and would amount to strong prima facie evidence of misconduct” o Any modification / change in approach of calculating reserve needs regulator’s approval and which depends on compliance with the extant regulations Conflict of Interest as per section 5 of PCS “Advise given by Actuary is unaffected by interest other than those of the clients” 8 Factors Affecting Reserves Factors Influencing Reserves Quality or credibility of data Claim Experience Impact of Claims Change in Segment Impact of new product/risk Level of prudence Reserve deficiency Rate revision Reinsurance arrangements Change in Underwriting guidelines Change in Regulation 10 Reserving Process Regulations Governing Reserves Type of Reserves Actuarial Practice standards 21 – Section 8.10 prescribes the reserve a company needs to hold : o The Unearned Premium Reserve (UPR) o The Unexpired risk reserve (URR) o Claim Reserves comprises 1. Outstanding Claim Reserve 2. Incurred but not reported claims (IBNR Claims) 3. Reported claims where the estimate of loss has not been fully assessed the reserve is referred to as Incurred But Not Enough Reported Claims (IBNER) o Expense Reserves UPR & URR are based on formula or methodology prescribed by regulation. 12 Regulations Governing Reserves Indian Regulations & Reserving Principles Indian Regulations for Non – Life Reserves The Insurance Regulatory & Development Authority (Assets, Liabilities & solvency Margins of Insurer) Regulations, 2000 & The Insurance Regulatory & Development Authority (Preparation of Financial Statement and Auditor’s report of Insurance company) Regulations, 2002” Reserving Principles o Reserves should be held on prudent basis (including appropriate MAD) for all liabilities arising out of the insurance business. o Reserves should take into consideration nature, term, currency and method of valuation of the associated assets. o The value placed on the liabilities must make appropriate provision for future expenses. o Keeping in view tax regime as applicable to general insurance companies, due allowance must be made for tax, taking into account the taxation provision of the company 13 Regulations Governing Reserves If the reserve ranges would have been applicable in Indian market General Insurance Business: Actuarial Reports (GN12- Faculty & Institute of Actuaries) o Reports on reserves may be produced in terms of point estimate or range of acceptability. o Where appropriate, report should indicate the sensitivity of the estimates to variations from the stated assumption. o When applying statistical methods of estimation, the actuary should be aware that, in addition to the effect of random variation, there may be significant sources of error associated with the choice of model or its parameters. The actuary should consider how these uncertainties should be communicated to the recipients of the report. 14 Finance Director’s Suggestion Finance Director’s Suggestion Considerations for Revised Reserve o Level of conservatism or prudence built in reserves. o Any point which has been over-looked for estimation of reserves o Any event or issue which have occurred after issue of report o Impact of change in reserves on profit. o Change in reserve recommended by FD, impact on profit. o Size of reserve after revision. o Reserving methodology or approach o FD recommending change in Outstanding Claim reserves or IBNR (incl. IBNER). 16 Finance Director’s Suggestion Challenges in reducing reserves o Inadequate Reserves - Reserves may not be sufficient to meet all the liabilities as and when they arise. o Fair Financial Statement of the company will not be disclosed to stakeholders. o Regulatory Interventions - regulator action against the company if reserves are not adequate. o Early emergence of profit due to low reserve, which may lead to higher increase in later years. o Requirement of higher capital in later years o Influence on investment strategy o Payment of Tax /Dividends , which will impact future profit 17 Options for Resolution of Issue Options for Resolution of Issue Step 1 Revision of Reserves a. b. c. d. e. 19 Revisit the reserve estimate to ensure that everything is covered, no errors, data issues etc. Revisit the margins built in the assumptions and assess the impact on reserves if margin are reduced. Establish if confidence on reduced reserves is possible Establish reason for higher reserves as compared to previous year (s). Review if the basis of reserve has been changed and establish reason for the change. Options for Resolution of Issue Step 2 (If AA suggest no revision in reserve) Discussion with Internal Stakeholder 20 a. Discuss with Underwriter & Claims Head to understand their view on future experience is same as AA or different. b. Discuss with other Directors in the company and assess their views Options for Resolution of Issue Step 3 (If AA unable to get consensus from internal stakeholders) Discussion with External parties o Discussion with counter-parts in other companies to assess if they have similar view on future experience of the business o Discussion with Consultants / Reinsurers to assess if experience of the industry has changed over years and issues faced by the industry or other companies o Discuss with previous AA and understand his basis for reserves for previous accounting period. 21 Options Available to Appointed Actuary Options available to AA Decision by Appointed Actuary o Reduce reserves 1. Revisit margin and reduce if earlier at higher level 2. Revise reserves and document the revised basis & assumptions in his report. 3. Discuss and explain to FD the rational for the change in reserve and seek his/her views on proposed reserves. o No change in the reserve estimates 1. Discuss with FD and explain the rational/ justification of the reserves 2. Discuss with other Directors of the company and explain the rational/ justification of the reserves and its impact on the company current and future financial conditions 3. Discuss with senior Actuary and seek advice. 4. Inform regulator his/her stand in case issue is not resolved after discussion with internal stakeholders. 23 Conflict of Interest Conflict of Interest Hefty Bonus/Shares or Options held by AA in the Company According to Section 5.2 of PCS In the event of any conflict or apparent conflict of interest, the client or clients involved must be notified at the earliest opportunity and if any advice given to a client is, or will be, influenced by interests other than those of that client or by any constraint other than that imposed by professional guidance or other guidance, this must be disclosed in the advice Steps to be taken by AA o The AA should be satisfied in his/her capacity that the recommended reserves is in the best interest of company. o The AA must ensure that his/her conduct and reach and depth of his/her functionalities enable him/her to discharge his/her duties and obligations in accordance with regulation (8) of AA Regulations. o The AA should have clear understanding with his/her insurer on the condition of Appointment and issues related to Bonus or Share should agreed and documented. 25 Conclusion Conclusion An Appointed Actuary should serve the public interest along with considering the 27 financial soundness of the company. Needs to maintain the highest standard of professionalism and ethics by highlighting the conflict of interest to relevant stakeholders Advice given by Appointed Actuary should be fair and free from any kind of biasness and should be in line with the regulations/guidance notes. In case of doubt, should seek advise from senior Actuary / Peer reviewer An Actuary should be open to discuss any issue with internal & external (relevant) stakeholder for resolution. He/ She should have access to information / data from the company which will help in taking appropriate action related to company. He should keep regulator/ relevant authority updated about the issues faced by the company and seek their views/ suggestion on proposed resolution. Questions ??? Thank You 28