Akira Nitta
advertisement

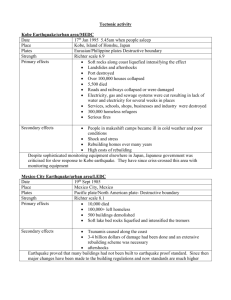
Anti-Seismic Measures on Water Supply Introduction and Overview Akira NITTA Water Supply Division Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare Government of Japan Significant earthquakes in the vicinity of Japan magnitude (From Jan. 1996 to Jul. 2006) Depth (km) Source:http://www.seisvol.kishou.go.jp/eq/higai/higai1996-new.html Recent Major Earthquakes in Japan ■ Kobe Earthquake - January 17,1995 ◆ Epicenter: beneath Kobe City ◆ Richter magnitude scale: 7.3 ◆ Fatalities : more than 6,000 ◆ Disruption of water supply : about 1.3 million households just after the disaster, the amount of damage reached about 56 billion JPY (460 million US$) ◆ Emergency restoration of water supply facilities : took about 3 months Kobe Earthquake - Jan 17,1995 - ←Damage to Buildings in Kobe City Damage to Water Pipes → (φ800mm) Kobe Earthquake - Jan 17,1995 - Fires happened frequently, and a lot of houses were burnt down. Kobe Earthquake - Jan 17,1995 - The sixth floor of the city office was crushed. Recent Major Earthquakes in Japan ■ The Mid Niigata Prefecture Earthquake - October 23, 2004 ◆ Epicenter: mountainous region ◆ Richter magnitude scale: 6.9 ◆ Fatalities : 40 ◆ Injuries : about 4,500 ◆ Disruption of water supply : about 130 thousand households ◆ Emergency restoration of water supply facilities : took from 1 to 2 months The Mid Niigata Prefecture Earthquake - Oct 23, 2004 – Damage to Small-scale Water Supply Facility due to Landslide The Mid Niigata Prefecture Earthquake - Oct 23, 2004 – Damage to water pipes under the ground The Mid Niigata Prefecture Earthquake - Oct 23, 2004 - Emergency Water Supply by Water Wagon Damage to water facilities at the Mid Niigata prefecture earthquake Damage to water treatment plants and distribution reservoirs ・Large plants and reservoirs were slightly damaged ・Small plants and reservoirs in the mountain area were seriously damaged by breakdown of surrounding ground. These were moved or sagged and their functions were crashed. ・Private electric generator for emergency didn’t start up immediately because of groundwater influx and damage to the peripheral pumps and equipments such as coolant water pumps. ・Antiseismic reinforced facilities were taken no damage. Damage to water facilities at the Mid Niigata prefecture earthquake Damage to pipe lines ・The ratio of damage to pipe lines was less than the Kobe earthquake. ・The most damage hit the soft grounds, developed lands banking area and slopes, which is the same tendency of the Kobe earthquake. ・The pipe lines in the mountain area were flown out with the slope and road failures. ・It was ascertained that antiearthquake measures to pipe lines and renewal of decrepit pipe lines based on the knowledge obtained by Kobe earthquake were effective. Measures at the hardware side Antiseismic reinforcement of water supply facilities Create earthquake-resistance standards of facilities Development of promotion program to enhance earthquake safety to facilities Promotion of improvement to supply main medical centers with quake proof water distributing pipes Urgent renewal of aging and weak pipelines Securing of reservoir capacity at distributing reservoir → securing capacity for 12 hours Installation of emergency cutoff valves Looping of pipe lines Multiplication of water resources Development of emergency water supply bases Effective precaution for water supply -BuildingsSeismic damage depends on ground condition and peripheral land form ・It is important to select location of facilities and foundation structure cautiously. ・Don’t select high groundwater level area, steep slope and mounded lands. Effective precaution for water supply -Pipe lines・Use earthquake-resistant pipes Coated steel pipes Ductile cast-iron pipes with earthquakeresistant joints Polyethylene pipes with electric fusion joint ・Construct bypass and looped pipelines Cost-effectiveness analysis is necessary Earthquake-resistant joint of Ductile Cast-Iron Pipe Rate of earthquake-resistant waterworks facilities and pipelines 耐震化率(%) Rate of earthquake-resistant(%) 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 30% 14% 20% 10 0 Water浄水場 treatment plants 配水池 Distribution reservoirs 基幹管路 Main pipelines Emergency cut-off valves Emergency water supply bases Emergency water supply bases in Tokyo source:http://www.waterworks.metro.tokyo.jp/pp/suido/kyusui_point.htm Measures at the software side Development of emergency water supply planning - Securing of other water supply method and water resource and emergency water delivery route for residents Cooperation agreement between waterworks - Emergency supply and rehabilitation assistance to the waterworks affected by earthquake from other unaffected waterworks Cooperation with relevant institutions such as sewerage - Communicate information about influx to water resources from raw sewage and industrial wastewater - Coordination of restoration of water supply and sewage line Rescue operation ・Information gathering Enhancement of emergency water supply ・Emergency repair ・water supply by transport ・Secure manpower and accept support from other ・water supply at base points Fast restoration Waterworks Vision Measures to Improve the Quality of the Future Water Supply Service (November 1990) Long-Term Objectives for Development of the Water Supply Service for the 21st Century (Clean Water Supply Service) (June 1991) Ideal Water Supply Service and Water Administration in the 21st Century (Panel on Basic Issues Concerning Waterworks, July 1999) Partial Amendment to the Waterworks Law in 2001 Changing environment surrounding the water supply in Japan Growing concerns over issues related to waterworks Analysis and evaluation of the current and future prospects of the service Ideal water supply service in the future Setting common goals among parties involved in the service Defining future policy issues Clarifying specific measures and actions to be taken Waterworks Vision (2004) Ideal water supply service Water supply system that strives to be a leading player in the world Setting higher goals and making steady progress Service that customers are always satisfied with and are willing to support Providing a worldclass service in various contexts <Safety > < Stability > < Sustainability > < Environment > < Globalization > Policy objectives Promotion of measures 1) Safety Supply people with safe and good-tasting tap water 2) Stability A stable supply of water for domestic use anytime, anywhere 3) Sustainability • Strengthening the basis of the water supply system taking local characteristics into account • Preserving and developing practices and skills accumulated in the water supply service • Improving the water supply service based on customer needs 4) Environment Contribute to environmental conservation 5) Globalization Contribute to the world by transferring our experiences to other countries (1) Strengthening the basis of the water supply system (2) Ensuring a safe and convenient water supply (3) Improving disaster prevention (4) Improving environmental and energy measures (5) International contributions in the water supply service through international cooperation Thank you very much for your kind attention!