Tectonic activity - The Appleton School
advertisement

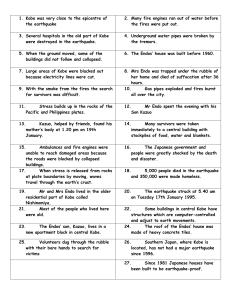
Tectonic activity Kobe Earthquake/urban area/MEDC Date 17th Jan 1995 5.45am when people asleep Place Kobe, Island of Honshu, Japan Plates Eurasian/Philippine plates Destructive boundary Strength Richter scale 6.9 Primary effects Soft rocks along coast liquefied intensifying the effect Landslides and aftershocks Port destroyed Over 100,000 houses collapsed 5,500 died Roads and railways collapsed or were damaged Electricity, gas and sewage systems were cut resulting in lack of water and electricity for several weeks in places Services, schools, shops, businesses and industry were destroyed 300,000 homeless refugees Serious fires Secondary effects People in makeshift camps became ill in cold weather and poor conditions Shock and stress Rebuilding homes over many years High costs of rebuilding Despite sophisticated monitoring equipment elsewhere in Japan, Japanese government was criticised for slow response to Kobe earthquake. They have since criss-crossed this area with monitoring equipment Mexico City Earthquake/urban area/LEDC Date 19th Sept 1985 Place Mexico City, Mexico Plates Pacific plate/North American plate- Destructive boundary Strength Richter scale 8.1 Primary effects 10,000 died 100,000+ left homeless 500 buildings demolished Soft lake bed rocks liquefied and intensified the tremors Secondary effects Tsunamis caused along the coast 3-4 billion dollars of damage had been done and an extensive rebuilding scheme was necessary aftershocks Earthquake proved that many buildings had not been built to earthquake proof standard. Since then major changes have been made to the building regulations and now standards are much higher