The Cell
advertisement

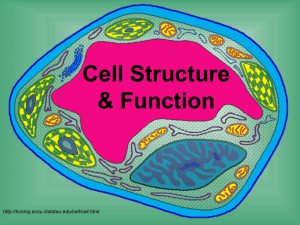
THINK BEFORE YOU PRINT: The Cell The Cell is the basic unit of life. Robert Hooke (1635 – 1723) discovered the ‘cell’ while looking at slices of cork under a primitive microscope. The Latin word, ‘cellulae’, meaning “little rooms”. The generally accepted parts of cell theory include: 1. 2. The cell is the fundamental unit of structure and function in living things. All cells come from pre-existing cells by division. 3. All known living things are made up of cells. Energy flow (metabolism and biochemistry) occurs within cells. Cells contain hereditary information which is passed from cell to cell during cell division All cells are basically the same in chemical composition. Some organisms are unicellular, made up of only one cell. Others are multicellular, composed of countless number of cells. • A cell is a compartmentalized unit of life, and can containing specialized structures, known as ‘organelles’. Most Cells are microscopic. Organelles are membrane bound structures that perform specialized functions. Did You Know? • • • The largest cell in the world is the Ostrich egg. The smallest cell is a bacteria cell. The longest cell is a nerve cell. Microscopes are used to study cells: The compound microscope : white light is transmitted through the specimen can magnify up to 1500 X. The electron microscope: uses an electron beam and can magnify a sample 200,000 times. The size of a cell is restricted by Surface Area. Large cells have a smaller surface area than small cells. Size matters. Large cells are then limited in uptake of nutrients and cell supplies. There are two types of cells: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Origin and Evolution of Cells The 1st cell formed 3.5 BYA, it was prokaryotic. One billion years later, 2.5 BYA, prokaryotic cells began membrane infolding and endosymbiosis of two prokaryotes cells gave rise to a eukaryotic cell following mutation and change in pre-existing prokaryotic cells. Two types of Cells Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic. Plant, animal, fungal and protist cells are eukaryotic. Bacterial (Monera) cells are the only prokaryotic cells Prokaryotic Cells and Their Characteristics • • • These are cells of the Kingdom Monera which contain all bacteria cells. Size = Most bacteria are from 2 – 8 micrometers in size. Pro = primitive; karyon = nucleus. These have primitive nucleus. The DNA is free-floating, with no nuclear envelope. Also known as ‘nucleoid’. • • • • • • • No organelles are present. Only cell membrane, cytoplasm and ribosomes Ribosomes are used to make proteins. Plasma membrane encloses the cytoplasm. Cell wall surrounds the plasma membrane. Some bacteria have a protective, mucillagenous sheath around the cell-wall, known as ‘capsule’. Some bacteria have pili (singular = pilus) to attatch to surfaces. Some bacteria have long projections – flagella – help in locomotion. Diagram of a typical prokaryotic cell Differences Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells • Prokayotic Cells include all bacteria (Kingdom Monera), are simple, have no nucleus (false nucleus = nucleoid), Organelles are absent / without membranes. The Flagellar structure is different. • Eukaryotic Cells include all living organisms besides bacteria (Protista, Fungi, Plant andAnimal), are complex, have a true nucleus, have organells and the Flagellar structure is different from that in prokaryotes. Two Types of Eukaryotic Cells: Plant and Animal The Autotrophic Plant Cell • Cell wall made of cellulose is present. The wall protects and supports. • Chloroplasts containing the green pigment, chlorophyll – are present. • • • • • Autotrophs – can make their own food. Cells are angular shaped. Large central vacuole is present. Centrioles absent. Flagellae are uncommon. Organelles unique to plant cells, cell wall, large central vacuole, chloroplasts. All other organelles are common to both plants and animals. Animal Cells are HETEROTROPHIC and Eukaryotic Cell wall is absent. • • Chloroplasts are absent. • • Cells are rounded and not very regular. • • Centrioles are present. Heterotrophs – depend on other organisms for food. Lysosomes (instead of vacuoles) are small and scattered . Flagellae may be present. Diagram of a typical eukaryotic cell, showing subcellular components. Organelles: (1) nucleolus (2) nucleus (3) ribosome (4) vesicle (5) rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) (6) Golgi apparatus (7) Cytoskeleton (8) smooth ER (9) mitochondria (10) vacuole (11) cytoplasm (12) lysosome (13) centrioles Eukaryotic Cellular Organelles in Plant Cell and Animal Cell: 1. Nucleus: Houses the genetic material (DNA) of the cell. Identify the Nucleus, the nuclear envelope, the pores DNA associated with proteins are present as long, threadof the nucleus like fibers, known as ‘chromatin’. (During cell-division, now identify the endoplasmic reticulum chromatin coils up into thick, condensed strands known as ‘chromosomes’. The nucleus is surrounded by a double-membrane with pores, known as the ‘nuclear envelope’. Within the nucleus is the nucleolus. This is where ribosomes are synthesized and assemble. 2. Endoplasmic Reticulum: is a network of interconnected membranes and is of two types: Rough E.R. and smooth E.R. • Rough E.R. is rough due to the presence of ribosomes on the surface. This is where most proteins are made in cells (site of protein synthesis) • Smooth E.R. Have no ribosomes on the surface.Help to synthesize lipids.Regulate blood-sugar released from the liver cells.Breakdown drugs and harmful substances. Helps in muscle contraction. 3. Golgi Apparatus • GA are stacks of flattened sacs – named after the Italian scientist, Camillo Golgi, who discovered them. • They receive transport vesicles with proteins from the E.R., modify them and then transport them back out where they may be needed. 4. Lysosome/ ‘Suicide Capsules’. Typically considered animal digesting organelle, but plants can have lysosomes. • Lysosome is produced by the rough E.R. and the Golgi apparatus. • It contains hydrolytic digestive enzymes which: • • digest food by fusing with food vacuoles. Digest harmful bacteria contained in white blood cells. • • Digest worn out / damaged organelles. Aid in embryonic development – prevent webbing of fingers of embryo by destroying cells of the web. 5. Vacuoles: Only found in Plants. Regulate Water • These are membraneous sacs like lysosomes. Eg. Food vacuole; plant’s large central vacuole, contractile vacuole in paramecium, etc.. • May contain nutrients and water for growth of cells, pigments in flowers,waste products, important chemicals for cellular metabolism, poisons, help to maintain internal environment of cells eg. In paramecium, help in cellenlargement. 6. Chloroplasts (found only in plant cells) • Chloroplasts convert solar energy to chemical energy in sugar molecules. • • They help to carry out photosynthesis in plants. Has three compartments: intermembrane space, stroma and grana (part of thyllakoid membrane system). Identify the cristae and the 7. Mitochondrion = Power House of a Cell (found in plant and animal cells) • • matrix. Converts energy from one chemical form to another. Carries out cellular respiration where chemical energy of foods is converted into chemical energy of ATP = cellular fuel molecule. • Has two compartments: Mitochondrial matrix and cristae. • Mitochondria are all maternally derived. Endomembrane System is the prevailing theory today: This is a system of membranes that surround the organelles and may or may not form a continuous interconnectedness with each other).This system would serve to further divide the cell into compartments and this increases its surface area. Organelles included in the endomembrane system are numbered 2-5: Label all structures inside the cell :=). Which are considered as a part of the endomembrane system? Abnormalities of Lysosomes: This can lead to fatal diseases such as: 1. Lysosome storage disease – the abnormal lysosomes get full of indigestible substances, which then interfere with cellular functions. 2. Pompe’s disease – harmful amounts of glycogen accumulate in the liver cells. 3. Tay Sachs disease – lysosomes lack a lipid digesting enzyme and nerve cells in the brain are damaged due to excess lipid accumulation. Internal Skeleton is called the CYTOSKELETON The cellular organelles are held in place and given structural support by a fine proteins which form the cytoskeleton of the cell. The cytoskeleton includes: Microfilament 7nm, Actin subunit Intermediate filament 10 nm, Fibrous Subunits meshwork of Microtubule, 25 nm, tubulin subuntis Cytoskeletal proteins: Microfilaments, Intermediate filaments and Microtubules (arranged from smallest to largest). Microfilaments help cells change shape. They are long filamentous proteins made of beads of actin protein linked together. They move cells and cell content and help change cell shape. Intermediate Filaments help determine permanent structure. They are intermediate in size.. They are made of a combination of proteins. In animals IF produces hair, nails, feathers and scales. Microtubules are the largest and play a role in cell movement. They are long hollow tubes made of spherical proteins call alpha and beta tubulin. They are a part of the propelling appendages “cilia” and “flagella”. They are less common because few plant cells move (only sperm). They are used by plants to transport packages of substances in a monorail-like fashion. Cytoplasm/Cytosol: inside the membrane of the cell aqueous semi-fluid in which structures and organelles are found. The pH of the cytoplasm kept constant with buffers. Plasmamembrane: all cells are surrounded by a hydrophobic structure called the plasmamembrane. The plasmamembrane is semi-permeable (selectively). Made of phospholipids, cholesterol and proteins. Proteins act as receptors, used in transport. Osmosis and Diffusion involved in keeping concentration of substances in balance. Too little water inside cells leads to plasmolysis. Turgor is achieved as cell take up water. Helps hold plant upright. Plastids are of many type and have many functions in plant cells. They are named according to the chemicals they either make or store. Choloroplast are green and photosynthetic, Amyloplast store starch (amylose), Eliaoplast store oil, Chromoplast store different pigments , are some examples. Cell Walls Protect and Support Plant cells and define cell shape: Most water enters cells by osmosis through the plasma membrane. Plants form Primary and Secondary Cell walls. They are chemically different. The primary cell wall is outside of the cell membrane of all plant cells and is comprised of cellulose. Mature plants and woody plants produce a secondary cell wall that is thicker than the primary wall. Primary Cell walls are made of cellulose. Cellulose microfibrils can be linked together by pectins (protein jelly like carbohydrate substances) or hemicellulose (glue or gumlike carbohydrates). When linked together they form bigger, stronger strands called macrofibrils. The primary cell wall is a single layer thick. Between two cells is a thin lay called a middle lamella, The middle lamella is composed mainly of pectin. Pectins are useful for cooking. They thicken jellies. The secondary walls of plants become embedded with lignin (tar-like). The secondary cell wall forms in between the plasma membrane and the primary cell wall, see image. It will prevent the cell from growing or extending. Pits are formed in secondary wall. The secondary cell wall becomes thinner or disappears. Pits allow for more rapid transfer of water and minerals from cell to cell. Primary walls are permeable to water and dissolved solutes but secondary walls are not. . Plasmodesmata are found within cell walls. They are channels that connect the cytoplasm of two or more plant cells. They are involved in communicationStrands of cell content flow through the plasmodesmata. The Middle Lamella: Two plant cells are joined together by the middle lamella, which is largely pectin. Note the term symplast and apoplast in the figure. They refer to living and non-living compartments withing the plant. Animal cells can be connected via 3 different junctions (Tight Junctions: Form a tight seal:Urinary bladder; Connecting or gap junctions: Cell to cell communication:Cardiac cells; Anchoring Junctions(Desmosomes): Cells anchored in their own Extracellular matrix: Skin cells).