Solutions Review
advertisement

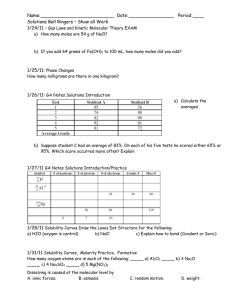
Solutions Review Sheet 1. Solute- substance being dissolved Solvent- Substance doing the dissolving 2. Like dissolves Like – Polar solvents dissolve polar solutes Nonpolar solvents dissolve nonpolar solutes 3. Table F – Substances that are soluble will dissolve and turn into ions substances that are not soluble will precipitate. 4. Table G - Any point on line represents a saturated solution Any point under line represents an unsaturated solution Any point over line represents a supersaturated solution Lowest line is least soluble at that temperature Highest line is most soluble at that temperature Saturated solutions represent the maximum amount of solute that will dissolve at a certain temperature in 100gms of water. If given a different amount of water make a proportion. 5. Table H – Boiling points of different solutions at various vapor pressures. Boiling point is when vapor pressure equals atmospheric pressure Normal boiling point when atmospheric pressure is 1atm or 101.3Kpa 6. Colligative properties – Boiling point and Freezing point of a solution are concentration dependent. The more particles dissolved the higher the boiling point and lower the freezing point. Remember ionic substances will break into more than one particle. 7. Concentrations – Percent Mass of part over mass of whole X 100 Molarity is number of moles per liter of solution. M=m/L Moles equal molarity X liters Parts per million equals mass of solute divided by mass of solution times 1 million.