Skeletal Muscular Systems Packet Answer Key
advertisement

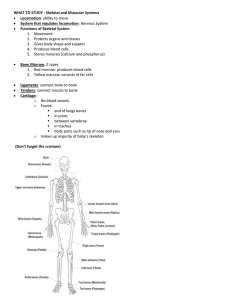
Protect, support, and bond together Bones, ligament, fat Lines and covers surfaces Skin, lines internal tubes and cavities (such as the mouth) Produces movement Attached to bones, heart, bladder, digestive tract, arteries Receive stimuli and conduct impulses Brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves, cranial nerves, spinal nerves skull/cranium Clavicle/collar bone Scapula/shoulder blade sternum/breast bone ribs humerous radius vertebrae pelvis ulna carpels metacarpels phalanges femur Patella/knee cap tibia fibula tarsals phalanges metatarsals Bones of the body or the skeleton Some are flat, some are long, some are hollow, and some are round. They are hard on the outside and soft on the inside. Marrow, blood vessels, nerves Soft material inside the bone Give the body shape, protect the body from getting hurt, protect organs like the heart and lungs, hold the body together, A C B A D B D B D A Voluntary Striated Attached to bones Involuntary Striated Heart Involuntary Nonstriated Digestive System, arteries… D C B C A A B B D D B 600 Walking, running, breathing, moving, pumping blood throughout the body, moving food through your digestive system, Contracting/shortening 1/3 its resting length myofibrils myofibrils neurotransmitters neurotransmitters A B C D muscles bone pairs Contract Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle