4. Periodic Table
advertisement

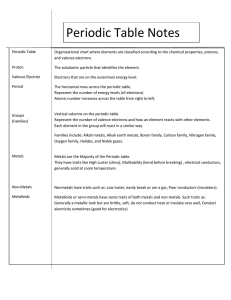
Review – Periodic Table • The modern periodic table is not arranged by increasing atomic mass, but rather increasing atomic number • Periodic Law: States that the properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers • The placement of an element on the Periodic Table gives an indication of the chemical and physical properties of that element Periods Periods are horizontal rows on the periodic table Period 1 contains H and He The number at the beginning of the period indicates the energy level where valence electrons are located for atoms in that period Groups or Families Vertical Columns Elements in a group have the same number of valence electrons. Elements in a group have similar properties and react similarly because they have the same number of valence electrons (this is known as Periodic Law) Common Group Names Group 1: Alkali Metals Group 2: Alkaline Earth Metals Groups 3-12: Transition Elements (metals) Group 17: Halogen Group Group 18: Noble Gases Properties of Elements Physical Properties of Metals Metallic luster (shine) Malleable (can be made into sheets) Ductile (can be made into wires) Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity • Most metals are solids at room temperature or STP which stands for standard temperature and pressure (exception is mercury which is liquid at room temperature). • • • • Properties of Elements Physical Properties of Non-metals, Metalloids, and Noble Gases • Non-metals: Lack metallic luster and are brittle in the solid phase; they are poor conductors of heat and electricity; non-metals are usually gases, molecular solids or network solids (exception is bromine which is a liquid at room temperature). • Metalloids: Have some properties of both metals and nonmetals. • Noble Gases: Are all gases. Have 8 valence electrons (helium is the exception with 2). • SOLIDS: Most of the elements of the PT • LIQUIDS: Hg & Br • GASES: 11 TOTAL (always reactive)H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, (typically non-reactive) Noble Gases Periodic Trends (Table S) Ionization Energy (IE): The energy required to lose an electron. • The lower the IE, the easier it is to lose an electron • Remember, metals want to lose electrons, and non-metals want to gain Ionization energy down a group As you go down a group ionization energy decreases because the number of PELS increase, and so the valence electrons are further away from the positive nucleus; there is less attraction which results in less energy needed to remove electrons Look at the ionization energies on Table S Li 520 Na 496 K 419 Rb 403 Ionization Energy across a Period As you go from left to right ionization energy increases because as you go across a period, the number of valence electrons increase by 1, and therefore the less likely an element wants to lose an electron (on the contrary, they want to gain them). Look at ionization energies on Table S Li (520) Ne (2081) Periodic Trends (Table S) Electronegativity (EN): The affinity to gain an electron. • The larger the EN the more the atom attracts electrons • Remember, metals want to lose electrons, and non-metals want to gain Electronegativity energy down a group • As you go down a group EN decreases because as you go down a group, the number of electron orbitals increase, and therefore the outermost shell of electrons is further from the positively charged nucleus making the attraction for electrons decrease. • Look at the electronegativities on Table S Li 1.0 Na .9 K .8 Rb .8 Electronegativity across a Period • As you go from left to right EN increases because as you go across a period, the number of valence electrons increase by 1, and therefore the more likely an element wants to gain an electron (metal nonmetal) • Look at ionization energies on Table S Li (1.0) F (4.0) Periodic Trends (Table S) Atomic Radius (AR): Is the distance from the nucleus to the outer valence electrons. radius increases. Ionic Radius • RULE: Positive Ion LOSING AN ELECTRON MEANS THAT THE IONIC RADIUS IS LESS THAN THE ATOMIC RADIUS (LOSE = LESS) AR > IR • RULE: Negative Ion GAINING AN ELECTRON MEANS THAT THE IONIC RADIUS IS GREATER THAN THE ATOMIC RADIUS (GAIN = GREATER) AR < IR