ch13-ch14-16-review.doc
advertisement

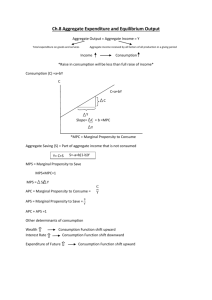
Review Questions Ch.13 , Ch .14&16 True or False : 1. The aggregate supply curve shows the total output of final goods and services that will be produced at each price level. T 2. As the price level rises, interest rates will increase, and investment and consumption will fall. T 3. Aggregate demand shows the total amount of goods and services that will be produced and sold at each price level. F 4. An increase in the government expenditure will shift the aggregate supply curve to the right. F 5. The equilibrium level of real GDP occurs where the aggregate supply curve and the aggregate demand curve intersect. T 6. A decrease in aggregate supply will result in an increase in the price level. T 7. Aggregate demand is the aggregate quantity of goods and services demanded by all buyers at various different price levels. T 8. Macroeconomic equilibrium is a situation in which the quantity of real GDP demanded equals the quantity of real GDP supplied .T 9. nominal wage is the Real wage divided by the price level .F 10. Real wage is the nominal wage divided by the price level . T 11. The marginal propensity to save (MPS) is the change in consumption divided by the change in income. F 12. Changes in government expenditure (G) and/or exports (X) can result in an increase in GDP through the multiplier effect . T 13. The marginal propensity to consume is equal to 1 minus the marginal propensity to save. T 1 14. The multiplier tells us that an increase in investment by $100m will give rise to a smaller than $100m increase in GDP . F 15. Through changes in overall levels of spending and taxing, government can help keep the economy running smoothly. T 16. Fiscal policy refers to government spending (government expenditure) and taxation. T 17. Monetary policy refers to government spending and taxation. F 18. A recessionary gap exists when equilibrium output is below the full-employment level of output. T 19. An inflationary gap exists when output is above the economy’s equilibrium level of output. F 20. The multiplier is 5 when the marginal propensity to save is 0.20.T 21. A production shortage exists when the output level is to the right of the point of intersection of the aggregate spending line and the 45 line. F 22. A fiscal policy is to be used to eliminate the recessionary gap is an expansionary fiscal policy. T 23. A tax raise is a fiscal tool to reduce aggregate demand, and it has no effect on aggregate supply. F MCQ : 1. Which of the following will NOT cause the aggregate demand curve to shift? A. a change in government spending. B. a change in expectations. C. a change in net exports . D. a change in the overall price level. 2. A recessionary gap occurs when A. aggregate supply exceeds aggregate demand, B. the aggregate spending line intersects the 45 line at an output level to the right of the full-employment level of output, C. the aggregate spending line intersects the 45 line at an output level to the left of the full-employment level of output, D. the aggregate spending line intersects the aggregate supply curve at a lower price level. 2 3. When actual output is to the right of the intersection of the 45 line and the aggregate spending( expenditure) line, A. there is a production surplus, B. output is not at the equilibrium level, C. inventories will pile up, D. all of the above, E. none of the above. 4. There is a multiplier effect from changes in investment spending because A. aggregate supply is related to the level of output, B. consumer spending is positively related to the level of output, C. consumer spending is negatively related to the level of output, D. exports are positively related to the level of output. 5. The multiplier measures the rate of change in A. output resulting from a change in total spending (or aggregate expenditure). B. consumption resulting from a change in output, C. output resulting from a change in consumption, D. investment resulting from a change in output. 6. When the marginal propensity to consume is 0.80, the value of the multiplier is A. 2, B. 3, C. 4, D. 5. 7. The aggregate demand curve is A.the total quantity of an economy’s intermediate goods demanded at all price levels. B.the total quantity of an economy’s intermediate goods demanded at a particular price level. C.the total quantity of an economy’s final goods and services demanded at a particular price level. D.the total quantity of an economy’s final goods and services demanded at different price levels. E.none of the above. 3 8. The relationship between the total quantity of an economy’s final goods and services demanded at different price levels is A. the aggregate supply curve. B. the aggregate demand curve. C. the Phillips curve. D. the aggregate expenditure function. E. both (b) and (d) of the above. 9. The aggregate supply curve is A. the total quantity of raw materials offered for sale at different prices. B. the total quantity of final goods and services offered for sale at the current price level. C. the total quantity of final goods and services offered for sale at different price levels. D. the total quantity of intermediate and final goods and service offered for sale at different price levels E. the total quantity of final services offered for sale at different price levels. 10. The aggregate demand curve shifts to the right when A. the money supply increases. B. net exports increase. C. taxes are increased. D. all of the above. E. (a) and (b) 11.The aggregate demand curve decreases when A. government spending is decreased. B. net exports decline. C. taxes are increased. D. all of the above. E. both (a) and (b) of the above. 4 12.The aggregate demand curve shifts to the left when A. the money supply falls. B. the price level increases. C. taxes are increased. D. all of the above. 13.Which of the following does not cause the aggregate demand curve to shift to the right? A. An increase in net exports B. An increase in government spending C. An increase in taxes D. An increase in the money supply 14.Which of the following does not cause the aggregate demand curve to shift to the left? A. A decrease in net exports B. A decrease in government spending C. A decrease in taxes D. A decrease in consumer optimism 15.The aggregate supply curve shows the relationship between A. the level of inputs and aggregate output. B. the price level and the level of inputs. C. the wage rate and the level of employment. D. the price level and the level of aggregate output supplied. 16.Along a given aggregate supply curve an increase in the price level leads to an increase in aggregate output because A. firms increase production in response to higher profits. B. workers work more hours, due to the increase in the real wage. C. workers work more hours, due to the decrease in the real wage. D. none of the above is true. 5 17.Which of the following statements are true of the aggregate supply curve? A. The aggregate supply curve describes the relationship between the quantity of output supplied in the short run and the price level. B. The aggregate supply curve shifts leftward when costs of production increase. C. The aggregate supply curve shifts rightward when costs of production decrease. D. All of the above. 18. A shift in the aggregate supply is likely to: A. Reduce the general price level and reduce national income B. Reduce the general price level and increase national income C. Increase the general price level and reduce national income D. Increase the general price level and increase national income 19.The aggregate demand will increase if: A. Consumption falls B. Investment falls C. Exports fall D. Imports fall 20.Which of the following would increase the aggregate demand? A. Increased saving B. Increasing import spending C. Increased taxation revenue D. Increased investment 21.Which of the following would decrease the aggregate demand? A. Increased consumption B. Increasing export revenue C. Increased taxes D. Increased investment 22.Improved training of employees would: A. Shift aggregate supply to the right B. Shift aggregate supply to the left C. Shift aggregate demand to the right D. Shift aggregate demand to the left 6 23.Increased unemployment benefits and less incentive to work would: A. Shift aggregate supply to the right B. Shift aggregate supply to the left C. Shift aggregate demand to the right D. Shift aggregate demand to the left 24. Which of the following will NOT cause the aggregate demand curve to shift? A. a change in government spending. B. a change in expectations. C. a change in net exports. D. a change in the overall price level. 25. If the MPC were 0.75 the expenditure multiplier would be: A. 1.25 B. 0.25 C. 0.4. D. 4 26. The most appropriate fiscal policy that might use to combat a recessionary gap is: A. decreasing G. B. increasing T. C. decreasing G and T by equal dollar amounts. D. increasing G or cutting T. 27. A decrease in the money supply will: A. raise interest rates, reducing investment and GDP B. raise interest rates, increasing investment and lowering GDP C. reduce interest rates, increasing investment and GDP D. reduce interest rates, reducing investment and GDP 28. The aggregate demand curve is downward sloping to the right because a lower price level: A. increases exports and reduces imports B. increases the supply of money, reducing the interest rate C. increases consumer incomes D. causes consumers to buy more lower-priced goods, substituting away from higherpriced goods 7 29. . An increase in the demand for money caused by an increase in the price level will: A. increase the interest rate, reduce investment, and shift the aggregate demand curve to the left B. increase the interest rate, reduce investment, and decrease the quantity of real output demanded C. increase the interest rate, increase investment, and shift the aggregate supply curve to the right D. reduce the interest rate, increase investment, and shift the aggregate demand curve to the right 30. If inventories are unexpectedly declining at the current level of GDP: A.GDP exceeds the level of current expenditures B.GDP is at its equilibrium level C.current expenditures exceed the level of GDP and GDP will fall D.GDP is below its equilibrium level 31. The effect of an increase in businesses taxes is: A. a reduction in real output and a higher price level B. a reduction in real output and a lower price level C. a reduction in real output and either a higher or lower price level D. an increase in real output and a lower price level 32. An increase in the price level will: A. increase net exports B. reduce the value of household debt and increase investment C. increase production costs and reduce aggregate supply D. reduce the purchasing power of household wealth and reduce consumption 33. When the marginal propensity to saving is 0.2, the value of the multiplier is A. 2, B. 3, C. 4, D. 5. 8 34. The magnification of small changes in spending( expenditure) into larger changes in output and income is produced by : A. the average propensity to consume . B. the paradox of thrift . C. the multiplier effect . D. saving. 35. Assume the MPC is 0.6. If investment spending increases by 8 million, the level of GDP will increase by : A. 8 million B. 20 million. The multiplier=2.5 then the increase in GDP=2.5×8= 20 million C. 13.3 million . D. 15 million 36. An initial increase in investment expenditure will generate : A. less of an increase in real GDP than the initial increase because of the multiplier effect . B. more of an increase in real GDP than the initial increase because of the multiplier effect . C. An equal increase in real GDP to the initial increase D. Non of the above . 37. In a closed economy with no government, an increase in autonomous investment of 25 million increases GDP from 600 million to 700 million. The marginal propensity to consume and the multiplier are : A. B. C. D. MPC=0.25 MPC=0.50 MPC=0.75 MPC=0.80 and the multiplier is 4 . and the multiplier is 2 . and the multiplier is 4 . and the multiplier is 5. The multiplier= the change in GDP÷ the change in investment = 4 The multiplier 1 4 1 - MPC MPC 0,75 9 38.Which of the following is NOT a tool of the fiscal policy? A. A tax cut B. An increase in the money supply C. An increase in the government expenditure on goods and services D. decrease in the transfer payments 39.An example of transfer payment A. profits B. wages paid to the governmental employees C. government purchases of goods & services D. unemployment benefits 40.According to the multiplier effect, if government expenditure on goods and services increases by $3000 and the MPC is 0.8 then GDP will increase by: A. $ 2400 B. $ 6000. C. $ 15000. D. $ 24000. 41.Which of the following will decrease AD A.A decrease in the tax rate. B.A decrease in government expenditure on goods and services. C.An increase in the budget deficit. D.A raise in the transfer payments. 10 42.According to the above figure, the equilibrium happens A.at full employment. B.above full employment and a contractionary fiscal policy must be used C.below full employment and an expansionary fiscal policy must be used D.below full employment and a contractionary fiscal policy must be used 43.Other things being constant, an increase in tax rates will A. encourage people to work more hours. B. increase the aggregate demand. C. decrease the supply of labor and reduce its productivity. D. Cause all of the above. 44.The sum of planned consumption expenditure, planned investment, planned government purchases, and planned net exports is ________________. real GDP aggregate planned expenditure the expenditure approach to real GDP aggregate expenditure 45.The consumption function is the relationship between consumption expenditure and ___________________, other things remaining the same. disposable income saving potential GDP the 45 degree line 46.The marginal propensity to consume ____________________. plus the marginal propensity to save equals 1 is the fraction of GDP consumed is the amount of disposable income consumed is the fraction of disposable income consumed 11 47.The marginal propensity to save is _____________. equal to the slope of the saving function always greater than the marginal propensity to consume equal to 1 plus the slope of the consumption function equal to the inverse of the marginal propensity to consume 48.The part of aggregate planned expenditure that does not vary with real GDP _______________. is autonomous expenditure equals equilibrium expenditure equals zero is induced expenditure 49.The multiplier is the amount by which ____________________ is multiplied to determine __________________. the change in autonomous expenditure; the change in real GDP the change in induced expenditure; the change in potential GDP autonomous expenditure; real GDP induced expenditure; real GDP 12