Notes - part 2b Types Chem Rxns (cont)edited
advertisement

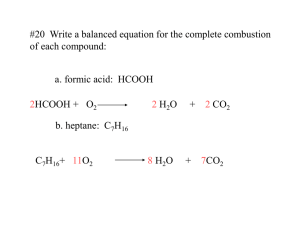
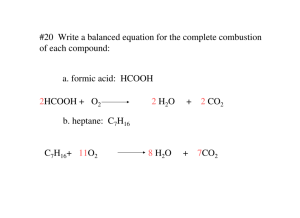
5 Types of Chemical Reactions (continued) 1 Combustion also called “burning” representative equation: CxHyOz + O2 CO2 + H2O 2 Synthesis (also called combination or composition) means “putting together or building up” representative equation: A + B AB 3 Decomposition means “breaking down or breaking apart” is the opposite of a synthesis reaction representative equation: AB A + B Single replacement (single displacement) one element replaces a similar element in a compound reactants: an element and a compound products: a different element and a new compound representative equations: A + BC B + AC A is a metal. representative equations: Y + BC C + BY Y is a non-metal. Usually a halogen (group 17) A metal element will try to replace the cation of the compound; a nonmetal element will try to replace the anion of the compound. Whether a single replacement reaction will occur can be predicted by the activity series chart An element can replace elements below it. Can Ba replace Zn? Y Can Sn replace Pb? Y Can Al replace Li? N Can Fe replace Co? N Can Cl replace Br? Y examples __K + __NaCl __KCl + __Na __Li + __H2O __LiOH + __H2 __Hg + __H2O NR __Cl2 + __CuBr2 __CuCl2 + __Br2 __AgNO3 + __Cu __Ag + __Cu(NO3)2 __I2 + __NaBr _______ + _______ __Ca + __HCl _______ + H2 Double replacement (double displacement) cations and anions in two compounds switch places reactants: two compounds, usually ionic compounds in aqueous solutions products: For these reactions to take place, one of the following must be a product: • a precipitate (a new compound that is not soluble) see Solubility table • Water (H2O) • a gas (such as CO2 , H2S or NH3) representative equation: AB + CD AD + CB examples AgNO3 + NaCl AgCl + NaNO3 CuS + HNO3 H2S + Cu(NO3)2 KOH + H2SO4 H2O + K2SO4 BaCl2 + Li2SO4 Mg(NO3)2 + NaCl