Chemistry Mid-Year Review L2 Into Unit
advertisement

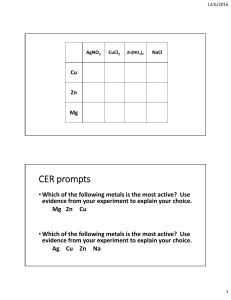
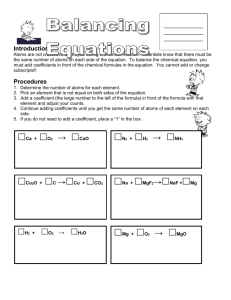
Name:______________________________ Chemistry Mid-Year Review L2 Into Unit 1. Why is Chemistry often called the central science? 2. What are the different branches of Chemistry? 3. State the Law of Conservation of Matter. _____4. Group 1 _____5. Group 18 _____6. Group 17 _____7. Group 2 A. B. C. D. E. F. Transition metals Alkali metals Alkaline Earth metals Noble gases Inner transition metals Halogens Scientific Method A. Experiment D. Conclusion G. Observation B. Variable E. Hypothesis H. Law C. Control F. Theory 10. ______ In an experiment, one ____________ is tested at a time to determine how it affects result. 11. ______ This is a Statement of what happens without explaining why 12. ______ This explains why/ how things happen 13. ______When you don’t do anything different than normal in an experiment, it serves as a __________ group. 14. ______ Is a possible answer to a question Name:______________________________ Math in Chemistry 15. List the SI base units for the following: Distance __________ Mass _____________ Time _______________ Temperature __________ 16. For the following, list the number of significant figures in each: A. 0.0000095________________ B. 745672345 _________________ C. 0.0346001________________ D. 29480000___________________ 17. How many liters in 1 Mega liter? 18. How many seconds in 0.75 years? 19. Herbert has to make some measurements. He takes a 16oz weight, and masses it to be 32.21oz, 32.19oz, 32.20oz, and 32.32oz. Do his measurements exhibit high precision? ______________ Do his measurements exhibit high accuracy?______________________ Explain! 20. Measurements are always uncertain because A. Instruments aren’t designed for measurements B. All measurements involve some estimation C. People don’t know how to use instruments D. None of the above E. All of the above 21. 598 mL – 6.6 mL = a. 591.4 mL c. 604.6 mL b. 591 mL d. 605 mL 22. 42800 / 401 a. 107 c. 106.73 b. 106.7 d. 106.733 Name:______________________________ 23. Complete the following: 564 cm = ________ meters a. 564 m b. 56.4 m c. 5.64 m d. 56400 m 24. 8.56 L X 6.2315 L X 4.163 L = a. 222.1 L3 b. 222.06 L3 3 c. 220 L d. 222 L3 25. What is the density of a wood block with a volume of 16.5 mL and a mass of 6.39g? a. 0.3872 g/mL b. 0.387 g/mL c. 0.388 g/mL d. 0.39 g/mL 26. Calculate the density of matter that has a volume of 12.4 ml and a mass of 4.20 grams. 27. Assuming that one drinks 24oz of coffee a day, 365 days a year, how many Liters of coffee does the person consume in a year? (1.000oz= 29.57 mL) 28. Hugh was born 6.391875 X 103 days ago. How old (in years, with 1yr= 365.25 days) is Hugh? Matter 29. An element a. can be broken down into simpler substances b. are used to make other elements c. are used to make compounds d. are never found in the periodic table of elements 30. Physical means can be used to separate a. elements b. pure substances b. mixtures d. compounds 31. Anything that takes up space and has mass is called a. matter b. mass c. volume d. stuff Name:______________________________ 32. A change in the force of Earth’s gravity on an object will affect its a. mass b. density c. weight d. kinetic energy 33. Chemical proprieties a. include changes of state of a substance b. include mass and color c. include changes that alter the identity of a substance d. can be observed without altering the identity of a substance 34. Identify each as an element, compound, or mixture. For mixtures, identify it as homogeneous or heterogeneous. _______________________ A. Orange juice _______________________ B. NaCl _______________________ C. Fog _______________________ D. Ink _______________________ E. 14 Karat gold _______________________ F. Ice _______________________ G. Molybdenum _______________________ H. octane (C8H18) 35. The four states of matter are: __________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________. 36. State below if the form (shape) of each state is constant, as well as the volume. 37. Explain the arrangement of molecules in solids, liquids, and gases. Name:______________________________ 38. Classify each of the following as either a physical or chemical change. _______________________ A. Bending a piece of wire _______________________ B. Burning coal _______________________ C. Cooking a steak _______________________ D. Dissolving sugar in water _______________________ E. Souring milk _______________________ F. Stretching a rubber band The Atom 39. For the following elements, provide information as to group, block and metal status as indicated on the top of the chart. Element K 19 Ba 56 Ti 22 Al 13 Se 34 Sb 51 Xe 54 Pm 61 Group name Metal, Nonmetal, or Metalloid? Name:______________________________ 40. Write the complete chemical symbol for an atom with 35 protons, 45 neutrons, and 36 electrons. 41. Element X has two natural isotopes. The isotope with mass 62.9265 amu has a relative abundance of 69.17%. The isotope with mass 64.9278 amu has a relative abundance of 30.83%. What is the average atomic mass of element X? What is the identity of element X? 42. Fill in the sections of the table that are empty. Element # of protons # of neutrons Cr # of electrons Mass # Charge (+, , 0) 52 0 28 37 48 36 Br 36 80 5 11 I 3+ 74 0 Nomenclature 43. Give the common ion for the following: S O C B N Cl I H 44. What are the 3 types of bonds? 45. Which type of bond occurs with a transfer of electrons? Na Ca Mg Ag Name:______________________________ 46. Which type of bond occurs with a sharing of electrons? 47. Beryllium Bromide (BeBr2) has which type of bond? 48. When are Roman numerals used in naming compounds? 49. Name the following compounds. Both ionic and covalent molecules are here, and they are mixed! A. NaOH ___________________________ B. CaO _____________________________ C. N2O _____________________________ D. N2O5 ____________________________ E. SO2 _____________________________ F. H2SO4 ___________________________ G. AgC2H3O2 _________________________ H. CuCl22H20 _______________________ 50. Give the correct formula for the following: A. Iron (III) sulfate __________________________ B. Iron (II) sulfate __________________________ C. Oxygen gas _______________________ D. Nitric Acid ______________________________ E. Lead (IV) chromate _______________________ F. Sulfur hexaflouride ________________________ G. Dinitrogen dioxide ________________________ H. Barium hydroxide _________________________ I. Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate ______________________________ J. Hydrogen gas _______________________ K. Sodium metal_______________________ Name:______________________________ Reactions and Equations A. Coefficient B. Reactant C. Product D. Balanced E. Endothermic F. Exothermic G. Subscript H. Precipitate I. Diatomic J. Aqueous _____ 51. A reaction that releases heat. _____ 52. A reaction that absorbs heat. _____ 53. A whole number that appears before a formula in an equation. _____ 54. A starting substance in a chemical reaction. _____ 55. A new substance formed in a chemical reaction. _____ 56. Equation obey the laws of conservation of mass if they’ve been properly ___. _____ 57. A solid product. _____ 58. A number within a formula representing the number of atoms of each element present in the formula. _____ 59. A solid compound dissolved in water. _____ 60. Elements that do not exist alone! Write out a word equation for the following equations. 61. H2SO4 + NaOH ---------------> NaSO4 + H2O 62. Ba(OH)2 + MgCl2 -----------> 63. Why do we balance equations? Mg(OH)2 + BaCl2 Name:______________________________ Substitute symbols and formulas for names, and then write a balanced equation for each of the following reactions. 64. Copper combines with sulfur to form copper (I) sulfide. 65. Chlorine gas reacts with aqueous sodium bromide to form aqueous sodium chloride and liquid bromine. Balance the following reactions. 66. ___ WO3 + ___ H2 ___ W + ___ H2O 67. __ PdCl2 + ___ HNO3 Pd(NO3)2 + ___ HCl 68. ___ Cr + ___ O2 ___ Cr2O3 69. ___ CuS2 + ___ O2 ___ Cu + ___ SO2 Identify the type of chemical reaction shown below as synthesis (S), decomposition (D), single replacement (SR), double replacement (DR), or combustion (C). 70. KI + Pb(NO3)2 KNO3 + PbI2 71. Fe + H2O Fe2O3 + H2 72. Ag2O Ag + O2 73. CH3OH + O2 CO2 + H2O 74. S8 + O2 SO3 Name:______________________________ Given the following reactants predict the products. 75. Li + Br2 76. NaCl 77. Na (s) + P(s) 78. AgNO3 + NaCl 79. AgNO3(aq) + Cu(s) (2+) 80. H2SO4(aq) + Ca(OH) 2(aq) 81. Ag(s) + Cu(NO3)2(aq) 82. SnF4(s) 83. C6H14(g) + O2(g) → 84. CaCl2(aq) + NaNO3(aq) 85. What is the activity series, and why is it important when working with single replacement reactions? The Mole 86. Calculate the mass of 2.56 moles of barium phosphate. 87. Determine the number of particles in 8.20 g of potassium sulfate. 88. Determine the volume of 312 g of Bromine gas at STP. Name:______________________________ 89. Determine the percent composition for each element in Phosphorus trichloride. 90. Calculate the molecular formula of the compound whose molar mass is 60.0g and empirical formula is CH4N.