Drive Motors
advertisement

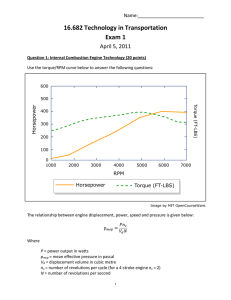
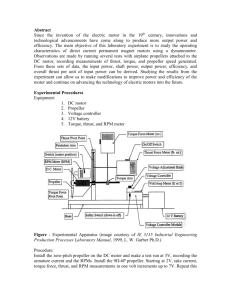
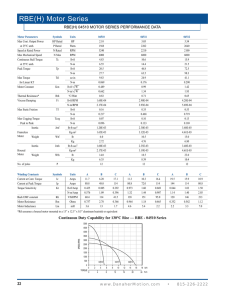
Drive Motors EE 5351 – Lecture 6 Consider a mobile platform: Vehice Mass: 20 kg (5 kg supported by each wheel) Drive Motors: 2 Wheel Diameters: 6 cm Performance Requirements: • Top Speed: 2 m/sec • Acceleration (0 to 2 m/sec): 3 sec • Maximum Incline: 5% (1:20) • Operating Surface: Indoor, hard surface (Crr=0.15) Calculation of Forces • Rolling Resistance: Frr = mgcrr = 20*9.81*(0.15) = 29.5 N • Grade Resistance: Fgr = mg*sin(α), α=tan-1(1/20) = 20*9.81*(.05) = 9.8 N • Force for Acceleration up the grade: • Facc = [ma] = [m(1 + crr + sin(α))*Δv/Δt ] = [20(1 + 0.15 + 0.05)*(2/3)] = 16 N • Total Motive Force: Facc+Frr+Fgr = 55.3 newtons Torque and RPM • Torque on each Wheel: • T = F x d / 2 wheels= Ftot * Radius / 2 = (55.3 * (.06/2))/2 = 0.83 N-m (7.35 in-lb) • Wheel RPM at Top Speed: • N = Vel* (1/πD) * 60 = (2* 60) / (π * 0.06) = 637 RPM Power Required when Accelerating to Top Speed: P = Tω = 0.83 * 637 * 2* π / 60 = 56 watts per motor Sizing of the Motor: • DC Motors tend to be High RPM, Low Torque • Require a Gear-Head to translate to Low RPM, High Torque • Gear-Head has Significant Losses – 30% • Motor also has Losses – 20%-30% • Pin = Pshaft/(ηm*ηgh) = 56/(.7*.7) = 112 W Motor Sizing… • So, looking for a 100 Watt Motor that can produce about 1 N-m of Torque at 700 RPM • Choice #1: Banebot RS-545 motor with 26:1 Gearhead: – 60 W motor, 14000 RPM, 0.3 in-lb Torque – With Gearhead: 540 RPM, 7.8 in-lb • A Bit Small…. Motor Sizing … • Choice # 2: Banebot RS-550 and 26:1 gearhead – 120 W motor at 17000 RPM, 4.4 in-lb motor – With gearhead: 650 RPM, 114.4 in-lb (13 N-m) • Overkill? • Motor draws 10 amperes at full load, 1.2 A at no load. Can we supply enough battery capacity to provide a useful operating life for 2 of these motors? Batteries