PLATE TECTONIC THEORY THE LANGUAGE OF THE EARTH – PART V
advertisement

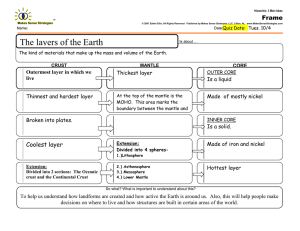
THE LANGUAGE OF THE EARTH – PART V PLATE TECTONIC THEORY Plate Tectonic Theory The Earth’s outer shell (lithosphere) is composed of rigid plates that are moving relative to one another. Internal Structure of the Earth Compositional Layers Physical Layers Plate Tectonics Drives Two Stages of Crust-making A. Mantle partially melts to make ocean crust B. Ocean crust partially melts to make continental crust What Moves the Plates? Mantle Push Ridge Slide Slab Pull Types of Plate Boundaries Divergent Plate Boundaries Mid-ocean Ridges Where Stage 1 Crust is Made Basalt Rock Type of the Ocean Crust Remember: Melting the mantle makes Pillow Lavas mafic magma!! Always Hydrothermal Alteration of Ocean Crust Preparing it for Stage 2 Melting “Black Smokers”metal-rich hydrothermal waters venting into the ocean floor Continental Rifting The creation of new ocean basins Continental Rifting and The Break-up of Pangea Age of the Atlantic Ocean Crust Beginning the Break-up 225 Ma Recording the Break-up Youthful Oceanic Crust Convergent Boundaries Making 2nd Stage Crust Ancient Continental Crust Convergent BoundariesWhere the Action Is!! Ocean - Ocean Earthquakes OceanContinent Volcanoes Continent - Continent Consequences of Convergence Explosive Volcanism Mt. St. Helens May 18, 1980 Consequences of Convergence Mountain Building and Rock Deformation Consequences of Convergence Earthquakes Banda Ache, Dec. 26, 2004 OROGENESIS The Culmination of Convergence Transform Fault Plate Boundaries The San Andreas Fault San Francisco Earthquake April 18, 1906 Mag 7.8 Mantle Plumes/ Hotspots Mantle Hotspots in the Oceans Sites of overthickened crust and the formation of ocean islands and plateaus Famous Hotspots Yellowstone Hawaii Iceland The Grand Unifying Theory of the Earth Paradigm -