Vocabulary for Plate Tectonics Unit
advertisement

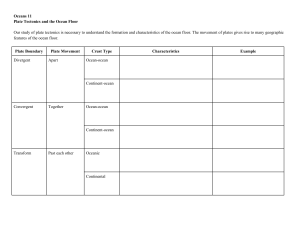
Vocabulary for Plate Tectonics Unit (page #s indicate pages in text where diagrams or pictures can be found) Continent—land. We live on the North American Continent (316) Drift—move slowly. The continents drift slowly around the earth over millions of years. Fossils—remains of plants or animals buried in the earth (page 373) Technology—tools. Sonar is a technology used to see the ocean floor. Mid-ocean ridges—cracks on the sea floor where sea floor is spreading apart (pages 376, 379, and 387) Crust—the hard, outer layer of the earth (page 312) Mantle—the warm, soft layer below the crust (page 312) Core—center or middle. The core of the earth is very hot. (page 312) Ocean crust—sea floor; the land under the water (316) Theory of Plate Tectonics—the earth’s crust is broken into pieces that slowly move around. Tectonic plate—a piece of the earths crust (381) Convection—warm material rises and cool material sinks (384) Rise—go up Sink—go down Molten—melted edge or boundary-- Most earthquakes and volcanoes happen at the edges or boundaries of tectonic plates. (377) Subduct—to dive down (379 and 386) Trench—deep places on the ocean floor where the edge of one plate subducts under the edge of another plate. (379 and 386) Converge—move together (379 and 386) Diverge--move apart (379 and 387)