cell adaptation -2
advertisement

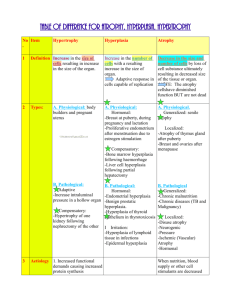
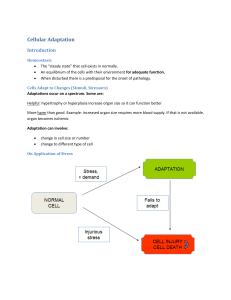
Lecture # 17 CELL ADAPTATION - 2 Dr. Iram Sohail Assistant Professor Pathology College Of Medicine Majmaah University CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF CELL ADAPTATION OBJECTIVE • Explain the clinical significance of cell adaptation • When cell faces any physiologic stresses or pathologic stimuli, first the cell goes to adaptation. • Adaptation means acquiring a new steady state and preserve the viability & function of cell. CLINICAL SIGNIFICANE • Adaptation is very necessary for our body to adjust in a new environment and also to preserve the function and viability of cells. Examples of clinical significance of hypertrophy 1. Uterine hypertrophy during pregnancy • As the pregnancy progresses, the growing fetus requires more space for his development. • Uterine smooth muscle cannot replicate (cannot divide and increase in numbers) • So that’s why under the stimulation of pregnancy hormone (estrogen) they only increase in size (hypertrophy). 2. Skeletal muscle hypertrophy in weightlifter • In response to increased workload during weightlifting and exercise, the individual skeletal muscle cell will undergo hypertrophy and shows a strong physique. 3. Heart enlargement in hypertension & aortic valve disease • In hypertension & aortic valve disease, heart has to contract forcefully to fulfill the requirement of body. For this forceful contractility the cardiac muscle cells goes into hypertrophy.(because they cannot divide and can’t go into hyperplasia) Examples of clinical significance of hyperplasia 1. Hyperplasia of female breast at puberty & pregnancy • Under the influence of female hormones, the glandular epithelium of breast proliferates at puberty and during pregnancy. 2. Compensatory hyperplasia in liver • This type of hyperplasia occurs when a portion of an organ is removed or diseased. Example • When some portion of liver is removed in the process of transplantation, the remaining portion of liver starts replication and eventually the normal weight of liver will be restored. • The stimulus for this restoration is growth factors, produced by the remaining liver cells. • After restoring the normal weight, the growth is turned off by growth inhibitors. 3. Endometrial hyperplasia • The endometrial lining of uterus is maintained at a normal thickness by growth stimulatory & growth inhibitory pituitary and ovarian hormones. • When this hormonal balance is disturbed by any disease, the thickness of endometrium is increased and eventually results in endometrial hyperplasia. • This endometrial hyperplasia can change into cancer. Examples of clinical significance of atrophy 1. Loss of innervation – In polio virus ----- loss of innervation ----- atrophy of limb 2. Loss of blood supply – In atherosclerosis ------ atrophy of brain 3. Decreased workload – In fracture ------ because of immobilization ------- atrophy of limb 4. Ageing – Brain & other body parts atrophy 5. Loss of endocrine (hormonal) stimulation – Postmenopausal atrophy of female genital organs Examples of clinical significance of metaplasia 1. Metaplasia in smokers • In smokers, the normal columnar ciliated epithelium of respiratory tract is replaced by stratified squamous epithelium. • This metaplasia will enable respiratory tract to survive under tough circumstances that has created by cigarette smoke. It may lead to lung cancer in future. 2. Vitamin A deficiency – causes metaplasia in respiratory tract and eye. 3. Esophageal metaplasia • In gastric esophageal reflux disease, the normal squamous epithelium of lower esophagus is replaced by columnar epithelium. 4. Bone metaplasia – Sometimes bone is formed in soft tissue especially after injury.