CHEM 1411 # 2 2014.doc
advertisement

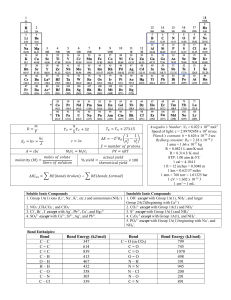
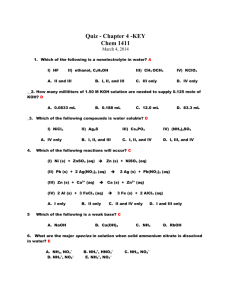
Houston Community College System Chemistry 1411 EXAM # 2 Activity Series of Metals in Aqueous Solution CHEM 1411 Exam #2 (Chapters 4,5,6) Nov.7, 2014 Part I- (3 points each) - Please answer the following multiple choicequestions (in scantron) .Show all your work for part II and bonus questions in the space provided. . 1. Which of the following would you expect to be a weak electrolyte? A. CH3COOH B. HCl C. NaCl D. H2O E. H2SO4 2. Which is (are) the spectator ion(s) in the following precipitation reaction? (NH4)3PO4 (aq) + Al2(SO4)3 (aq) AlPO4 (s) + (NH4)2SO4 (aq) A. NH4+, PO4 B. Al3+, SO42- D. Al3+, PO43 C. NH4+, SO42- E. NH4+ 3. Which of the following ionic compounds is insoluble in water? A. NaCl B. MgBr2 C. ZnCl2 D. AgBr 4. What is the correct formula of the salt formed in the neutralization reaction of hydrochloric acid with calcium hydroxide? A. CaO B. CaCl2 C. CaH2 D. CaCl 5. What are the major species in solution when solid ammonium nitrite is dissolved in water? A. NH3, NO3 B. NH4+, H NO3 C. NH3, NO2 D. NH4+, NO2 E. NH4+, NO3 6. A 10.0 cm3 container of helium is sealed at 22.0 °C and 1.0 atm pressure. What pressure would be exerted by the helium if the container were heated to 220 °C? A. 10.0 atm B 1.67 atm C. 2.01 atm D. 1.08 atm 7. What is the oxidation number of chlorine in ClO4 ? A. +8 8. In the chemical reaction, B. -8 C. +7 D. +5 E. +9 2 Na(s) + 2H2O(l) 2 NaOH(aq) + H2(g), which of the following is correct? A. metallic sodium is the reducing agent. C. hydrogen in water is oxidized. E. two of these B. metallic sodium in oxidized D. oxygen in water is reduced 2 9. Which of the following do you need to know to be able to calculate the molarity of a salt solution? I. II. III. IV. the mass of salt added the molar mass of the salt the volume of water added the total volume of the solution A. I, III B. I, II, III C. II, III D. I, II, IV E. you need all the information 10. Calculate ΔHrxn for 2C2H2(g) + 5O2(g) 4CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) given the following ΔH°f values (kJ/mol) C H (g) ΔH° = +226.7 CO (g) ΔH° = -393.5 A. -1692 kJ C. +2599 kJ 2 2 f 2 B. -2599 kJ f D. -1456 kJ H O(l) ΔH° = -285.8 2 f E. -453 kJ . 11. A system receives 575 J of heat and delivers 425 J of work. Calculate the change in internal energy of the system. A. 150 J B. – 1000 J C. 1000 J D. 575 J E. – 150 J 12. Calculate the mass in grams of 2.74 L of CO gas measured at 33 oC and 945 mmHg. A. 0.263 g B. 2.46 g C. 3.80 g D. 35.2 g E. 206 g 13. A 4.691 g sample of MgCl2 is dissolved in enough water to give 750 ml of solution. What is the magnesium ion concentration in this solution? A. 3.70 x 10 -2 M C. 0.118 M B. 1.05 x 10 -2 M D. 6.57 x 10 -2 M 14. The heat combustion for one mole of carbon is 410 KJ. C (s) + O2 (g) -------- CO2 (g) How many KJ of heat be liberated on complete combustion of 60 g of C. A. 2050 KJ B. 18040 KJ C. 4920 KJ D. 24600 KJ 15. If 100. ml of a 0.500 M solution of sodium nitrate were diluted to exactly 500. ml, the molarity of the diluted solution would be-----. A. 2.50 M B. 0.500 M C. 0.100 M D. 1.00 M 16. What is the density in g/L of N2O at 1.53 atm and 45.2oC ? A. 18.2 g/L B. 1.76 g/L C. 0.388 g/L 3 D. 2.58 g/L 17. Calculate the amount of heat necessary to raise the temperature of 22.8 g of copper from 20.0 oC to 875 oC. The specific heat of copper = 0.385 J/ g oC A. 1.97 x 10 -5 J B. 1.0 x 10 -2 J C. 329 J D. 7.51 KJ E. 10.5 KJ 18. What is the volume occupied at STP by a mixture of 4.00 g of He(g), 2.00 g of H2(g) and 32.0 g of O (g)? 2 A. 6.15 L B. 11.2 L C. 22.4 L D. 44.8 L E. 67.2 L 19. A gas sample occupies a volume of 16.4 L at 27 °C and 0.300 atm. How many moles of gas are present? A. 0.200 B. 0.450 C. 3.50 D. 10.0 20. 2.56 g of an unknown gas occupies a volume of 111 mL at 753 torr and 22 °C. Calculate the molar mass of the gas. A. 0.563 g/mol B. 0.741 g/mol C. 42.0 g/mol D. 563 g/mol E. 6870 g/mol 21. A chemical reaction that absorbs heat from the surrounding is said to be -------- and has a-------- value of H. A. C. Endothermic , positive Exothermic , negative B. Endothermic , negative D. Exothermic , positive 22. Which one of the following is a weak acid? A. HNO3 B. HCl C. HI D. HF 23. Which of the following is / are characteristic of gases? A. high compressibility B. relatively large distance between molecules C. formation of homogenous mixture D. all of the above 24. What is the resulting molarity of solution when 2 g of NaOH is dissolved in 500 mL of water? (formula weight of NaOH = 40.) A. 0.01 M B.0.05 M C. 0.1 M D. 0.5 M 25. How much kinetic energy ( in J ) is possessed by a 23.2 g object moving at a speed of 81.9 m/s ? A. 145 J B. 0.95 J C. 77.8 J 4 D. 1900 J PART II- ( 5 points each) Please show all your work. 1. Neutralization of 18.02 mL of H2SO4 required 13.14 mL of 0.35M NaOH. Write a complete balance equation for this reaction. What is the molar concentration of H2SO4? 2. A 53.0 g metal alloy ingot at 93.0 °C is added to 290 g of water at 22.0 °C in an insulated calorimeter. The final temperature of the mixture is 31.1 °C. What is the specific heat capacity of the metal alloy? (specific heat of water = 4.184 j/g.oC) 3. Sodium sulfate reacts with barium iodide. Write a complete molecular, ionic, and net ionic equation for the reaction and identify the spectator ions. 4. A sample of hydrogen gas is contained in a balloon. The volume of the balloon is 2.15 L at 15 C . The temperature is changed until the volume of the balloon is 3.25 L. What is the new temperature of the gas in C ? 5 5. Calculate the root mean square speed of nitrogen molecules in m/s at 25 oC. R = 8.314 J/K.mol 1J = 1 Kg. m2/ s2 BONUS question-Show all your work.(10 points) Using Hess’s law of constant heat of summation and given: I) ∆H = 44.1 kJ H2O(l) H2O(g) II) CH3COCH3(l) + 4O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 3H2O(l) ∆H = 1787 kJ III) CH3COOH(l) + 2O2(g) 2CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) ∆ H = 835 kJ determine the enthalpy of reaction for CH3COCH3 (l) + 2 O2(g) CH3COOH(l) +CO2(g) + H2O(g) 6 CHEM 1411 EXAM # 2 (Key) (Fall 2007) PART - I 1. A 2. C 3. E 22.A PART -II 26. 4. D 5. D 6. B 23. B 7. C 8. E 9. D 24. A 10. B 11. B 12. C 25. C 13. D 14. D 15. B 16. E 17. B 18. D 19. E 20. A 21. D H2SO4 + 2 NaOH K2SO4 + 2 H2O nb Vb Mb (1) (13.14) (0.35) Ma = ------------ = -------------------------- = 0.13 M naVa (2) (18.02) 27. m1C1T1 = m2C2T2 (53.0) (C1) (93 31.1) = (290) (4.184) (313.1-22) ; C1(metal) = 3.37 J/g.oC 28. E = (hc/ λ) = 2.18x10 –18 ( 1/ni2 – 1/nf2) = (6.33x10-34 J.sec)(3.00x108 m/sec) / λ = 2.18x10 –18 (1/62 – 1/22 ) = 2.18x10 –18 (1/36 – 1/4 ) λ = 4.13x10-7 m 29. At constant pressure ; V1/T1 = V2/T2 T2 = ( T1V2 / V1) = ( 288 x 3.25) / (2.15) = 435.35 K 435.35 -273.15 = 162 oC 30. m = ( 4.0 amu)((1.0 g/6.02x1023 amu) = 6.64x10-24 g = 6.64x10-27 kg λ d = ( h / mv) = (6.63x10-34) / (6.64x10-27)(1.70x107) λ d = 6.18x10-18 m BONUS: RX (I) + RX (II) + reverse RX (III) = (- 44.1) + (-1787) – (-835) = -996.1 kJ 7