Review Chapter5.doc
advertisement

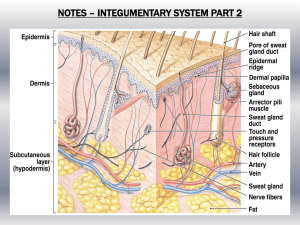
Chapter5 This activity contains 7 questions. Label the following components in the diagram of the integumentary system. For each item below, use the pull-down menu to select the letter that labels the correct part of the image. 1.1 Reticular layer [hint] 1.2 Sweat gland 1.3 Epidermis 1.4 Sebaceous gland Label the following components in the diagram of the integumentary system. For each item below, use the pull-down menu to select the letter that labels the correct part of the image. 2.1 Papillary layer [hint] 2.2 Subcutaneous layer (hypodermis) 2.3 Hair follicle Label the following components in the diagram of the integumentary system. For each item below, use the pull-down menu to select the letter that labels the correct part of the image. 3.1 Lamellated corpuscle 3.2 Tactile corpuscle 3.3 Dermis Label the layers of the epidermis. For each item below, use the pull-down menu to select the letter that labels the correct part of the image. 4.1 Dermis 4.2 Stratum granulosum 4.3 Stratum germinativum 4.4 Stratum corneum Label the layers of the epidermis. For each item below, use the pull-down menu to select the letter that labels the correct part of the image. 5.1 Stratum lucidum 5.2 Stratum spinosum 5.3 Basal lamina Label the structures associated with hair anatomy. For each item below, use the pull-down menu to select the letter that labels the correct part of the image. 6.1 Hair bulb 6.2 Hair shaft 6.3 Connective tissue root sheath 6.4 Arrector pili muscle 6.5 Sebaceous gland 6.6 Hair root Label the structures associated with nail anatomy. For each item below, use the pull-down menu to select the letter that labels the correct part of the image. 7.1 hyponychium 7.2 eponychium 7.3 Nail body 7.4 Nail root 7.5 Lunula This activity contains 6 questions. Place the following layers of the epidermis into the proper order, starting from the innermost layer (1) to the outermost layer (5). Using the pull-down menus, match each item in the left column to the corresponding item in the right column. 1.1 1 stratum germinativum 1.2 2 stratum lucidum 1.3 3 stratum corneum stratum granulosum 1.4 4 stratum spinosum 1.5 5 Match the condition to the proper cause: Using the pull-down menus, match each item in the left column to the corresponding item in the right column. 2.1 melanocyte function loss, may be autoimmune cyanosis 2.2 metabolic product of vitamin D3 ulcer 2.3 localized shedding of an epithelium jaundice calcitriol 2.4 oxygen lack in blood to skin causes blueness vitiligo 2.5 bile excretion in liver fails, skin turns yellow Put the following layers of the hair shaft and surrounding hair follicle into the proper order, starting at the center (1). Using the pull-down menus, match each item in the left column to the corresponding item in the right column. 3.1 1 medulla 3.2 2 cuticle external root sheath 3.3 3 glassy membrane 3.4 4 internal root sheath cortex 3.5 5 3.6 6 Put the following steps in integumentary repair in the proper order by matching them from (1) to (5). Using the pull-down menus, match each item in the left column to the corresponding item in the right column. 4.1 1 4.2 2 4.3 3 epidermal cells undermine the scab and fibrin clot disintegrates dermal fibroblasts produce scar tissue that elevates epidermis scab is shed and epidermal regrowth is complete scab forms and clotting isolates region 4.4 4 Match the description of each accessory structure with the appropriate structure: Using the pull-down menus, match each item in the left column to the corresponding item in the right column. 5.1 Holocrine gland with a waxy, oily secretion Sebaceous follicle Ceruminous glands 5.2 Large gland that lubricates the epidermis and is not associated with hair follicles Sebaceous gland nails 5.3 Sweat production that begins with puberty. Merocrine sweat glands Apocrine sweat glands 5.4 Sensible perspiration 5.5 Producing modified sweat that mixes with nearby sebaceous gland secretions to protect the eardrum 5.6 Protection for exposed tips of digits Match the term with the correct definition Using the pull-down menus, match each item in the left column to the corresponding item in the right column. 6.1 Nail body Thickened stratum corneum near free edge of nail 6.2 Hyponychium Visible portion of the nail Epidermis beneath nail 6.3 Eponychium Epidermal fold where nail is produced Stratum corneum of the nail root that extends over the exposed nail 6.4 Nail bed Pale crescent shape at base of nail 6.5 Nail root 6.6 Lunula This activity contains 25 questions. The integumentary system consists of the hypodermis and mesodermal layers. the dermis and subcutaneous layers. the cutaneous membrane and associated structures. the epidermis and deep fascia. Which of the following is NOT a function of the integumentary system? absorption of nutrients protection maintenance of body temperature storage of nutrients Beginning at the basement membrane and working toward the free surface, the layers of the epidermis are stratum basale, stratum corneum, keratohyaline, and keratinocytes. stratum germinativum, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, and stratum corneum. keratinocytes, Merkel cells, fibroblasts, and melanocytes. stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, and stratum germinativum. Ultraviolet radiation is beneficial in small amounts. causes melanin production to accelerate. can cause cumulative damage, leading to premature aging. all of the above Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) can be synthesized from food. can be converted to calciferol. can be absorbed from food. all of the above Which of the following statements about vitamin D is NOT true? It controls the metabolic rate of the body. Ultraviolet radiation produces it from steroids in the skin. It controls the absorption of calcium from the diet. It is added to most dairy products in the United States. Which of the following is an effect of epidermalgrowth factor? promotes the division of cells in the stratum germinativum accelerates the production of keratin in epidermal cells stimulates secretion by epidermal glands all of the above The major components of the dermis are desmosomes and microvilli. keratinocytes and melanocytes. papillary layer and reticular layer. basal cells and Merkel cells. Which of the following sensory cells is located in the epidermis? lamellated corpuscles tactile corpuscles Merkel's or tactile discs all of the above Nails, sweat glands, hair follicles, and sebaceous glands originate from the dermis. are epidermal derivatives. grow continuously throughout life. all of the above What is the function of sebum? excretes water and electrolytes cools the skin trap. particles in the ear inhibits bacteria and lubricates the keratin of hair Apocrine sweat glands are found in the armpits, groin, and around the nipples. produce a watery, salty secretion. cool the surface of the skin. are far more numerous than eccrine sweat glands. Which of the following glands produces earwax? merocrine (eccrine) glands ceruminous glands mammary glands apocrine glands The root hair plexus surrounds the base of each hair. causes hairs to stand erect. is responsible for deep pressure sensations. none of the above The eponychium extends under the nail. is the nail cuticle. is a pale crescent at the base of the nail. is found at the free edge of the nail. The body of the nail is covered by the cuticle. is not affected by diseases. is beneath the hypochondrium. consists of dead, tightly compacted cells. The four stages in the regeneration of skin in the correct order are clot dissolution, granulation, fibroblast activity (regeneration), and scab formation. swelling, heat, tenderness, and pain. bleeding, scab formation, fibroblast activity (regeneration), and scab shedding. scab formation, degeneration, fibroblast activity (regeneration), and bleeding. The color of skin is the result of carotene. dermal blood supply. melanin. all of the above Melanin is a brown-black pigment. found in large amounts in albinos. produced in keratinocytes. an orange-yellow pigment found in squash. Lines of cleavage are clinically significant because a cut parallel to a cleavage line will remain closed. they promote wound healing. wounds heal more slowly if they run parallel to lines of cleavage. a cut at right angles to a line of cleavage will remain closed. Decubitus ulcers are growths of excess skin tissue. result in excess pigmentation or "birthmarks." result from a lack of circulation. all of the above The protective scab that forms over an injury consists of collagen fibers. fibrin. granulation tissue. cellulite. What forms when scar tissue continues beyond the requirements of tissue repair? granulation tissue stretch marks keloid scab Older people are more prone to skin injuries as a result of the number of Langerhans cells decreasing. reduction in melanocyte activity. the thinning of the epidermis. all of the above The reduction in sebum production due to aging can lead to sunburn. wrinkles. dry and scaly skin. overheating in warm environments. This activity contains 5 questions. Apocrine sweat glands are associated with hair follicles. True False Vellus hairs are found on your head, eyebrows, and eyelashes. True False The blood clot that forms at the site of an epidermal injury is called granulation tissue. True False Another name for the eponychium is cuticle. True False The secretions of sudoriferous glands have antibacterial action. True False This activity contains 3 questions. The integumentary system contains two components, the outer the underlying dermis, along with several accessory structures. The dermis is divided into an upper layer. and layer and the deeper reticular in the stratum germinativum form patterns of depressions and elevations that are especially noticeable on the fingertips.