Integumentary System Notes Part 2
advertisement
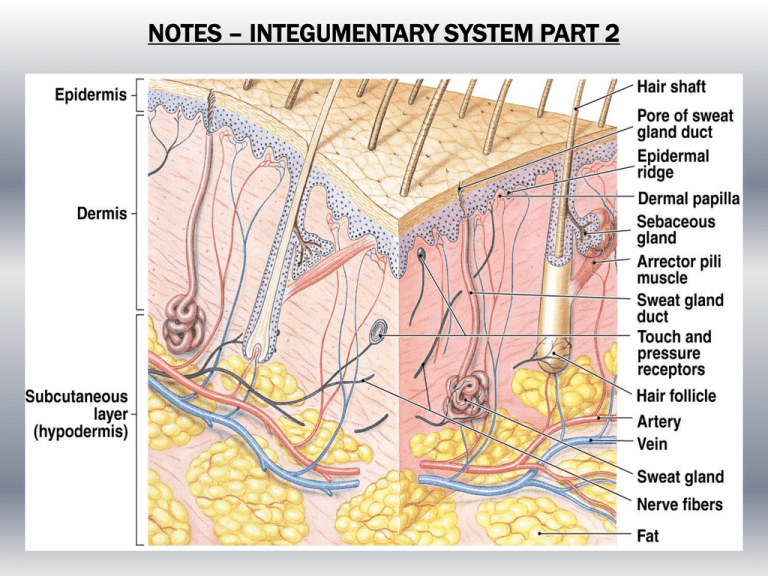
NOTES – INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART 2 SKIN FACTS Fingernails grow nearly 4 times faster than toenails. Which layer of the Integumentary System is mostly loose connective tissue and adipose tissue? The hypodermis is mostly loose connective tissue and adipose tissue. Which layer of skin is where most cell division occurs? The dermis is the layer of skin where most cell division occurs. What is the top layer of skin called? The top layer of skin is called the epidermis. Which layer of the dermis is the deepest? The deepest layer of the dermis is the reticular layer. Which layer of the dermis is responsible for fingerprints? The papillary layer is the layer of the dermis responsible for fingerprints. Which layer of the epidermis have cells undergone a chemical change and formed layers (sometimes 25 layers thick)? The layer of the epidermis that has undergone a chemical change and formed layers is the stratum corneum or keratinized layer. Which layer of the epidermis is the stratum where most cell division occurs? The layer of the epidermis where most cell division occurs is the stratum basale. Which layer of the epidermis is the stratum where dandruff, calluses, and corns occur? The layer of the epidermis where dandruff, calluses and corns occur is the stratum corneum. What is the pigment called that gives our skin its color? What is the cell that produces this pigment? The pigment that gives our skin its color is melanin and the cell that produces this pigment is a melanocyte. • ACCESSORY SKIN STRUCTURES (4) 1. HAIR • hair is dead, keratinized epithelial cells • hair is produced in the hair bulb (part of the hair follicle), which rests on a papilla in the dermis • growth stage / resting stage • hair is held during resting stage, when next growth stage begins, the old hair falls out • hair color • mostly due to melanin 2. ARRECTOR PILI MUSCLES • bundles of smooth muscle that cause hairs to “stand up” (goose bumps) • useless in humans but used for insulation in animals 3. GLANDS • Sebaceous (oil) Glands • produces sebum (oil), which prevents drying & inhibits some bacteria • a build up of sebum & dirt causes acne • Sweat Glands (2 types) • ECCRINE sweat glands • Location: • everywhere on body • composed of water & salts • function is to cool the body • also released during stress • APOCRINE sweat glands • Location: • attached to hair in axillae and genitalia • sweat is organic and odorless • when combined with bacteria it produces odor 4. Nails • made of dead stratum corneum and very hard keratin • Nail Parts • nail body • visible part of the nail • nail root • covered by skin • cuticle • stratum corneum • nail matrix • under proximal end of nail • lunula • visible part of nail matrix











