SLNG 1307 ambers2012course_syllabus.doc
advertisement
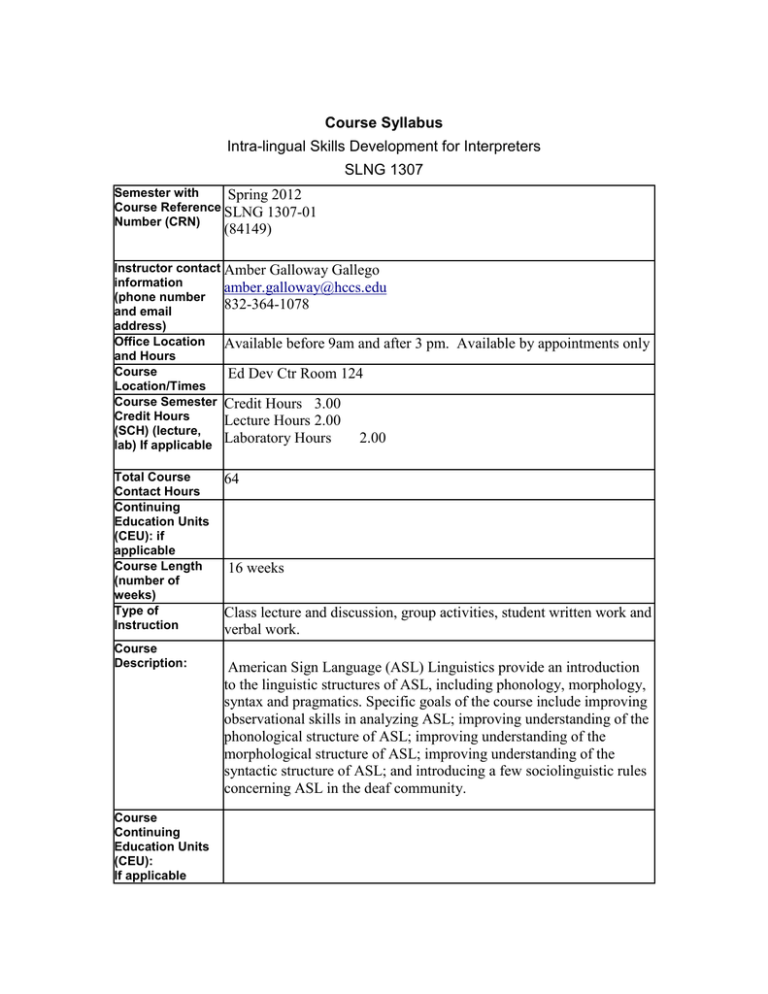
Course Syllabus Intra-lingual Skills Development for Interpreters SLNG 1307 Semester with Spring 2012 Course Reference SLNG 1307-01 Number (CRN) (84149) Instructor contact Amber Galloway Gallego information amber.galloway@hccs.edu (phone number 832-364-1078 and email address) Office Location Available before 9am and after and Hours Course Ed Dev Ctr Room 124 Location/Times Course Semester Credit Hours 3.00 Credit Hours Lecture Hours 2.00 (SCH) (lecture, Laboratory Hours 2.00 lab) If applicable Total Course Contact Hours Continuing Education Units (CEU): if applicable Course Length (number of weeks) Type of Instruction Course Description: Course Continuing Education Units (CEU): If applicable 3 pm. Available by appointments only 64 16 weeks Class lecture and discussion, group activities, student written work and verbal work. American Sign Language (ASL) Linguistics provide an introduction to the linguistic structures of ASL, including phonology, morphology, syntax and pragmatics. Specific goals of the course include improving observational skills in analyzing ASL; improving understanding of the phonological structure of ASL; improving understanding of the morphological structure of ASL; improving understanding of the syntactic structure of ASL; and introducing a few sociolinguistic rules concerning ASL in the deaf community. Course None Prerequisite(s) Academic 1. Discipline/CTE Program Learning Outcomes 2. Course Student Learning Outcomes (SLO): 4 to 7 Develop receptive and expressive skills in American Sign Language and Fingerspelling; Develop knowledge and awareness of the differences between the Deaf culture/deaf community and the hearing community 3. Accurately interpret and transliterate between ASL and English in a variety of settings: face-to-face, small group settings, monologue and/or large group settings; and 4. Apply professional standards, practices, and ethics, not limited to the tenets of the Code of Professional Conduct, to their work. The student will demonstrate an understanding of various intra-lingual skills as they relate to English with a minimum of 70% accuracy The student will demonstrate the ability to apply various intra-lingual skills to English material with a minimum of 70% accuracy. The student will demonstrate the ability to assess and evaluate the accuracy of paraphrased material with a minimum of 70% accuracy The student will demonstrate at least a basic understanding of a broad range of knowledge, thus expanding cultural literacy with a minimum of 70% accuracy. Learning Objectives (Numbering system should be linked to SLO e.g., 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, etc.) Learning Outcome 1: The student will be able to define phonology and identify the key components of phonology with a minimum of 70% accuracy. Performance objectives for this outcome: 1.01 The student will differentiate the parts of signs as well as their internal structure. 1.02 The student will name the five basic parts of a sign, including handshape, movement, location, palm orientation and non manual signals. 1.03 The student will identify symbols in Stokoe’s System used to describe signs. 1.04 The student will explain why sequence is a key concept in the description of signs. 1.05 The student will explain the basic principles of the MovementHold Model. 1.06 The student will apply basic phonological processes in their ASL work, including; movement epenthesis, hold deletion, metathesis, and assimilation. Method of Measurement: written quizzes/exams, homework and class discussion. Learning Outcome 2: The student will be able to define morphology and identify the key components of morphology with a minimum of 70% accuracy. Performance objectives for this outcome: 2.01 The student will discuss how nouns are derived from verbs in ASL. 2.02 The student will be able to explain how compound words are formed in ASL. 2.03 The student will be able to explain lexicalized fingerspelling and loan signs in ASL. 2.04 The student will be able to discuss and explain numeral incorporation in ASL. 2.05 The student will understand the role of location in ASL morphology , including the use of space. 2.06 The student will be able to explain classifier predicates in ASL. 2.07 The student will be able to identify three movement roots including, stative, descriptive, process and contact root. 2.08 The student will list 7 different classifier handshapes. 2.09 The student will be able to explain subject-object agreement in ASL. 2.10 The student will understand pronouns and determiners in ASL. 2.11 The student will understand the basic concept of temporal aspect SCANS and/or Core Curriculum Competencies: If applicable The student will demonstrate an understanding of various intralingual skills as they relate to English with a minimum of 70% accuracy The student will demonstrate the ability to apply various intralingual skills to English material with a minimum of 70% accuracy. The student will demonstrate the ability to assess and evaluate the accuracy of paraphrased material with a minimum of 70% accuracy The student will demonstrate at least a basic understanding of a broad range of knowledge, thus expanding cultural literacy with a minimum of 70% accuracy. Workplace Competencies are defined in five areas: (a) resources, (b) interpersonal skills, (C) information, (d) systems, and (e) technology. The following SCANS Competencies will be included in this course: Resources: A worker must identify, organize, plan, and allocate resources effectively. C1- Time: select goal-relevant activities, rank them, allocate time, and prepare and follow schedules. Information: A worker must be able to acquire and use information. C5- Acquire and evaluate Information. C6- Organize and maintain information. C7- Interpret and communicate Information. Interpersonal Skills: A worker must work with others effectively. C9- Participate as member of a team: contribute to group effort. C10Teach Others New Skills. C12- Exercise leadership: communicate ideas to justify position, persuade and convince others, responsibly challenge existing procedures and policies. C13- Negotiate: work toward agreements involving exchange of resources, resolve divergent interests. C14- Work with Diversity: work well with men and women from diverse backgrounds. Basic Skills: A worker must read, write, perform arithmetic and mathematical operations, listen, and speak effectively. These skills include: The following foundation skills will be included in this course: Foundation Skills are defined in three areas: (a) basic skills, (b) thinking skills, and (C) personal qualities. F1- Reading: locate, understand, and interpret written information in prose and in documents such as manuals, graphs, and schedules. F2- Writing: communicate thoughts, ideas, information, and messages in writing, and create documents such as letters, directions, manuals, reports, graphs, and flow charts. Thinking Skills: A worker must think creatively, make decisions, solve problems, visualize, know how to learn, and reason effectively. These skills include: F6- Creative thinking: generate new ideas. F7- Course Calendar Instructional Methods Student Assignments Student Assessment(s) Instructor's Requirements Lecture, class discussion, weekly quizzes, collaborative learning project, written midterm and final exams. Student Involvement The faculty members of the Interpreter Training Program are committed to your successful completion of our classes without lowering the college’s academic standards. I understand that students face additional pressures from work and family, as well as have other obligations outside of their academic pursuits. I realize that at times issues beyond the control of a student interfere with class requirements. If you experience any circumstance that has a negative impact on your participation in this course, please make me aware of it as soon as possible. I may be able to assist or accommodate your particular circumstance. Do not wait until the end of the semester to ask for advice. Communication between students and instructors can be quite valuable. Program/Disciplin e Requirements: Global Awareness If applicable This class will encourage an understanding of the importance of diversity and difference in the college, the community, and the country. HCC Grading Scale Instructor Grading Criteria Instructional Materials HCC Policy Statement: A = 100- 90 4 points per semester hour B = 89 - 80: 3 points per semester hour C = 79 - 70: 2 points per semester hour F = 69 and below 0 point per semester hour W(Withdrawn) 0 points per semester hour I (Incomplete) 0 points per semester hour The student must re-enroll to receive credit. To compute grade point average (GPA), divide the total grade points by the total number of semester hours attempted. The grade "I" does not affect GPA. Access Student Services Policies on their Web site: http://hccs.edu/student-rights Distance Education and/or Continuing Education Policies Access DE Policies on their Web site: http://de.hccs.edu/Distance_Ed/DE_Home/faculty_resources/PDFs/DE _Syllabus.pdf Access CE Policies on their Web site: http://hccs.edu/CE-student-guidelines Grading Policy: 1. Homework Assignments (10) 100 points 2. Quizzes (4) (25 points each quiz) 100 points 3. Written Tests (4) (100 points each test) 400 points 4. Collaborative Research Proposal and Project 100 points 5. Mid-Term Examination 100 points 6. Final Examination 200 points Tentative Instructional Outline: Week 1: New syllabus review and expectations Background and introductions Phonology of ASL Part Two, Units 1-3: Stokoe, Sequentiality, Johnson-Liddell Homework: Part 1 & Part 2 and do assignments #1-4 Week 2: Phonological processes Movement Epenthesis Hold deletion Metathesis Assimilation Pair up individuals for group presentations & assign topics. Homework Week 3: Exam #1 Review Part one and Two for Midterm Exam: Week 4: Midterm Exam Morphology, Phonology vs. morphology Deriving nouns from verbs Homework Week 5:Compound Lexicalized Fingerspelling Morphology, Numeral incorporation: Rule of 5; Rule of 9 The Function of Space Verbs Homework Week 6: (Sub) Week 7: Week 8: Morphology Simple Sentences Classifier Predicates Morphology Classifier Predicates and Signer Perspective Temporal Aspect Derivational and Inflectional Morphology Homework Morphology Syntax, "Major" lexical categories Nouns Predicates Simple predicates Predicate nouns Predicate adjectives Auxiliaries used with predicates Adjectives Adverbs Homework Morphology Syntax "Minor" lexical categories Determiners Auxiliary verbs Prepositions Conjunctions Pronouns Homework Week 9: Morphology Basic sentence types: review Questions Yes-no Wh- Question mark Rhetorical Negation Commands Topicalization (topic-comment) Conditionals Non-Manual grammatical signals Time in ASL Homework: Part 4 Unit 1 & 2 and do assignment 16 & 17 Review Part 3 for Exam. Week 10: Exam #2 Semantics The meaning of individual signs The meaning of sentences Homework Week 11: Semantics, Variation and historical change ASL discourse Language in Use Bilingualism and language contact ASL Literature Percussion signing Drama Deaf humor Homework Week 12: Assign topic to group Homework: Review Exam #3 Homework: Prepare group presentations Week 13: Part Six Analyzing Signs Signs Have Parts: A Simple Idea American Sign Language: The Phonological Base The Confluence of Space and Language in Signed Languages Indicating Verbs and Pronouns: Pointing Away from Agreement Analyzing Variation in Signed Languages: Theoretical and methodological Issues Sociolinguistic Aspects of the Black Deaf Community Variation: Basic Concepts Discourse Analysis Language Contact in the American Deaf Community Homework: Review Part 6 for Exam. Week 14: Review for exam 4 Week 15: Exam #4 Cumulative Review Week 16: Final Exam