Unit C: Biological Molecules Notes Chapter 2, pp. 32-41
advertisement

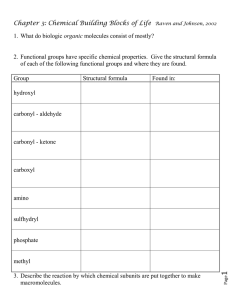
Unit C: Biological Molecules Notes Chapter 2, pp. 32-41 Prescribed Learning Outcomes (it is expected that you will know...) C1. Demonstrate a knowledge of synthesis and hydrolysis as applied to organic polymers (p. 32) C2. Distinguish among carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids with respect to chemical structure (p. 32-40) C3. Recognize the empirical formula of a carbohydrate (p. 32) C4. Differentiate among monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides (p. 32-33) C5. Differentiate among starch, cellulose, and glycogen (p. 33) C6. List the main functions of carbohydrates (p. 32) C7. Compare and contrast saturated and unsaturated fats in terms of molecular structure (p. 34) C8. Describe the location and explain the importance of the following in the human body: a) Neutral fats b) Steroids c) Phospholipids. p. (34-35) C9. Draw a generalized amino acid and identify the amine, acid (carboxyl), and R-groups (p. 37) C10. Differentiate among the primary, secondary, tertiary, & quaternary structure of proteins (p.38-39) C11. List the major functions of proteins (p. 37) C12. Relate the general structure of the ATP molecule to its role as the “energy currency” of cells (p.41). VOCABULARY (check off what you know and make cards for what you don’t know): _____ Adenine _____ Adipose _____ ADP _____ Alpha helix _____ Amino acids _____ Amino group _____ ATP _____ Carbohydrate _____ Carboxyl group _____ Cellulose _____ Cytosine _____ Dehydration synthesis _____ Denature _____ Deoxyribose _____ Double helix _____ Empirical formula _____ Emulsify _____ Fatty acid _____ Glucose _____ Glycerol _____ Glycogen _____ Guanine _____ Hydrolysis _____ Lipid _____ Maltase _____ Maltose _____ Neutral fat _____ Nucleic acid _____ Nucleotide _____ Peptide (di, tri, and poly) _____ Peptide bond _____ Phospholipid _____ Polymer _____ Primary structure _____ Protein _____ Purine _____ Pyrimidine _____ Quaternary structure _____ Ribose _____ Saccharide (mono, di, tri, and poly) _____ Saturated _____ Secondary structure _____ Simple Sugar _____ Starch _____ Steroid _____ Tertiary structure _____ Thymine _____ Unsaturated Synthesis and Hydrolysis The most important biological compounds are _______________________ POLYMERS (poly = _________ ) The polymers are: __________, ____________, _________ (fats), and __________________ (DNA/RNA). A polymer is made up of a chain of many ______________ linked together MONOMERS (mono = ________ ) Monomers are: ________________, _____________, ____________, and ___________________. These are made (_____________________) or broken down (_______________) over and over in living cells. Large polymers are also called ________________________ Macromolecules are formed by _________________, usually by reactions involving the loss of water = ________________________. DEHYDRATION SYNTHESIS ____________ are joined together during dehydration synthesis. Chains of monomers are called __________________________ Note: enzymes that speed up dehydration synthesis reactions are called ______________________. HYDROLYSIS The breaking of a polymer into units is ___________________ (i.e. done by adding water to polymer). Note: enzymes that speed up hydrolysis reactions are called ____________________________ CARBOHYDRATES Where does the name come from? Hydrated Carbons: _____________________ Carbohydrates have the empirical formula of (CH20)n where n = the # of times the chain is repeated. The carbons, hydrogens and oxygens are found in the ratio of _____________ and are made up of a repeating chain of sugars. Sugars are also known as __________________________. Carbohydrates usually end in ‘_______’. Can you think of any examples? a) CARBOHYDRATES: ______________________________ The basic sugar molecule is _____________: __________. Glucose has a _________ structure. Other monosaccharides include ____________, ___________, deoxyribose b) CARBOHYDRATES: ________________________ When two sugars bind together via ________________ _________________ a disaccharide is formed. Glucose + Glucose -------------------------------> ________________________ glucose + glucose forms the sugar ___________________ glucose + fructose forms the sugar ___________________ galactose + glucose forms the sugar __________________ c) CARBOHYDRATES: ___________________________ When many sugars bind together via dehydration synthesis four types of polysaccharides may be formed: • A) _______________ • B) _______________ • C) _______________ • D) _______________ LABEL THE FOLLOWING PICTURES AS: A, B, C, or D 1. CARBOHYDRATES: polysaccharides ______________________ • • • • • The ______________ of plants are made of cellulose They are _____________ of glucose molecules with ___________________. The linkage between the Carbon atoms of the sugars is different than starch and glycogen No mammal can break this bond This is why we _____________ cellulose = _________ 2. CARBOHYDRATES: polysaccharides _____________________ • __________________________________ as starch • • Starch is made up of many glucose molecules linked together Starch has _______________ 3. CARBOHYDRATES: polysaccharides ______________________ • _____________________________ (extra glucose) as glycogen • • • We store glycogen in our ______________________ Glycogen is made up of many glucose molecules linked together Glycogen has _________________ 4. CARBOHYDRATES: polysaccharides _______________________ Made by ___________________ Long glucose chains linked with _______________ bonds. Very ______________ Makes structures like ___________________, fingernails, ______________, and beaks MAIN FUNCTIONS OF CARBS 1. _______________: when the ________ between Carbon atoms are broken, the energy ___________ can be used by cells. Carbohydrates are the primary energy molecules for all life. 2. _____________: Cellulose is the major structural compound in plants (is used in the _______________________). LIPIDS Lipids are made up of the elements ___________ but in no set ratio. Lipids are large molecules that are _______________. Neutral Fats: ____________________________ 1. Composed of __________ bonded to ____________. 2. Fatty acids contain a _____ _________ of 1618 Carbons with an acid end. 3. Glycerol is a ___________ ____________ with 3 alcohol (OH) groups 4. These two molecules bind together via dehydration synthesis There are 2 Types of Triglycerides: 1. __________________________: There are __________________ in the carbon chains of the fatty acids. The carbons are filled with ____________. _______________. They mostly come from ___________. Become ________ at room temperature. Examples: lard, ________, animal fats… 2. ___________________________: There are one (________unsaturated) or more __________ (_____unsaturated). Mostly come from plants. They are _________ at room temperature. _______________ Examples: __________, corn oil, palm oil… PHOSPHOLIPIDS: Are used to make up the two layered _____________ of all cells. In phospholipids, the __________ fatty acid group of a triglyceride is ____________ by an inorganic _____________ group (______). This creates a _______________: The _________ end is water soluble (hydro_______) The _________ is not water soluble (hydro_______) STEROIDS: Steroids structurally look very different from lipids, but are also _________ _____________. They are made up of ______________ molecules fused together. Examples: ____________, estrogen, ______________, and vitamin ____. Used as ________________ Uses of Lipids 1. ____________________ for ___________ (more efficient spacewise than glycogen or starch). 2. ____________ and _____________ in animals 3. Making some ____________ (steroids) 4. Structure of __________________. Without lipids, we would have no cells. Proteins 1. Proteins are made up of the elements _______________ (but in no set ratio). 2. Proteins are chains of _________________ (usually ______ or more) that bond together via dehydration synthesis. 3. ______ of the average human body is made up of protein. 1. The building blocks of Proteins are amino acids. 2. There are ____________ to an amino acids: 1. __________Group (NH2 or NH3+) acts as a base (accepts H+) 2. __________Group (COOH or COO-) acts as an acid (donates H+) 3. _____ Group: there are ______ different possible R groups 20 Different Amino Acids: Amino acids bond together via dehydration synthesis. The amino acids bind together with a ________________. The PEPTIDE bond is formed between ____________ and one water is lost (dehydration synthesis). When the original two amino acids form the beginning of the chain (with one peptide bond) it is called a _______________. Then the chain grows to become a ______________. Ultimately you end up with a _________________ (which can have anywhere between _____________ amino acids). Another name for a polypeptide is ____________ Every protein is different because the ________________ ___________ is different. The chains come together differently due to the order of the different _______________________ and how they __________ together. This structural difference also makes the polypeptides (proteins) functionally different. Levels of Protein Structure 1. ___________________________ structure o This is the __________ of how proteins are formed. o It is simply the _______________________ joined together with peptide bonds. o It is the amino acid sequence that determines the nature and chemistry of the protein. o If you ________________ of amino acids, the protein may not be able to _____________. 2. ___________________________ structure o This is the second step in the formation of a protein. o When a peptide bond is formed, a double bonded oxygen is left over, which is partially __________ (the carboxyl group: _____). o It is attracted to the ________________ amino group from other amino acids in the chain. o This attraction forms a _____________________. o This causes the chain to twist into either a spiral called an ______ __________ or a _____________________________. 3. ____________________________ structure o The next interactions take place ___________________. o Some R groups are ___________ and will interact with other reactive R groups in the chain. These are the amino acids that are either ___________ or that have a ________________. o The interactions ( ________ attractions and ____________) will fold the molecule over into a highly _______________________ ____________. o It is the 3-D shape that will determine the protein’s _________ or role in the body. 4. ____________________________ structure o The last level in protein formation is _________ in all proteins. o However, some proteins are actually ___________ molecules joined to form a functional protein. They are held together with an _______________. o Two examples: _____________ has _____ subunits _____________ has _____ subunits. The Whole Process 1o ____________ Bonds 2o ____________ Bonds 3o Interactions between ____________ 4o ____________ Bonds DENATURATION: The final shape of a protein (its tertiary or quaternary structure) is very __________ and enables it to do its job/function. Any ____________ in a proteins’ __________ will affect its _________ Denaturation is when a protein's tertiary structure is lost. This happens when the bonds between the ______ ________ are ___________ When a protein is denatured, the protein can’t do its job and becomes _________________. How can this happen? There are three common ways: 1. _________________: High temperatures affect the weak Hydrogen bonds and can ___________________ them, thus changing the structural shape. A slight increase in temperature an cause a ____________ change (ie: fever). A high temperature increase can cause an _____________ change (ie: cooking an egg). 2. ___________________: Heavy metals such as ___________________ are large atoms that are attracted the R groups of amino acids. They bond to the ______________ and distort the protein’s shape. This is usually _______________ (they usually don’t want to ‘let go’). 3. ___________________: As some of the R groups are acids and some are bases, every protein (enzyme) has a _________________. Any change in pH causes a change in the _____________ _________ interactions and this will change the __________ of the protein. Functions of Proteins 1. Structural: proteins help make up all structures in living things a. Actin & Myosin: __________ proteins b. _________: nails, hair, horns, feathers c. ________: bones, teeth, cartilage, tendon, ligament, blood vessels, skin matrix 2. Functional: other proteins help us to keep our bodies _____________________ and to ____________________. a. __________: are proteins that are ____________ which speed up reactions and control all cell activities. 3. ________________: once we have used up all of our carbohydrates and fats, proteins will be used for energy. Proteins are worth the ________ amount of ___________ per gram. NUCLEIC ACIDS Nucleic acids are ____________ molecules that are found in the ____________ of cells. There are two types, both of which are very __________. 1. DNA: __________________________ 2. RNA: __________________________ All nucleic acids are composed of units called _____________, which are composed of three submolecules: 1. _______________ (ribose or deoxyribose) 2. _____________________ 3. _____________________ (purine or pyrimidine) Nitrogen base: ____________________ _________________ and ________________ Have ______ rings Found in _________________ Memory Trick: Nitrogen base: ___________ __________, ___________ and ___________ Have only _______ ring Cytosine is in _______ DNA and RNA Thymine is in ___________ Uracil is in ____________ Memory Trick: Deoxyribonucleic Acid Structure of DNA: DNA is composed of ________ ___________________ of nucleotides. The two strands are joined by __________________ which form between complimentary nitrogen bases: _____________________ (A-T or T-A) They join with ____ hydrogen bonds ____________________ (C-G or G-C) They join with ____ hydrogen bonds When DNA is first made, it is just _______ _______________ of nucleotides joined together. Due to internal bonding, the DNA molecule then forms into a _________ __________ (twisted ladder). Functions of DNA a) ________________________________ by making all of the ___________ and _____________________. b) Contains all of the ___________________ necessary to make one complete organism of very exact specifications Ribonucleic Acid RNA is made by _________. It is not confined to the nucleus, it moves out of the nucleus ________________ of the cell. It has _______ sugar instead of Deoxyribose. It has no ___________, and uses _____________ instead. It is ________________ and therefore, no helix is formed. There are _____________ of RNA. The function of RNA is to _______________________________________________________ DNA 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 RNA Adenosine Triphosphate ATP is also thought of as a _________________ as it has the same _____________ as a nucleotide. The only difference is that it has ____________________________ instead of one. This is the _________________ for the body. Adenosine Triphosphate: Celllular Respiration Our ______________ turn the energy of __________ into __________. Why is it a good molecule to store energy? It takes a lot of __________ to put two phosphate molecules together (both –’ve). So when you _______ ______________, a lot of energy is _______________.