Question (24)
advertisement

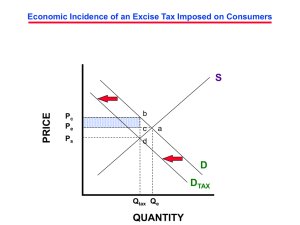
Question (24) 1. Explain how affirmative and negative majority votes can sometimes lead to inefficient allocations of resources to public goods. Is this problem likely to be greater under a benefits-received or an ability-to-pay tax system? Use the information in Figure 29.1a and b to show how society might be better off if Adams were allowed to buy votes. 2. Explain the paradox of voting through reference to the accompanying table, which shows the ranking of three public goods by voters Jay, Dave, and Conan. Public Good Jay Dave Conan Courthouse School Park 2d choice 3d choice 1st choice 1st choice 2d choice 3d choice 3d choice 1st choice 2d choice 3. Suppose that there are only five people in a society and that each favors one of the five highway construction options shown in Table 28.2 (include no highway construction as one of the options). Explain which of these highway options will be selected using a majority paired-choice vote. Will this option be the optimal size of the project from an economic perspective? 4. How does the problem of limited and bundled choice in the public sector relate to economic efficiency? Why are public bureaucracies alleged to be less efficient than private enterprises? 5. Distinguish between the benefits-received and the ability-to-pay principles of taxation. Which philosophy is more evident in our present tax structure? Justify your answer. To which principle of taxation do you subscribe? Why? 6. Suppose a tax is such that an individual with an income of $10,000 pays $2,000 of tax, a person with an income of $20,000 pays $3,000 of tax, a person with an income of $30,000 pays $4,000 of tax, and so forth. What is each person’s average tax rate? Is this tax regressive, proportional, or progressive? 7. What is meant by a progressive tax? A regressive tax? A proportional tax? Comment on the progressivity or regressivity of each of the following taxes, indicating in each case where you think the tax incidence lies: a. The Federal personal income tax b. A 4 percent state general sales tax c. A Federal excise tax on automobile tires d. A municipal property tax on real estate e. The Federal corporate income tax 8. What is the incidence of an excise tax when demand is highly inelastic? Elastic? What effect does the elasticity of supply have on the incidence of an excise tax? What is the efficiency loss of a tax, and how does it relate to elasticity of demand and supply?