Trends in Information Techonolgy
advertisement
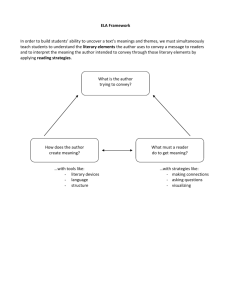
Information Systems: Concepts, Trends, Issues Ch 1-3 Turban, McLean, Wetherbe Why Study Information Technology? Moore’s Law: Chip capacity doubles every 18 Months. The Value of Technology Electric Power Growth Trends The Value of Technology IT Growth Trends Next Generation Information DATA: facts that are needed to operate a business. INFORMATION: data organized into a form needed by an application. INFORMATION SYSTEM: hardware, software and procedures that maintain data and convert it into usable information. Information System An information system (IS) collects, processes, stores, analyzes, and disseminates information for a specific purpose. Like any other system, an information system includes inputs (data, instructions) and outputs (reports, calculations). It processes the inputs by using technology such as PCs and produces outputs that are sent to users or to other systems via electronic networks and a feedback mechanism that controls the operation. Properties of Data Accuracy Completeness Cost Flexibility Relevance Granularity Timeliness Verifiability Value Basics of the MIS Discipline Technology Computing Telecommunications Development Data Process Network Management Operations Strategy Technology Development Management Computer Based Information System Hardware Software Data Network Procedures People More than hardware and software Hardware Software Application Data People Information System – Primary Purpose Collects data, processes it into information then converts information into knowledge for a specific purpose. Data » Elementary description of things, events, activities, and transactions that are recorded, classified, and stored, but not organized to convey any specific meeting Information » Data that has been organized so that they have meaning and value to the recipient Knowledge » Information that has been organized and processed to convey understanding, experience and expertise as they apply to a current problem or activity Information System - Classification By Support Function Senior Mgr Executive Support System •5-year sales trend •Profit Planning •5-year budget forecasting •Product development Management Information System Decision Support System Middle Managers Intelligent Support Systems Knowledge Management System Office Automation System Transaction Processing System Data Workers Operational Managers •Sales Management •Inventory Control •Annual budget •Production Scheduling •Cost Analysis •Pricing Analysis •Simulation •Pgm coding •System support •Word Processing •Desktop Publishing •Order Processing •Fulfillment •Material Movement •A/R, A/P, GL •Payroll •POS Functions of an Information System Collect Process Store Type II = = Type I Retrieve Analyze Disseminate Information Architectures Type I Systems Transaction based systems with many low value operations Type II Systems Decision enhancing system with few high value operations Development Approaches Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Prototyping Purchasing Outsourcing Competitive Environment Global Economy New Economics Complex Environment The Internet Technology Environment