Development Planning
advertisement

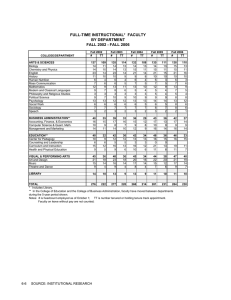
Development Planning Background • Great Depression • First Five-Year Industrialization Plan (1934-1939) • Second Five-Year Industrialization Plan (1938-) • War Years • Menderes Years • State Planning Organization (Development Plans) (Post-1960) First Five-Year Industrialization Plan • Initiated in 1934. • Worked through Sumerbank and its cooperation with other state apparati. • Affected from 30s zeitgeist. • As a counter-measure for 1929 crisis. Main Investment Lines • a — Fabric Industry • b — Mining Industry • c — Paper Industry • d — Chemical Industry • e — Ceramic Industry • Aimed at sustenance Sumerbank • Founded in 1933 • Handling State Economic Enterprises • Planning for future investments • Incentivizing private sector investments through credits, etc. • Achieve sustainable human capital formation • Given 45 million to accomplish said missions. (Milyon T L . ) Mali Toplam Toplam Borçlanmadan Yıl Gelir Borçlanma Hasüat Harcamalar Önceki Açık 1930-31 196,3 46,7 243,0 210,1 13,8 1931-32 165,2 30,8 196,0 181,9 16,7 1932-33 182,5 3,1 185,6 174,0 1933-34 170,2 12,0 182,2 — 173,6 3,4 1934-35 195,0 17,9 212,9 202,1 7,1 1935-36 218,3 20,1 238,4 223,7 5,4 1936-37 250,8 30,6 281,4 260,3 9,5 1937-38 275,8 59,9 332,7 303,5 27,7 1938-39 266,9 63,6 330,5 311,1 44,2 1939-40 273,4 133,9 407,3 398,7 125,3 Second Five-Year Industrialization Plan • 1938. • Budget is 112 million. • More of the previous. • Couldn’t be implemented because of the war mobilization efforts. State Planning Organization • The State Planning Organization which was founded in 1960 was reorganized as the Ministry of Development in June 2011 with Decree Law No. 641. • Ministry of Development of the Republic of Turkey is an expert based organization which plans and guides Turkey’s development process in a macro approach and focuses on the coordination of policies and strategy development. • To advise the government in determining Turkey’s economic, social and cultural development policies • Development Plans • 1963-1967 • • 1968-1972 • • 5th «5-year development plan» 1990-1994 • • 4th «5-year development plan» 1985-1989 • • 3th «5-year development plan» 1979-1983 • • 2nd «5-year development plan» 1973-1977 • • 1st «5-year development plan» 6th «5-year development plan» 1994 - onwards Plans – Page Numbers 1077 699 665 535 375 319 221 253 212 101 1 1963-67 2 1968-72 3 1973-77 4 1979-83 5 1985-89 10 9 8 7 6 1990-94 1996-20002001-20052007-20132014-2018 Plans – Word Count 2500 2000 1500 1000 agriculture industry 500 0 Plans – Word Count «Employment» 1400 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 0 1963-67 1968-72 1973-77 1979-83 1985-89 1990-94 1996-2000 2001-2005 2007-2013 2014-2018 1963-1967 1st «5-year development plan» • 7% growth rate target • Aim is increasing GDP • Slowing down population growth • Incentive for investment (tax-cut) • Focus on saving 1963-1967 Estimated change in working areas 1963-1967 Investment 1963-1967 1963-1967 Agriculture still highly matters 1963-1967 Proof from Şevket Pamuk 1963-1967 Export- Import 1967-1972 2nd «5-year development plan» • 7% growth rate target • 14% investment growth target • New point: control of capital inflow • Switch from agriculture to industry • Industry percentage in GDP aimed to increase 20,5 from 16,3 • Main focus on manifacturing industry 1967-1972 About Saving Targets of the first Plan 1967-1972 Estimated tax vs realized tax 1967-1972 Foreign Trade • Lack of export An example of production during this period TOFAŞ What is lack in TOFAŞ case? • There is a lack of incentive to create better quality as there is no competition. • There was an attempt to heavy industry but there was no chance to compete with big car industries. South Korea Example - Hyundai • They could do saving by huge taxations and government subsidizes hundai in the foreign market. • Focusing specific infant indystry Gross domestic savings (% of GDP) 35 South Korea 30 25 20 Turkey 15 10 5 1960 1961 1962 1963 1964 1965 1966 1967 1968 1969 1970 1971 1972 1973 1974 1975 1976 1977 1978 1979 1980 1981 1982 1983 1984 1985 1986 0 1973-1977 3rd «5-year development plan» • 9% GDP growth rate target • Industry percentage in GDP aimed to increase 23 from 40 • Agricultural percentage in GDP aimed to decrease 10 from 28. • New target: Switch from assembly industry to manufacturing industry • «Gecekondu» and urbanization matters 1973-1977 urbanization 1973-1977 Export import 1979-1983 4th «5-year development plan» • Manufacturing Industry is focus point again • Democracy first time mentioned • The previous plans are elaborated and criticized (following) • Much more related to international economy (Turgut Özal influence) 1979-1983 1985-1989 5th «5-year development plan» • Inlation matters a lot • Free currency • Macro economic targets are much more mentioned 1990-1994 6th «5-year development plan» • Convertible Turkish Lira Deposite • Turkish government guarantees, they will cover the losts caused by depreciation to increase FDI • Integration to EU matters Overview of Plans • different plans in differents terms have been influenced by current political conjecture in Turkish politics. • these plans do not only contend macroeconomic, financial, industrial, monetary and fiscal goals, but also focus on and give importance to some moral and ethic problems, youth problems, democratizing of everyday life structure, sport, freemdom of religion and working conditions etc. • Very detailed information Bibliography • Cumhuriyet gazetesi • http://www.kalkinma.gov.tr/Lists/Kalknma%20Planlar/Attachments/9/plan1.pdf • http://www.kalkinma.gov.tr/Lists/Kalknma%20Planlar/Attachments/8/plan2.pdf • http://www.kalkinma.gov.tr/Lists/Kalknma%20Planlar/Attachments/7/plan3.pdf • http://www.kalkinma.gov.tr/Lists/Kalknma%20Planlar/Attachments/6/plan4.pdf • http://www.kalkinma.gov.tr/Lists/Kalknma%20Planlar/Attachments/5/plan5.pdf • http://www.kalkinma.gov.tr/Lists/Kalknma%20Planlar/Attachments/4/plan6.pdf • http://www.kalkinma.gov.tr/Lists/Kalknma%20Planlar/Attachments/3/plan7.pdf