BAGIAN 3 The Analysis of Financial Statements
advertisement

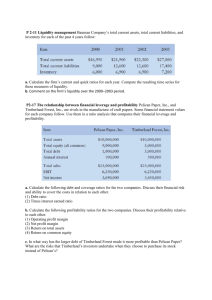
BAGIAN 3 The Analysis of Financial Statements The Analysis of Financial Statements This chapter will develop tools and techniques for the interpretation of financial information (C) 2004 Prentice Hall, Inc. 2 Tools and Techniques These include: Common-size financial statements Financial ratios Trend analysis Structural analysis Most important: Common sense and judgment Common-Size Financial Statements Express each account on the balance sheet as a percentage of total assets and each account on the income statement as a percentage of net sales Key Financial Ratios Standardize financial data in terms of mathematical relationships expressed in the form of percentages or times Liquidity Ratios: Short-Term Solvency Current Ratio Measures ability to meet short-term cash needs Current assets Current liabilitie s Liquidity Ratios: Short-Term Solvency Continued Quick or Acid-Test Ratio Measures ability to meet short-term cash needs more rigorously Current assets - Inventory Current liabilitie s Liquidity Ratios: Short-Term Solvency Continued Cash Flow Liquidity Ratio Focuses on ability of the firm to generate operating cash flows as a source of liquidity Cash Marketable securities CFO * Current liabilitie s *Cash flow from operating activities Liquidity Ratios: Short-Term Solvency Continued Average Collection Period Helps gauge liquidity of accounts receivable (ability to collect cash from customers) Accounts receivable Average daily sales Liquidity Ratios: Short-Term Solvency Continued Days Inventory Held Is the average number of days it takes to sell inventory to customers Inventory Average daily cost of sales Liquidity Ratios: Short-Term Solvency Continued Days Payable Outstanding Is the average number of days it takes to pay accounts payables in cash Accounts payable Average daily cost of sales Activity Ratios: Assets Liquidity, Asset Management Efficiency Accounts Receivable Turnover Another measure of efficiency of firm’s collection and credit policies Net sales Accounts receivable Activity Ratios: Assets Liquidity, Asset Management Efficiency Con’t Inventory Turnover Measures efficiency of inventory management Cost of goods sold Inventory Activity Ratios: Assets Liquidity, Asset Management Efficiency Con’t Payables Turnover Another measure of efficiency of inventory management Cost of goods sold Accounts payable Activity Ratios: Assets Liquidity, Asset Management Efficiency Con’t Fixed Asset Turnover Assesses effectiveness in generating sales from investment in fixed assets Net sales Net property, plant, equipment Activity Ratios: Assets Liquidity, Asset Management Efficiency Con’t Total Asset Turnover Assesses effectiveness in generating sales from investment in total assets Net sales Total assets Leverage Ratios: Debt Financing and Coverage Debt Ratio Measures the extent of firm’s financing with debt Total liabilitie s Total assets Leverage Ratios: Debt Financing and Coverage Con’t. Long-term Debt to Total Capitalization Measures the extent of firm’s financing with longterm debt Long - term debt Long - term debt Stockholde rs' equity Leverage Ratios: Debt Financing and Coverage Con’t Debt to Equity Measures the extent of firm’s financing with debt Total liabilitie s Stockholde rs' equity Leverage Ratios: Debt Financing and Coverage Con’t Times Interest Earned Indicates how well operating earnings cover fixed interest charges Operating profit Interest expense Leverage Ratios: Debt Financing and Coverage Con’t Fixed Charge Coverage Broader measure of how well operating earnings cover fixed charges Operating profit Rent expense Interest expense Rent expense Leverage Ratios: Debt Financing and Coverage Con’t Cash Flow Adequacy Measures firm’s ability to cover capital expenditures, long-term debt payments and dividends each year Cash flow from operating activities Capital expenditur es debt repayments dividends paid