8-Feb-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS Lowest Quintile Second Quintile
advertisement

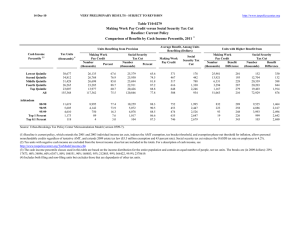
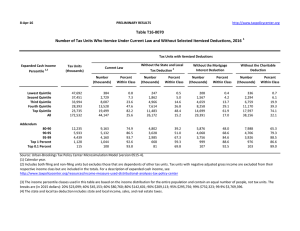
8-Feb-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Click on PDF or Excel link above for additional tables containing more detail and breakdowns by filing status and demographic groups. Table T10-0033 Administration's FY2011 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Law Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile, 2012 Summary Table Cash Income 2,3 Percentile Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Percent of Tax Units 4 With Tax Cut With Tax Increase Percent Change in After-Tax Income 5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change ($) 1 Average Federal Tax Rate6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 44.8 81.2 93.6 98.6 95.8 79.0 10.0 8.3 4.1 1.0 4.1 6.0 2.5 3.3 2.9 3.4 2.3 2.7 4.3 11.5 15.7 24.8 43.6 100.0 -278 -828 -1,233 -2,339 -4,695 -1,594 -2.4 -2.9 -2.4 -2.6 -1.7 -2.1 2.8 9.3 15.8 18.9 26.6 21.3 99.2 98.9 94.8 51.6 23.4 0.7 1.1 5.2 48.4 76.6 4.1 3.8 2.9 -0.5 -1.4 20.2 12.7 13.4 -2.7 -3.5 -4,318 -5,576 -7,230 5,748 73,402 -3.1 -2.8 -2.1 0.3 0.9 21.5 22.9 25.6 33.0 36.5 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509-4. Number of AMT Taxpayers (millions). Baseline: 19.5 Proposal: 4.0 (1) Calendar year. Baseline is current law. The proposal would: (a) extend the higher EITC credit value for families with 3 children and higher phase-out thresholds for married couples and allow it against the AMT; (b) modify the saver's credit making it equal to 50% of the first $500 of retirement savings ($1,000 for couples) and fully refundable; (c) create automatic 401(k)s and IRAs; (d) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; (e) extend child tax credit refundability with a $3,000 refundability threshold, extend the $1,000 credit, and allow against the AMT; (f) extend the higher 35 percent child and dependent care tax credit rate, raise the phaseout threshold to $85,000, and allow against the AMT; (g) change the threshold for the 36-percent tax bracket to $250,000 less the standard deduction and two personal exemptions for married couples filing jointly and $200,000 less the standard deduction and one personal exemption for single filers, indexed for inflation after 2009; (h) set the thresholds for the personal exemption phase-out and limitation on itemized deductions to $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; (i) impose a 20 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in the top two tax brackets and repeal the 8 percent and 18 percent rates for assets held for more than 5 years; (j) limit value of itemized deduction s to 28 percent; (k) maintain the estate tax at its 2009 parameters; (l) extend the 2001 and 2003 tax cuts for low and middle income individuals including marriage penalty relief, the 10,15, 25, 28 percent brackets, the 15 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in those brackets. Business provisions included were making the research and experimentation tax credit permanent, taxing carried interest as ordinary income, repealing LIFO, international corporate tax reforms, and reforms affecting the tax treatment of financial institutions. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% $19,356, 40% $37,493, 60% $65,656, 80% $111,659, 90% $161,739, 95% $226,402, 99% $599,181, 99.9% $2,727,123. (4) Includes both filing and non-filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After-tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 8-Feb-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T10-0033 Administration's FY2011 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Law 1 Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile, 2012 Detail Table Percent of Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All With Tax Increase Percent Change in After-Tax Income5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 44.8 81.2 93.6 98.6 95.8 79.0 10.0 8.3 4.1 1.0 4.1 6.0 2.5 3.3 2.9 3.4 2.3 2.7 4.3 11.5 15.7 24.8 43.6 100.0 -278 -828 -1,233 -2,339 -4,695 -1,594 -46.5 -23.6 -13.0 -12.2 -5.9 -8.9 -0.3 -0.7 -0.5 -0.7 2.2 0.0 0.5 3.7 10.3 17.6 67.9 100.0 -2.4 -2.9 -2.4 -2.6 -1.7 -2.1 2.8 9.3 15.8 18.9 26.6 21.3 99.2 98.9 94.8 51.6 23.4 0.7 1.1 5.2 48.4 76.6 4.1 3.8 2.9 -0.5 -1.4 20.2 12.7 13.4 -2.7 -3.5 -4,318 -5,576 -7,230 5,748 73,402 -12.7 -11.0 -7.6 1.0 2.5 -0.6 -0.2 0.2 2.8 1.6 13.7 10.1 16.1 28.0 14.3 -3.1 -2.8 -2.1 0.3 0.9 21.5 22.9 25.6 33.0 36.5 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes by Cash Income Percentile, 2012 1 Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Number (thousands) Percent of Total Average Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average AfterTax Income5 (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Rate6 Share of PreTax Income Percent of Total Share of PostTax Income Percent of Total Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total 38,450 34,947 31,868 26,646 23,298 157,348 24.4 22.2 20.3 16.9 14.8 100.0 11,600 28,852 52,224 88,978 280,229 76,169 599 3,509 9,475 19,164 79,103 17,826 11,001 25,343 42,749 69,814 201,126 58,343 5.2 12.2 18.1 21.5 28.2 23.4 3.7 8.4 13.9 19.8 54.5 100.0 4.6 9.7 14.8 20.3 51.0 100.0 0.8 4.4 10.8 18.2 65.7 100.0 11,720 5,734 4,655 1,190 120 7.5 3.6 3.0 0.8 0.1 138,385 196,549 345,574 1,825,188 8,367,274 34,076 50,547 95,585 595,812 2,978,313 104,309 146,002 249,989 1,229,376 5,388,961 24.6 25.7 27.7 32.6 35.6 13.5 9.4 13.4 18.1 8.4 13.3 9.1 12.7 15.9 7.0 14.2 10.3 15.9 25.3 12.7 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509-4). Number of AMT Taxpayers (millions). Baseline: 19.5 Proposal: 4.0 (1) Calendar year. Baseline is current law. The proposal would: (a) extend the higher EITC credit value for families with 3 children and higher phase-out thresholds for married couples and allow it against the AMT; (b) modify the saver's credit making it equal to 50% of the first $500 of retirement savings ($1,000 for couples) and fully refundable; (c) create automatic 401(k)s and IRAs; (d) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; (e) extend child tax credit refundability with a $3,000 refundability threshold, extend the $1,000 credit, and allow against the AMT; (f) extend the higher 35 percent child and dependent care tax credit rate, raise the phase-out threshold to $85,000, and allow against the AMT; (g) change the threshold for the 36-percent tax bracket to $250,000 less the standard deduction and two personal exemptions for married couples filing jointly and $200,000 less the standard deduction and one personal exemption for single filers, indexed for inflation after 2009; (h) set the thresholds for the personal exemption phase-out and limitation on itemized deductions to $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; (i) impose a 20 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in the top two tax brackets and repeal the 8 percent and 18 percent rates for assets held for more than 5 years; (j) limit value of itemized deduction s to 28 percent; (k) maintain the estate tax at its 2009 parameters; (l) extend the 2001 and 2003 tax cuts for low and middle income individuals including marriage penalty relief, the 10,15, 25, 28 percent brackets, the 15 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in those brackets. Business provisions included were making the research and experimentation tax credit permanent, taxing carried interest as ordinary income, repealing LIFO, international corporate tax reforms, and reforms affecting the tax treatment of financial institutions. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% $19,356, 40% $37,493, 60% $65,656, 80% $111,659, 90% $161,739, 95% $226,402, 99% $599,181, 99.9% $2,727,123. (4) Includes both filing and non-filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After-tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 8-Feb-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T10-0033 Administration's FY2011 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Law Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 20121 Detail Table Percent of Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All With Tax Increase Percent Change in After-Tax Income5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 44.8 73.9 88.6 98.3 96.1 79.0 9.0 8.9 6.5 1.3 3.6 6.0 4.1 3.7 3.1 3.2 2.2 2.7 5.5 11.1 14.9 23.4 45.0 100.0 -438 -857 -1,197 -1,960 -3,771 -1,594 -188.4 -30.5 -15.2 -12.1 -5.7 -8.9 -0.5 -0.8 -0.6 -0.6 2.5 0.0 -0.3 2.5 8.1 16.7 72.8 100.0 -4.0 -3.3 -2.6 -2.5 -1.6 -2.1 -1.9 7.5 14.4 18.4 26.4 21.3 98.6 98.8 96.0 55.9 26.1 1.0 0.9 4.0 44.1 73.9 3.5 3.5 3.0 -0.3 -1.3 18.6 13.1 15.0 -1.7 -3.5 -3,099 -4,359 -6,339 2,912 60,771 -10.8 -10.1 -7.9 0.6 2.3 -0.3 -0.2 0.2 2.8 1.6 15.0 11.4 17.3 29.1 14.8 -2.6 -2.6 -2.2 0.2 0.8 21.7 23.1 25.3 32.6 36.1 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2012 1 Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Number (thousands) Percent of Total Average Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average AfterTax Income5 (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Rate6 Share of PreTax Income Share of PostTax Income Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total Percent of Total Percent of Total 31,706 32,349 31,237 29,980 29,936 157,348 20.2 20.6 19.9 19.1 19.0 100.0 10,935 26,208 46,322 77,565 235,547 76,169 233 2,812 7,852 16,224 65,847 17,826 10,703 23,395 38,471 61,342 169,700 58,343 2.1 10.7 17.0 20.9 28.0 23.4 2.9 7.1 12.1 19.4 58.8 100.0 3.7 8.2 13.1 20.0 55.3 100.0 0.3 3.2 8.7 17.3 70.3 100.0 15,019 7,540 5,940 1,436 142 9.6 4.8 3.8 0.9 0.1 117,658 167,170 294,212 1,584,726 7,360,192 28,579 43,043 80,760 513,626 2,599,522 89,079 124,127 213,452 1,071,100 4,760,670 24.3 25.8 27.5 32.4 35.3 14.7 10.5 14.6 19.0 8.7 14.6 10.2 13.8 16.8 7.4 15.3 11.6 17.1 26.3 13.2 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509-4). Number of AMT Taxpayers (millions). Baseline: 19.5 Proposal: 4.0 (1) Calendar year. Baseline is current law. The proposal would: (a) extend the higher EITC credit value for families with 3 children and higher phase-out thresholds for married couples and allow it against the AMT; (b) modify the saver's credit making it equal to 50% of the first $500 of retirement savings ($1,000 for couples) and fully refundable; (c) create automatic 401(k)s and IRAs; (d) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; (e) extend child tax credit refundability with a $3,000 refundability threshold, extend the $1,000 credit, and allow against the AMT; (f) extend the higher 35 percent child and dependent care tax credit rate, raise the phase-out threshold to $85,000, and allow against the AMT; (g) change the threshold for the 36-percent tax bracket to $250,000 less the standard deduction and two personal exemptions for married couples filing jointly and $200,000 less the standard deduction and one personal exemption for single filers, indexed for inflation after 2009; (h) set the thresholds for the personal exemption phase-out and limitation on itemized deductions to $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; (i) impose a 20 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in the top two tax brackets and repeal the 8 percent and 18 percent rates for assets held for more than 5 years; (j) limit value of itemized deduction s to 28 percent; (k) maintain the estate tax at its 2009 parameters; (l) extend the 2001 and 2003 tax cuts for low and middle income individuals including marriage penalty relief, the 10,15, 25, 28 percent brackets, the 15 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in those brackets. Business provisions included were making the research and experimentation tax credit permanent, taxing carried interest as ordinary income, repealing LIFO, international corporate tax reforms, and reforms affecting the tax treatment of financial institutions. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% $13,219, 40% $24,782, 60% $41,864, 80% $68,188, 90% $97,830, 95% $138,709, 99% $361,983, 99.9% $1,670,467. (4) Includes both filing and non-filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After-tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 8-Feb-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T10-0033 Administration's FY2011 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Law 1 Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2012 Detail Table - Single Tax Units Percent of Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All With Tax Increase Percent Change in After-Tax Income5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 30.8 62.8 88.0 97.7 96.1 69.5 9.7 12.2 6.4 1.9 3.3 7.4 1.7 1.8 2.1 1.9 2.8 2.3 4.2 9.2 15.0 17.4 54.1 100.0 -133 -321 -581 -818 -3,056 -787 -21.7 -13.7 -9.4 -6.7 -7.0 -7.8 -0.2 -0.3 -0.2 0.3 0.5 0.0 1.3 4.9 12.3 20.7 60.8 100.0 -1.6 -1.6 -1.7 -1.5 -2.0 -1.8 5.7 10.1 16.4 20.5 26.6 21.1 97.6 98.2 96.0 61.1 25.6 1.7 1.1 4.0 38.8 74.4 2.8 3.3 4.2 1.0 -1.2 16.5 12.7 20.4 4.4 -2.3 -1,769 -2,906 -6,172 -6,597 39,976 -8.3 -9.1 -10.9 -1.8 2.0 -0.1 -0.2 -0.5 1.3 1.0 15.5 10.8 14.2 20.3 10.1 -2.1 -2.4 -3.0 -0.6 0.8 23.2 24.4 24.7 33.9 38.9 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2012 1 Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Average Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average AfterTax Income5 (Dollars) Number (thousands) Percent of Total 16,972 15,474 14,005 11,543 9,596 68,932 24.6 22.5 20.3 16.8 13.9 100.0 8,380 19,970 34,261 55,833 151,979 43,878 611 2,345 6,183 12,256 43,502 10,053 7,769 17,625 28,078 43,577 108,477 33,825 5,066 2,373 1,795 361 32 7.4 3.4 2.6 0.5 0.1 84,037 119,032 204,548 1,060,631 5,243,107 21,258 31,966 56,595 366,389 1,999,153 62,779 87,066 147,953 694,243 3,243,953 Share of PreTax Income Percent of Total Share of PostTax Income Percent of Total Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total 7.3 11.7 18.1 22.0 28.6 22.9 4.7 10.2 15.9 21.3 48.2 100.0 5.7 11.7 16.9 21.6 44.6 100.0 1.5 5.2 12.5 20.4 60.2 100.0 25.3 26.9 27.7 34.5 38.1 14.1 9.3 12.1 12.7 5.5 13.6 8.9 11.4 10.8 4.4 15.5 11.0 14.7 19.1 9.1 Average Federal Tax Rate6 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509-4). (1) Calendar year. Baseline is current law. The proposal would: (a) extend the higher EITC credit value for families with 3 children and higher phase-out thresholds for married couples and allow it against the AMT; (b) modify the saver's credit making it equal to 50% of the first $500 of retirement savings ($1,000 for couples) and fully refundable; (c) create automatic 401(k)s and IRAs; (d) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; (e) extend child tax credit refundability with a $3,000 refundability threshold, extend the $1,000 credit, and allow against the AMT; (f) extend the higher 35 percent child and dependent care tax credit rate, raise the phase-out threshold to $85,000, and allow against the AMT; (g) change the threshold for the 36-percent tax bracket to $250,000 less the standard deduction and two personal exemptions for married couples filing jointly and $200,000 less the standard deduction and one personal exemption for single filers, indexed for inflation after 2009; (h) set the thresholds for the personal exemption phase-out and limitation on itemized deductions to $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; (i) impose a 20 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in the top two tax brackets and repeal the 8 percent and 18 percent rates for assets held for more than 5 years; (j) limit value of itemized deduction s to 28 percent; (k) maintain the estate tax at its 2009 parameters; (l) extend the 2001 and 2003 tax cuts for low and middle income individuals including marriage penalty relief, the 10,15, 25, 28 percent brackets, the 15 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in those brackets. Business provisions included were making the research and experimentation tax credit permanent, taxing carried interest as ordinary income, repealing LIFO, international corporate tax reforms, and reforms affecting the tax treatment of financial institutions. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% $13,219, 40% $24,782, 60% $41,864, 80% $68,188, 90% $97,830, 95% $138,709, 99% $361,983, 99.9% $1,670,467. (4) Includes both filing and non-filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After-tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 8-Feb-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T10-0033 Administration's FY2011 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Law 1 Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2012 Detail Table - Married Tax Units Filing Jointly Percent of Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All With Tax Increase Percent Change in After-Tax Income5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 47.0 74.8 85.0 98.6 96.2 85.4 14.8 9.7 9.2 1.1 3.8 6.3 5.2 4.6 3.5 3.8 2.1 2.7 3.0 7.6 12.6 26.7 50.0 100.0 -734 -1,359 -1,757 -2,843 -4,298 -2,607 -171.5 -38.3 -18.7 -14.8 -5.5 -8.5 -0.3 -0.6 -0.6 -1.1 2.5 0.0 -0.1 1.1 5.1 14.3 79.5 100.0 -5.1 -4.1 -2.9 -3.0 -1.5 -2.1 -2.1 6.6 12.8 17.3 26.2 22.4 99.3 99.2 96.0 54.7 26.6 0.7 0.7 4.0 45.3 73.4 3.8 3.6 2.7 -0.5 -1.2 22.0 15.6 16.0 -3.5 -4.1 -3,966 -5,141 -6,575 5,544 63,293 -12.0 -10.5 -7.1 1.0 2.3 -0.6 -0.3 0.3 3.1 1.8 14.9 12.2 19.4 33.1 16.6 -2.9 -2.7 -2.0 0.3 0.8 21.0 22.7 25.5 32.2 35.6 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2012 1 Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Average Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average AfterTax Income5 (Dollars) Number (thousands) Percent of Total 6,622 8,956 11,470 15,032 18,609 61,357 10.8 14.6 18.7 24.5 30.3 100.0 14,526 33,405 59,671 95,023 281,842 126,020 428 3,549 9,392 19,237 78,238 30,803 14,098 29,855 50,279 75,786 203,604 95,217 8,860 4,843 3,890 1,015 102 14.4 7.9 6.3 1.7 0.2 138,312 192,091 337,723 1,748,464 7,890,377 33,025 48,811 92,709 557,743 2,743,003 105,286 143,280 245,014 1,190,721 5,147,375 Share of PreTax Income Percent of Total Share of PostTax Income Percent of Total Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total 3.0 10.6 15.7 20.2 27.8 24.4 1.2 3.9 8.9 18.5 67.8 100.0 1.6 4.6 9.9 19.5 64.9 100.0 0.2 1.7 5.7 15.3 77.0 100.0 23.9 25.4 27.5 31.9 34.8 15.9 12.0 17.0 23.0 10.5 16.0 11.9 16.3 20.7 9.0 15.5 12.5 19.1 30.0 14.9 Average Federal Tax Rate6 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509-4). (1) Calendar year. Baseline is current law. The proposal would: (a) extend the higher EITC credit value for families with 3 children and higher phase-out thresholds for married couples and allow it against the AMT; (b) modify the saver's credit making it equal to 50% of the first $500 of retirement savings ($1,000 for couples) and fully refundable; (c) create automatic 401(k)s and IRAs; (d) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; (e) extend child tax credit refundability with a $3,000 refundability threshold, extend the $1,000 credit, and allow against the AMT; (f) extend the higher 35 percent child and dependent care tax credit rate, raise the phase-out threshold to $85,000, and allow against the AMT; (g) change the threshold for the 36-percent tax bracket to $250,000 less the standard deduction and two personal exemptions for married couples filing jointly and $200,000 less the standard deduction and one personal exemption for single filers, indexed for inflation after 2009; (h) set the thresholds for the personal exemption phase-out and limitation on itemized deductions to $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; (i) impose a 20 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in the top two tax brackets and repeal the 8 percent and 18 percent rates for assets held for more than 5 years; (j) limit value of itemized deduction s to 28 percent; (k) maintain the estate tax at its 2009 parameters; (l) extend the 2001 and 2003 tax cuts for low and middle income individuals including marriage penalty relief, the 10,15, 25, 28 percent brackets, the 15 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in those brackets. Business provisions included were making the research and experimentation tax credit permanent, taxing carried interest as ordinary income, repealing LIFO, international corporate tax reforms, and reforms affecting the tax treatment of financial institutions. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% $13,219, 40% $24,782, 60% $41,864, 80% $68,188, 90% $97,830, 95% $138,709, 99% $361,983, 99.9% $1,670,467. (4) Includes both filing and non-filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After-tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 8-Feb-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T10-0033 Administration's FY2011 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Law 1 Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2012 Detail Table - Head of Household Tax Units Percent of Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All With Tax Increase Percent Change in After-Tax Income5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 73.1 94.5 97.3 99.5 96.6 88.6 2.6 1.6 1.4 0.2 2.8 1.8 6.0 4.9 4.0 3.3 1.9 4.0 19.8 30.2 24.6 16.3 9.0 100.0 -858 -1,366 -1,639 -1,999 -2,473 -1,384 108.9 -48.7 -18.5 -12.0 -5.2 -20.5 -6.1 -4.5 0.7 3.0 6.9 0.0 -9.8 8.2 28.1 31.0 42.4 100.0 -6.4 -4.5 -3.3 -2.6 -1.4 -3.3 -12.2 4.7 14.4 19.1 25.2 12.8 98.4 98.3 95.3 48.7 23.1 1.0 0.8 4.7 51.4 76.9 2.6 2.9 1.9 -0.6 -1.5 5.3 2.3 2.1 -0.5 -0.6 -2,222 -3,315 -4,048 5,563 66,475 -8.0 -8.4 -5.8 1.2 2.7 2.1 0.8 1.4 2.5 1.3 15.7 6.3 8.7 11.7 5.6 -2.0 -2.1 -1.5 0.4 1.0 22.7 23.2 23.8 32.8 36.2 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2012 1 Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Average Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average AfterTax Income5 (Dollars) Number (thousands) Percent of Total 7,840 7,497 5,095 2,777 1,242 24,547 31.9 30.5 20.8 11.3 5.1 100.0 13,490 30,617 50,275 76,881 178,521 41,760 -789 2,806 8,884 16,686 47,379 6,738 14,278 27,811 41,391 60,195 131,142 35,022 805 232 173 33 3 3.3 0.9 0.7 0.1 0.0 112,763 154,893 278,418 1,423,600 6,950,503 27,833 39,264 70,246 460,786 2,450,334 84,930 115,629 208,172 962,813 4,500,170 Share of PreTax Income Percent of Total Share of PostTax Income Percent of Total Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total -5.9 9.2 17.7 21.7 26.5 16.1 10.3 22.4 25.0 20.8 21.6 100.0 13.0 24.3 24.5 19.4 18.9 100.0 -3.7 12.7 27.4 28.0 35.6 100.0 24.7 25.4 25.2 32.4 35.3 8.9 3.5 4.7 4.6 2.0 8.0 3.1 4.2 3.7 1.5 13.5 5.5 7.3 9.2 4.3 Average Federal Tax Rate6 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509-4). (1) Calendar year. Baseline is current law. The proposal would: (a) extend the higher EITC credit value for families with 3 children and higher phase-out thresholds for married couples and allow it against the AMT; (b) modify the saver's credit making it equal to 50% of the first $500 of retirement savings ($1,000 for couples) and fully refundable; (c) create automatic 401(k)s and IRAs; (d) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; (e) extend child tax credit refundability with a $3,000 refundability threshold, extend the $1,000 credit, and allow against the AMT; (f) extend the higher 35 percent child and dependent care tax credit rate, raise the phase-out threshold to $85,000, and allow against the AMT; (g) change the threshold for the 36-percent tax bracket to $250,000 less the standard deduction and two personal exemptions for married couples filing jointly and $200,000 less the standard deduction and one personal exemption for single filers, indexed for inflation after 2009; (h) set the thresholds for the personal exemption phase-out and limitation on itemized deductions to $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; (i) impose a 20 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in the top two tax brackets and repeal the 8 percent and 18 percent rates for assets held for more than 5 years; (j) limit value of itemized deduction s to 28 percent; (k) maintain the estate tax at its 2009 parameters; (l) extend the 2001 and 2003 tax cuts for low and middle income individuals including marriage penalty relief, the 10,15, 25, 28 percent brackets, the 15 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in those brackets. Business provisions included were making the research and experimentation tax credit permanent, taxing carried interest as ordinary income, repealing LIFO, international corporate tax reforms, and reforms affecting the tax treatment of financial institutions. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% $13,219, 40% $24,782, 60% $41,864, 80% $68,188, 90% $97,830, 95% $138,709, 99% $361,983, 99.9% $1,670,467. (4) Includes both filing and non-filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After-tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 8-Feb-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T10-0033 Administration's FY2011 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Law Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 20121 Detail Table - Tax Units with Children Percent of Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All With Tax Increase Percent Change in After-Tax Income5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 79.9 98.0 99.1 99.7 96.0 94.1 1.8 0.7 0.6 0.2 4.0 1.4 7.3 6.3 4.6 4.8 2.2 3.7 8.7 15.3 18.2 28.1 29.7 100.0 -1,142 -1,963 -2,365 -3,812 -4,757 -2,710 118.2 -56.7 -20.8 -16.6 -5.4 -12.0 -1.3 -1.7 -1.1 -1.1 5.1 0.0 -2.2 1.6 9.5 19.4 71.7 100.0 -7.8 -5.7 -3.8 -3.7 -1.6 -2.8 -14.3 4.3 14.4 18.6 27.4 20.7 99.9 99.8 92.9 43.8 17.9 0.1 0.2 7.1 56.2 82.1 4.2 3.9 2.1 -0.8 -1.5 16.2 9.6 7.1 -3.1 -2.6 -4,890 -6,469 -6,032 11,190 96,342 -12.3 -10.9 -5.3 1.6 2.7 -0.1 0.1 1.3 3.7 1.9 15.8 10.8 17.5 27.6 13.4 -3.1 -2.9 -1.5 0.5 1.0 22.1 23.7 27.1 34.4 36.8 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2012 1 Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Average Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average AfterTax Income5 (Dollars) Number (thousands) Percent of Total 10,133 10,359 10,251 9,800 8,315 49,155 20.6 21.1 20.9 19.9 16.9 100.0 14,723 34,672 62,298 103,142 306,063 95,419 -967 3,464 11,351 23,023 88,566 22,496 15,690 31,209 50,947 80,119 217,497 72,923 4,398 1,976 1,567 374 36 9.0 4.0 3.2 0.8 0.1 157,496 224,546 400,356 2,088,455 9,839,694 39,721 59,571 114,595 706,992 3,520,023 117,775 164,974 285,760 1,381,462 6,319,671 Share of PreTax Income Share of PostTax Income Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total Percent of Total Percent of Total -6.6 10.0 18.2 22.3 28.9 23.6 3.2 7.7 13.6 21.6 54.3 100.0 4.4 9.0 14.6 21.9 50.5 100.0 -0.9 3.2 10.5 20.4 66.6 100.0 25.2 26.5 28.6 33.9 35.8 14.8 9.5 13.4 16.7 7.6 14.5 9.1 12.5 14.4 6.4 15.8 10.7 16.2 23.9 11.5 Average Federal Tax Rate6 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509-4). Note: Tax units with children are those claiming an exemption for children at home or away from home. (1) Calendar year. Baseline is current law. The proposal would: (a) extend the higher EITC credit value for families with 3 children and higher phase-out thresholds for married couples and allow it against the AMT; (b) modify the saver's credit making it equal to 50% of the first $500 of retirement savings ($1,000 for couples) and fully refundable; (c) create automatic 401(k)s and IRAs; (d) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; (e) extend child tax credit refundability with a $3,000 refundability threshold, extend the $1,000 credit, and allow against the AMT; (f) extend the higher 35 percent child and dependent care tax credit rate, raise the phase-out threshold to $85,000, and allow against the AMT; (g) change the threshold for the 36-percent tax bracket to $250,000 less the standard deduction and two personal exemptions for married couples filing jointly and $200,000 less the standard deduction and one personal exemption for single filers, indexed for inflation after 2009; (h) set the thresholds for the personal exemption phase-out and limitation on itemized deductions to $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; (i) impose a 20 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in the top two tax brackets and repeal the 8 percent and 18 percent rates for assets held for more than 5 years; (j) limit value of itemized deduction s to 28 percent; (k) maintain the estate tax at its 2009 parameters; (l) extend the 2001 and 2003 tax cuts for low and middle income individuals including marriage penalty relief, the 10,15, 25, 28 percent brackets, the 15 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in those brackets. Business provisions included were making the research and experimentation tax credit permanent, taxing carried interest as ordinary income, repealing LIFO, international corporate tax reforms, and reforms affecting the tax treatment of financial institutions. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% $13,219, 40% $24,782, 60% $41,864, 80% $68,188, 90% $97,830, 95% $138,709, 99% $361,983, 99.9% $1,670,467. (4) Includes both filing and non-filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After-tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 8-Feb-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T10-0033 Administration's FY2011 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Law Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 20121 Detail Table - Elderly Tax Units Percent of Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All With Tax Increase Percent Change in After-Tax Income5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 8.3 30.6 56.4 94.5 93.3 54.8 23.0 23.9 26.3 4.5 6.2 17.3 0.4 0.7 1.2 2.0 2.7 2.1 0.5 2.9 6.9 17.1 72.6 100.0 -37 -140 -454 -1,225 -5,085 -1,289 -13.3 -14.1 -16.0 -13.6 -7.4 -8.5 0.0 -0.1 -0.3 -0.6 1.0 0.0 0.3 1.7 3.4 10.1 84.6 100.0 -0.3 -0.6 -1.1 -1.7 -2.0 -1.7 2.3 3.8 5.8 11.1 24.8 18.3 95.4 96.8 96.6 59.3 30.1 3.6 2.8 3.4 40.7 69.9 3.5 3.9 4.6 0.5 -1.1 18.7 16.1 32.1 5.6 -5.0 -3,039 -4,653 -9,059 -5,120 46,022 -15.5 -14.0 -13.1 -1.1 2.0 -0.8 -0.6 -1.0 3.4 2.5 9.5 9.2 19.8 46.1 23.8 -2.9 -3.0 -3.4 -0.4 0.7 15.7 18.6 22.5 32.2 36.6 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2012 1 Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Average Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average AfterTax Income5 (Dollars) Number (thousands) Percent of Total 5,016 8,213 5,981 5,495 5,617 30,543 16.4 26.9 19.6 18.0 18.4 100.0 10,899 22,528 41,094 70,238 257,048 75,737 282 990 2,833 8,989 68,880 15,163 10,616 21,538 38,260 61,249 188,168 60,574 2,427 1,362 1,394 434 42 8.0 4.5 4.6 1.4 0.1 105,444 153,103 267,882 1,396,961 6,520,091 19,632 33,136 69,367 455,137 2,337,228 85,813 119,966 198,515 941,824 4,182,863 Share of PreTax Income Share of PostTax Income Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total Percent of Total Percent of Total 2.6 4.4 6.9 12.8 26.8 20.0 2.4 8.0 10.6 16.7 62.4 100.0 2.9 9.6 12.4 18.2 57.1 100.0 0.3 1.8 3.7 10.7 83.5 100.0 18.6 21.6 25.9 32.6 35.9 11.1 9.0 16.1 26.2 12.0 11.3 8.8 15.0 22.1 9.6 10.3 9.8 20.9 42.6 21.4 Average Federal Tax Rate6 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509-4). Note: Elderly tax units are those with either head or spouse (if filing jointly) age 65 or older. (1) Calendar year. Baseline is current law. The proposal would: (a) extend the higher EITC credit value for families with 3 children and higher phase-out thresholds for married couples and allow it against the AMT; (b) modify the saver's credit making it equal to 50% of the first $500 of retirement savings ($1,000 for couples) and fully refundable; (c) create automatic 401(k)s and IRAs; (d) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; (e) extend child tax credit refundability with a $3,000 refundability threshold, extend the $1,000 credit, and allow against the AMT; (f) extend the higher 35 percent child and dependent care tax credit rate, raise the phase-out threshold to $85,000, and allow against the AMT; (g) change the threshold for the 36-percent tax bracket to $250,000 less the standard deduction and two personal exemptions for married couples filing jointly and $200,000 less the standard deduction and one personal exemption for single filers, indexed for inflation after 2009; (h) set the thresholds for the personal exemption phase-out and limitation on itemized deductions to $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; (i) impose a 20 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in the top two tax brackets and repeal the 8 percent and 18 percent rates for assets held for more than 5 years; (j) limit value of itemized deduction s to 28 percent; (k) maintain the estate tax at its 2009 parameters; (l) extend the 2001 and 2003 tax cuts for low and middle income individuals including marriage penalty relief, the 10,15, 25, 28 percent brackets, the 15 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in those brackets. Business provisions included were making the research and experimentation tax credit permanent, taxing carried interest as ordinary income, repealing LIFO, international corporate tax reforms, and reforms affecting the tax treatment of financial institutions. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% $13,219, 40% $24,782, 60% $41,864, 80% $68,188, 90% $97,830, 95% $138,709, 99% $361,983, 99.9% $1,670,467. (4) Includes both filing and non-filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After-tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income.