Document 14476363
advertisement

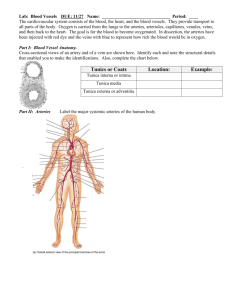
University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy –II Second Year Students Asaad Ismail Ahmad , Ph.D. Electrolyte and Mineral Physiology asaad50.2011@gmail.com 2012 - 2013 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY - II Brief Contents 1- Cardiovascular System 2- Blood 3- Lymphatic System 4- Urinary System 5- Male Reproductive System 6- Female Reproductive System 7- Sensory Function Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D in Electrolyte and Mineral Physiology College of Nursing – University of Baghdad / 2012 – 2013 asaad50.2011@gmail.com Text book Martini FH. Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology, 5th ed. Prentice Hall, New Jersey, 2001. References: 1.Barrett KE, Barman SM, Boitano S, Brooks HL. Ganong's Review of Medical Physiology, 23rd ed. McGraw Hill, Boston, 2010. 2.Drake RL, Vogl W, Mitchell AWM. Gray's Anatomy for Students. Elsevier, Philadelphia, 2005. 3.Goldberger ,E. 1975.A Primer of Water Electrolyte and Acid-Base Syndromes. 5th ed., Lea and Febiger ,Philadelphia. 4. Martini, FH and Welch K. Applications Manual Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology,4th ed., Prentice Hall, NewJersey, 1998. 5.Maxwell, MH and Kleeman CR. 1980.Clinical Disorders of Fluid and Electrolyte Metabolism. McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York. 6.McKinley M, and O'Loughlin VD. Human Anatomy, McGraw Hill, Boston, 2006. 7.Nutrition Foundation.1984.Present Knowledge in Nutrition. 5th ed., Nutrition Foundation, Inc , Washington, D.C. 8.Vander A, Sherman J, Luciano D., Human Physiology, 7th ed., McGraw Hill, Boston, 1998. Contents: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM I- ANATOMY OF THE HEART II- ANATOMY OF BLOOD VESSELS III- PHYSIOLOGY OF THE HEART IV- PHYSIOLOGY BLOOD VESSELS Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D in Electrolyte and Mineral Physiology College of Nursing – University of Baghdad / 2012 – 2013 asaad50.2011@gmail.com ANATOMY OF BLOOD VESSELS Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. in Electrolyte and Mineral Physiology Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D in Electrolyte and Mineral Physiology College of Nursing – University of Baghdad / 2012 – 2013 asaad50.2011@gmail.com SECOND LECTURE Anatomy of the Blood Vessels 1234567- Types of blood vessels Structures of the wall of Blood Vessels Coronary Circulation Pulmonary Circulation Systemic Circulation Hepatic Portal Circulation Fetal Circulation Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D in Electrolyte and Mineral Physiology College of Nursing – University of Baghdad / 2012 – 2013 asaad50.2011@gmail.com Contents: 1- Types of blood vessels TYPES OF BLOOD VESSELS 694 I- Arteries 1- Elastic arteries 2- Muscular arteries 3- Arterioles II- Capillaries 1- Continuous capillaries 2- Fenestrated capillaries 3- Sinusoids 4- Capillary bed III- VEINS 1- Veinules 2- Medium sized veins 3- Large veins 4- Venous valves HISTOLOGICAL STRUCTURE OF BLOOD VSSELS (694) ARTERIOLES AND SMOOTH MUSCLES Dead-end lymph capillaries found in tissue spaces. Structure of the capillary wall. Note especially the intercellular cleft, where the most water-soluble substances diffuse CAPILLARY FILTRATION 708 Exchanges between blood in a systemic capillary and the surrounding tissue fluid. TYPES OF CAPILLARIES ORGANIZATION OF A CAPILLARY BED (699) Contents: 2- Structures of the Wall of Blood Vessels STRUCTURES OF THE WALL OF BLOOD VESSELS (692-693) The wall of the arteries and veins contain or composed from three distinct layers: 1- TUNICA INTERNA (INTIMA) 2- TUNICA MEDIA 3- TUNICA EXTERNA (Adventitia) TUNICA INTERNA The innermost layer include endothelial lining and the underlying layer of connective tissue (elastic fibers) TUNICA MEDIA The middle layer, contains concentric sheets of smooth muscle tissue in framework of loose connective tissue (collagen fibers). Smooth muscle control the diameter of blood vessels. TUNICA EXTERNA The outermost layer and form connective tissue sheath around the vessel (collagen and elastic fiber). Muscular and elastic components control alterations in diameter as blood pressure or blood volume changes. MECHANISMS FACILITATE VENOUS RETURN 699 1234- Venous valves Skeletal muscle pump Respiratory pump Perforating vein VALVES IN VEINS FUNCTION OF VALVE IN VENOUS SYSTEM: (700) (Venous Return) Contents: 3- Coronary Circulation CORONARY CIRCULATION (CORONARY ARTERIES AND VEINS) (666-667) I- Left Coronary Artery Branches of left coronary artery 1- Circumflex artery 2- Anterior interventricular artery II- Right Coronary Artery Branches of right coronary artery 1- Psterior interventricular artery 2- Marginal artery Continue: CORONARY CIRCULATION III- CORONARY VEINS 1- Great cardiac vein 2- Small cardiac vein 3- Middle cardiac vein 4- Coronary sinus CORONARY CIRCULATION ANTERIOR VIEW OF CORONARY CIRCULATION: CARDIAC ARTERIES POSTERIOR VIEW OF THE CORONARY CIRCULATION: CARDIAC VEINS Contents: 4- Pulmonary Circulation PULMONARY CIRCULATION 724 1- Pulmonary trunk 2- Left pulmonary artery 3- Right pulmonary artery 4- Pulmonary veins 5- Pulmonary capillaries PULMONARY CIRCULATION POSTERIOR SURFACE OF THE HEART Contents: 5- Systemic Circulation SYSTEMIC CIRCULATION 725 General Distribution of arteries 1- Ascending aorta 2- Aortic arch 3- Carotid artery (L&R) 4- Subclavian artery (L&R) 5- Descending thoracic aorta 6- Intercostal artery (L&R) Continue : Systemic Circulation 7- Celiac trunk (gastric, splenic, hepatic) 8- Superior mesentric artery 9- Renal artery (L&R) 10-Inferior mesentric artery 11-Gonadal artery (L&R) 12-External iliac artery (L&R) 13-Internal iliac artery (L&R) 14-Femoral artery (L&R) Structure of the heart, and course of blood flow through the heart chambers and heart valves. Contents: 6- Hepatic Portal Circulation HEPATIC PORTAL CIRCULATION 741 Is a venous network that drains the GIT and shunts the blood to the liver. The blood exit the liver through hepatic veins to inferior vena cava (liver is the only digestive organ that drains directly into inferior vena cava). hepatic portal System begins in capillaries of the digestive organs and ends as the hepatic portal vein discharges into liver sinusoid. HEPATIC PORTAL CIRCULATION compose from: 1- Hepatic portal vein (portal vein) 2- Hepatic vein BRANCHES OF VEINS MERGE TO FORM HEPATIC PORTAL VEIN 123456789- Gastric veins Splenic vein Pancreatic veins Colic veins Inferior mesentric vein Superior rectal veins Intestinal veins Ileocolic vein Superior mesenteric vein HEPATIC PORTAL CIRCULATION Contents: 7- Fetal Circulation: FETAL CIRCULATION: COMPARES OF FETAL AND NEONATAL STRUCTURES 742 Fetal structure 1- Ductus arteriosus 2- Ductus venosus 3- Foramen ovale 4- Umbilical arteries 5- Umbilical veins Postnatal structure 1- Ligamentum arteriosus 2- Ligamentum venosum 3- Fossa ovalis 4- Medial umbilical ligaments 5- Round ligament of liver