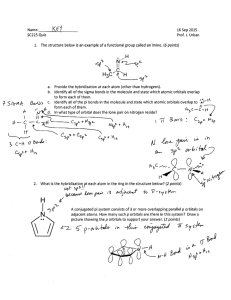
methane, CH H C 4
advertisement

H H C H methane, CH4 H 109.5° less repulsion between the bonding pairs of electrons 90° H .. H C H H N H H H ammonia NH3 less repulsion between the bonding pairs of electrons H .. H C H H N H H H .. H O .. H water, H2O 109.5° (109.5°) 109.5° (107°) 109.5° (104.5°) H C H H H N H H H H O H Ozone O3 O O O Formaldhyde H2CO H C H O Hydrogen Cyanide HCN H C N H C H H H H H C O H C N H C H H H H H C O H C N Are there atomic orbitals on C, Si, N and O to accommodate the bonding electrons of the shapes predicted by VSEPR? 3 p orbitals s orbital x x y y z z Are there atomic orbitals on C, Si, N and O to accommodate the bonding electrons of the shapes predicted by VSEPR? x x y y z z Are there atomic orbitals on C, Si, N and O to accommodate the bonding electrons of the shapes predicted by VSEPR? 4 sp3 orbitals x y z Are there atomic orbitals on C, Si, N and O to H accommodate the bonding electrons of the shapes predicted by VSEPR? 4 sp3 orbitals C x H y z H H s + px + py = 3 sp2 orbitals H H C O pz orbital H H C O H H H C O C H O H H C O H H C O s + px = 2 sp orbitals H Py orbital Pz orbital C N H C N C N H C N C N H C N C N H C N C N H H C N C N bonding hybrid orbitals VSEPR shape tetrahedral sp3 trigonal planar sp2 linear sp Review: Ethane 3 sp Csp3-Hs Csp3-Csp3 Review: Ethane Csp3-Hs 3 sp H H C ● ● C H H H Csp3-Csp3 H Hybrid atomic orbitals + s orbital and p orbital x s+ p x Why are hybrid orbitals used in chemical bonding? .. . . s- p x molecular orbitals. a C-C bond Csp3 energy Csp3 molecular orbitals. a C-C bond Csp3 energy Csp3 molecular orbitals. a C=C bond Csp2 energy Csp2 A model of ethene using hybrid and atomic orbitals. · ·· · H C H σ-bond H C H H H C C H H π-bond molecular orbitals. a C=O bond H C O H In contrast to the rotation about single bonds, the rotation about double bonds is very difficult. C 12 kJ energy z y x 2s 2px 2pz 2py Important consequences of Quantum Mechanics The locations of the electrons are described by atomic orbitals. A given orbital can contain only 2 electrons. (Pauli exclusion principle.) Each orbital has an associated energy and electrons will occupy the lowest energy orbitals first. Atomic orbitals on different atoms will can combine to give molecular orbitals, but only if their symmetry matches. good s bond bad – wrong symmetry No bonding! These atomic orbitals and their hybrids will be used extensively in our models of chemical bonding. p orbitals s orbital x H y z C, N, O Common hybrid orbitals used in bonding of carbon, nitrogen and oxygen. sp x y z 2s 2px 2py 2pz Common hybrid orbitals used in bonding of carbon, nitrogen and oxygen. sp hybrid orbital angle 180° pz sp sp py 2s 2px 2py 2pz Common hybrid orbitals used in bonding of carbon, nitrogen and oxygen. 2 sp hybrid orbital angle 120° pz 2s 2px 2py 2pz Common hybrid orbitals used in bonding of carbon, nitrogen and oxygen. 3 sp 2s hybrid orbital angle 109.5° 2px 2py 2pz Methane 3 sp Csp3-Hs H H C H H Ethane 3 sp H C H H H Ethane 3 sp H H C ● ● C H H H H Ethane Csp3-Hs 3 sp H H C ● ● C H H H Csp3-Csp3 H Ethane 3 sp Csp3-Hs Csp3-Csp3